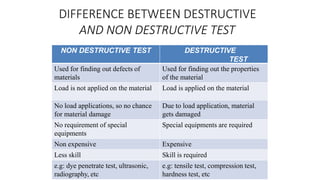
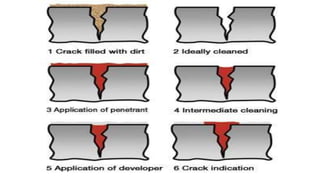
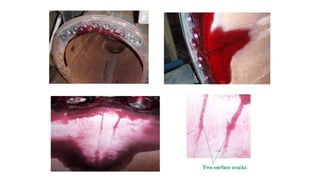
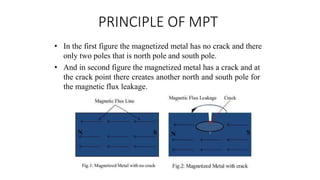
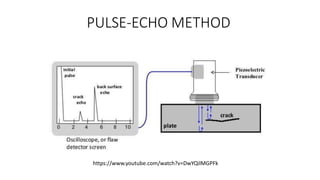
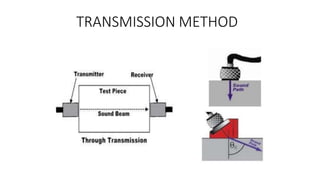
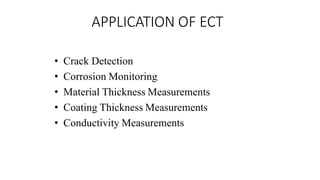
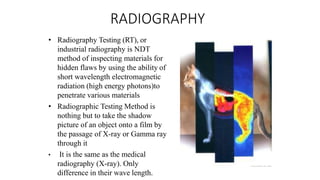
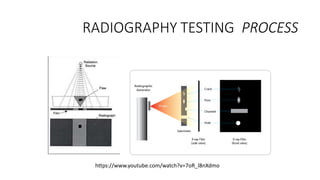
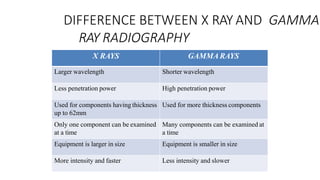
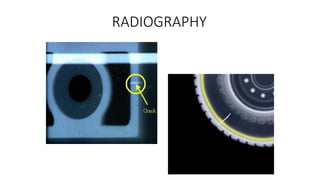
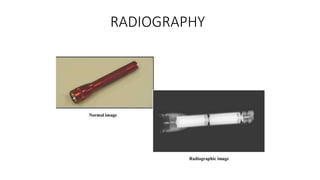
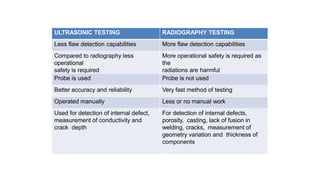
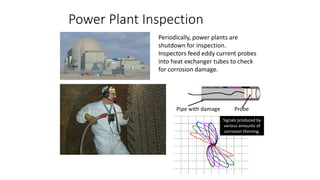
NDT is a group of analysis techniques used to evaluate materials, components, or systems without damaging them. Some common NDT methods include dye penetrant testing, magnetic particle testing, ultrasonic testing, eddy current testing, and radiography testing. NDT is useful for detecting internal and surface flaws in materials and components, evaluating assemblies and systems, validating integrity and reliability, and maintaining safety. It allows for inspection and evaluation to take place without destroying the sample being analyzed.