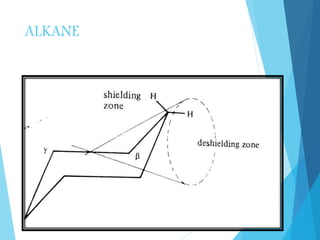
This document discusses chemical shift in NMR spectroscopy. It begins by defining chemical shift as the shift in the NMR signal resulting from shielding and deshielding by electrons. Protons near electronegative atoms experience deshielding and absorb at lower fields, while protons near electropositive atoms experience shielding and absorb at higher fields. Tetramethylsilane (TMS) is commonly used as an internal reference standard due to its non-reactivity and single peak. Factors that influence chemical shift include electronegativity, anisotropy, hydrogen bonding, and molecular structure. Common isotopes used in NMR include 1H, 13C, 19F, and 31P. Reference standards are necessary for quantitative NMR and include T


![ Greater the electron density around the
proton greater will be the induced secondary
magnetic field.
[ local diamagnetic effect]
currents induced by fixed magnetic field
result in secondary fields which can either
enhance or decrease the field to given a
proton responds.
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicalshift-170202062530/85/Chemical-shift-3-320.jpg)