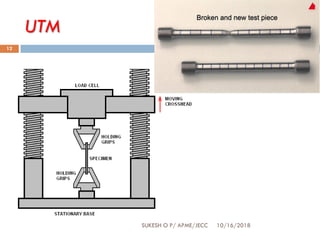
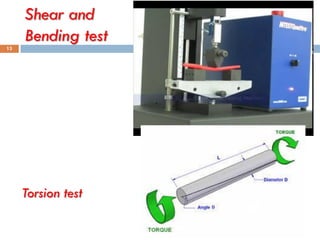
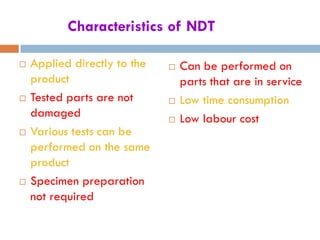
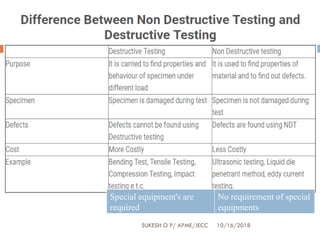
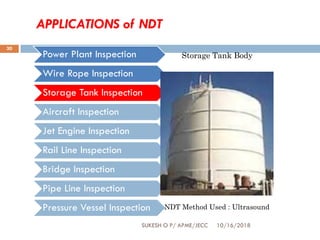
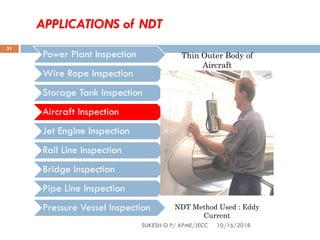
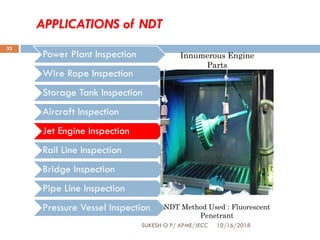
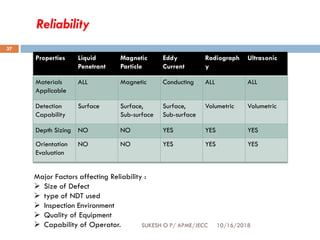
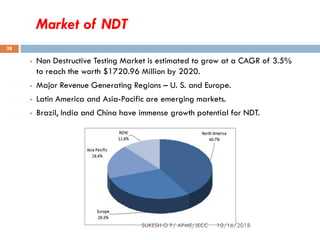
This document provides an overview of non-destructive testing (NDT) techniques. It discusses various NDT methods like visual inspection, liquid penetrant testing, magnetic particle testing, ultrasonic testing, and radiography testing. The document also compares destructive and non-destructive testing, highlights the importance, scope, advantages and difficulties of NDT. It provides examples of NDT applications in various industries and discusses the future progress expected in the field.