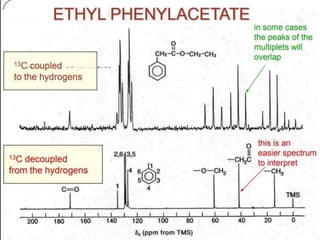
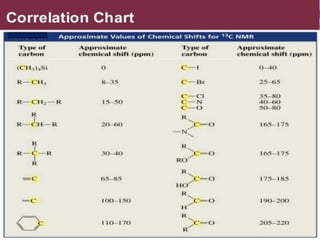
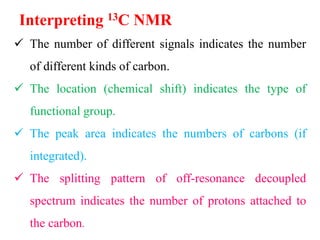
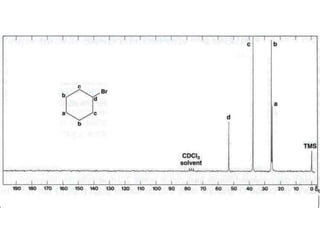
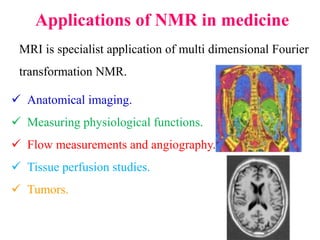
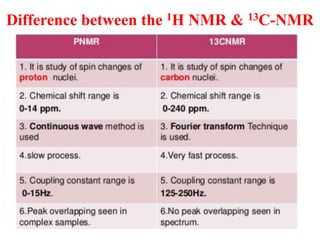
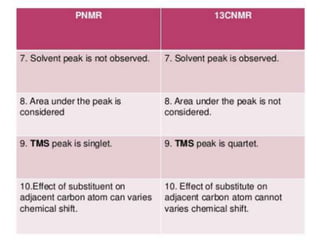
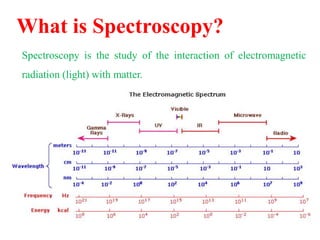
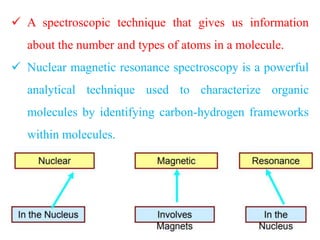
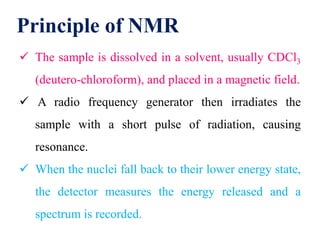
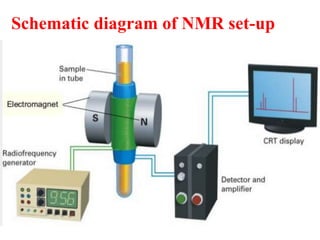
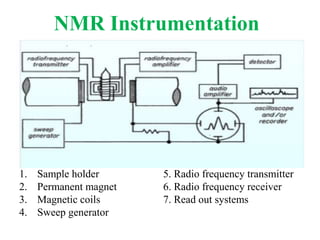
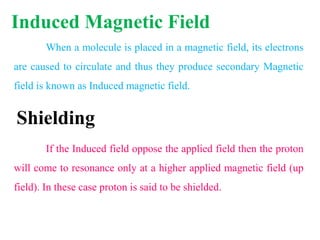
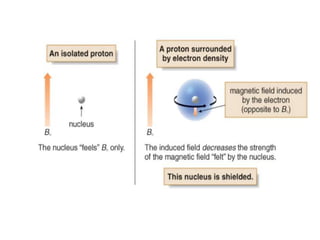
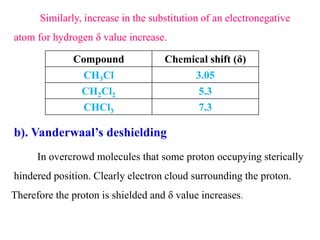
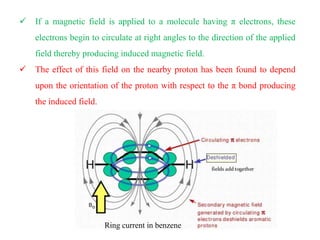
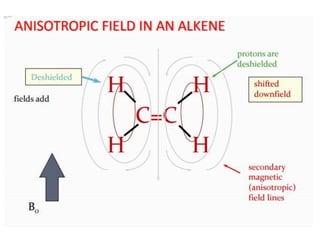
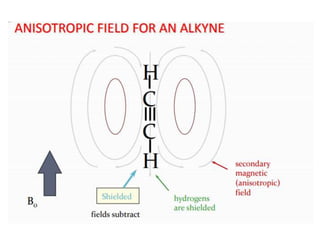
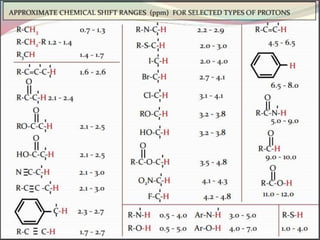
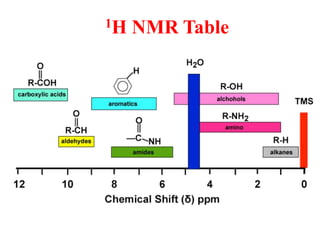
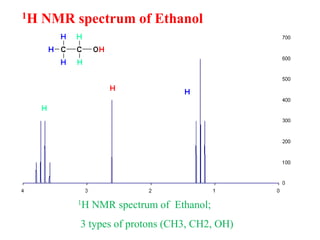
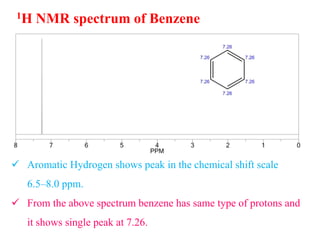
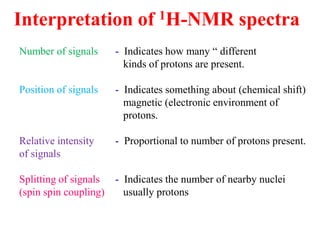
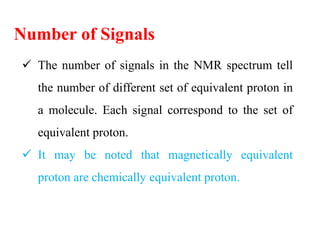
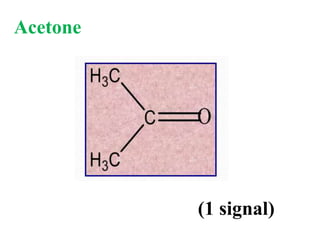
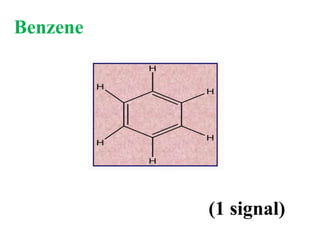
