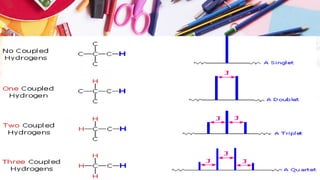
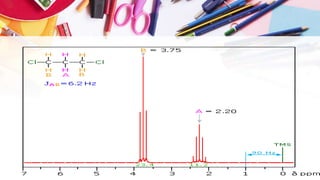
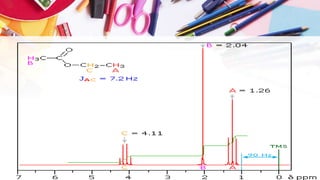
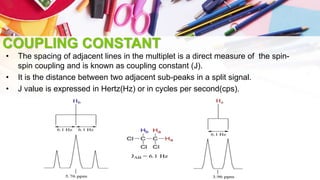
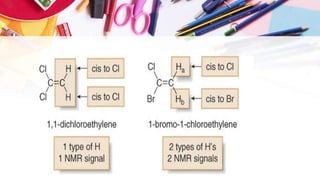
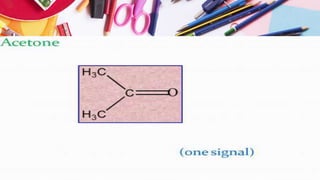
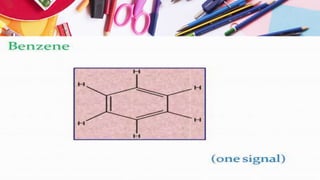
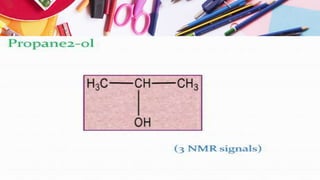
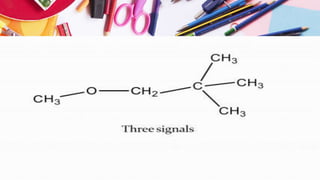
NMR spectroscopy involves the use of radiofrequency waves to induce transitions in the magnetic energy levels of atomic nuclei. Key concepts include relaxation processes (longitudinal and transverse), chemical shift measured in parts per million (ppm) with TMS as the standard, and factors influencing chemical shifts such as electronegativity, steric effects, and hydrogen bonding. Splitting of signals and coupling constants are also discussed, with the n+1 rule guiding the prediction of signal patterns.