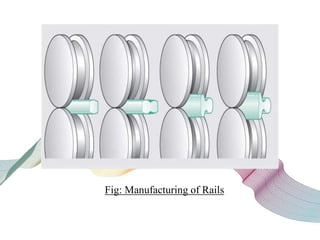
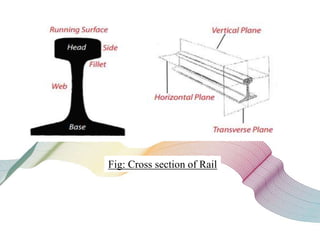
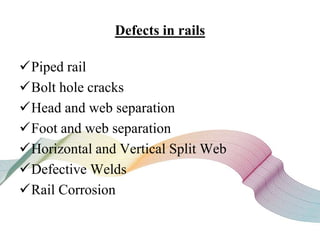
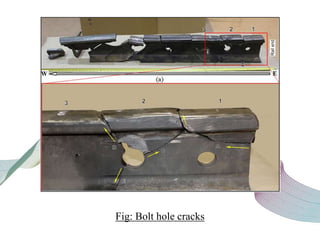
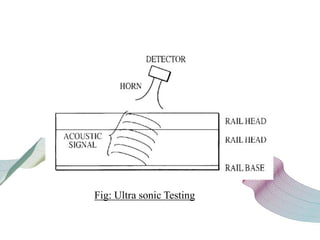
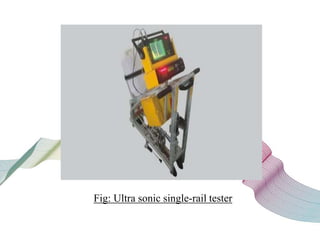
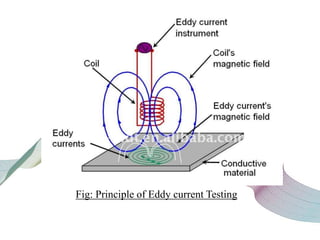
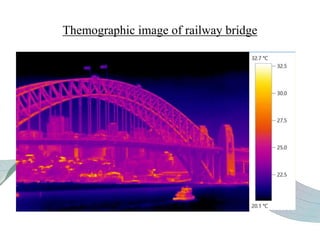
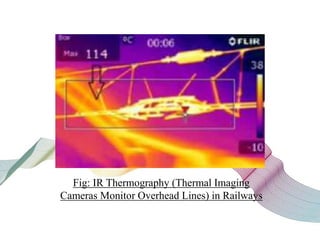
This document discusses non-destructive testing (NDT) in railways. It provides an overview of common NDT methods like ultrasonic testing, eddy current testing, magnetic particle inspection, and thermography that are used to inspect critical railway components without damaging them. These methods help verify quality, assess degradation, and detect defects in rails, wheels, axles and other components. Ultrasonic testing and eddy current testing can find internal flaws in rails, while visual inspection, magnetic particle inspection and thermography examine rails, wheels, axles and other surfaces for cracks or defects. NDT plays an important role in maintaining railway integrity and safety by monitoring component condition.