This document provides an overview of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. It begins by defining spectroscopy as the study of interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter. It then explains that NMR spectroscopy involves absorbing radiofrequency radiation by atomic nuclei placed in a magnetic field. It notes that 1H and 13C NMR are most commonly used to determine the structure of organic molecules by identifying carbon-hydrogen frameworks. The document also provides details on NMR instrumentation, principles, and how NMR spectra are interpreted.



















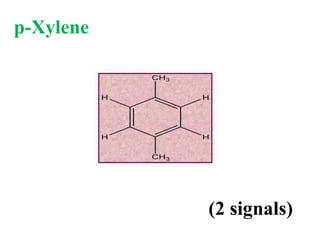
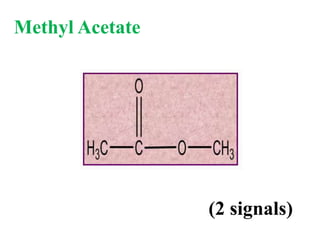
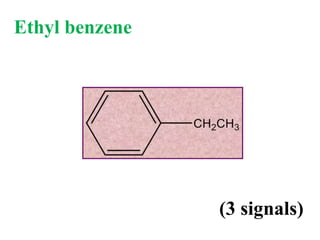
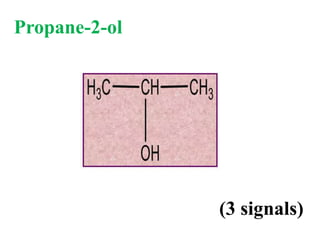







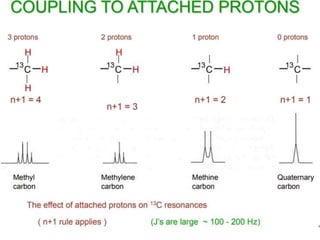
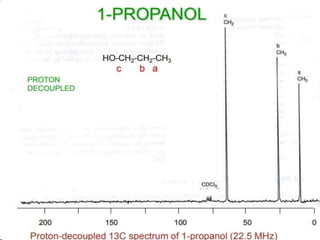
![Types of 13C spectra
1) Proton coupled 13C spectra
2) Proton decoupled 13C spectra
a) Homoannular coupling
1) Proton coupled 13C spectra
The probability of finding 13C adjacent carbon is very
less. Therefore, homonuclear [carbon-carbon] splitting is
rearaly seen.
b) Hetronuclear coupling
It involving two different atoms [carbon- hydrogen].
Here splitting arises due proton attached directly to 13C carbon.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmr-krishna-200106161808/85/NMR-KRISHNAN-59-320.jpg)