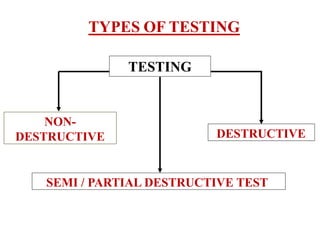
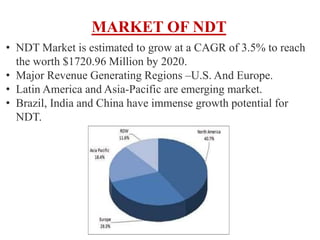
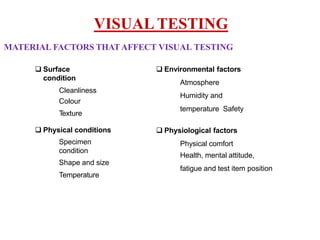
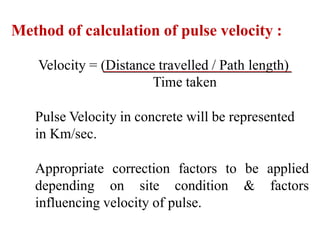
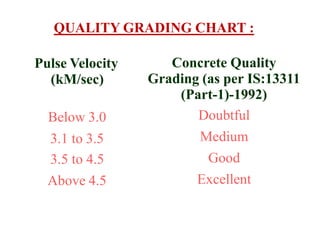
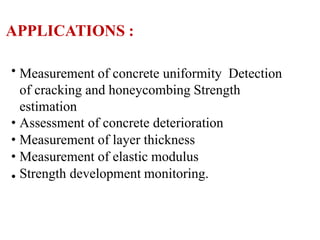
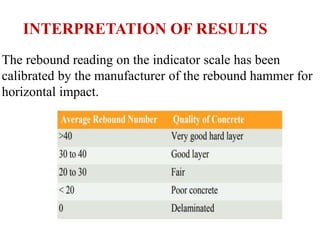
The document discusses various testing methods focused on non-destructive testing (NDT), semi-destructive testing, and destructive testing of materials. It highlights the importance and advantages of NDT, including cost-effectiveness, reliability, and safety, while also detailing specific NDT methods such as visual inspection and ultrasonic pulse velocity tests. Additionally, it outlines the growth potential of the NDT market and mentions several testing techniques for assessing the quality and properties of materials.