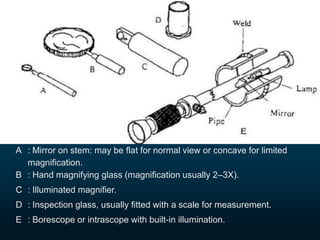
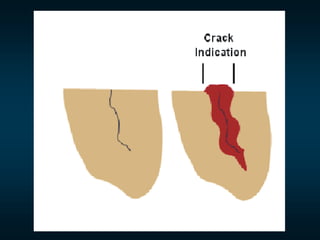
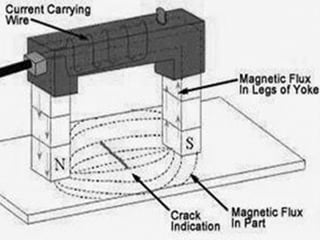
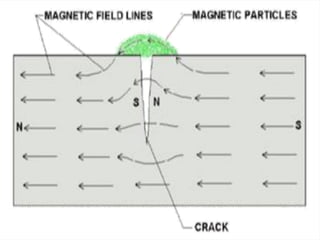
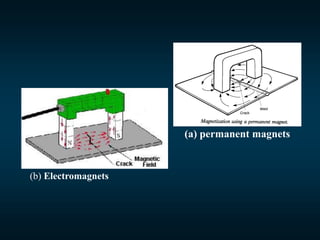
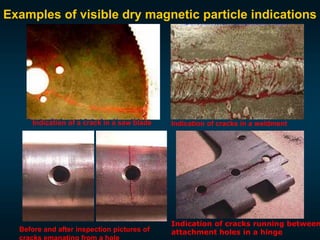
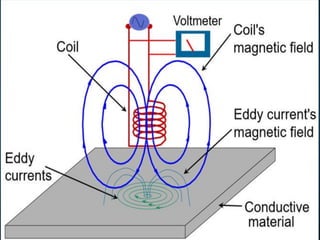
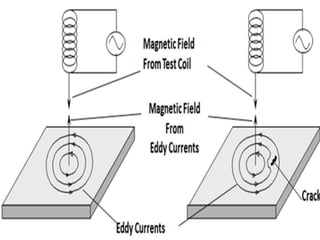
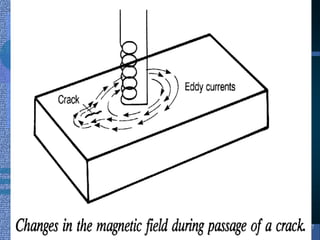
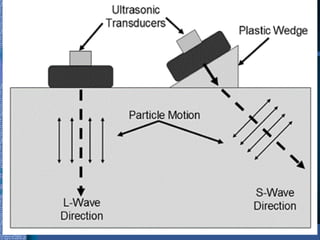
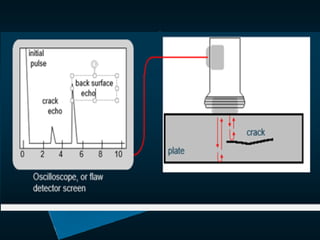
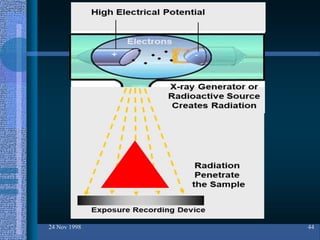
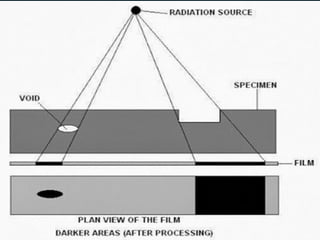
Non-destructive testing (NDT) is crucial for evaluating the integrity of materials and components without causing damage. Common methods include visual testing, dye penetration, magnetic particle testing, eddy current testing, ultrasonic testing, and radiographic testing, each with specific applications and limitations. NDT is widely used in industries such as oil and gas, aerospace, and manufacturing to enhance safety, reduce costs, and improve product quality.