Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique used to characterize organic molecules by identifying carbon-hydrogen frameworks. It exploits the magnetic properties of atomic nuclei, such as 1H and 13C, and determines the physical and chemical properties of atoms in a molecule. Common types of NMR spectroscopy are 1H NMR, which determines the number and type of hydrogen atoms in a molecule, and 13C NMR, which determines the type of carbon atoms. NMR provides detailed information about molecular structure, dynamics, and chemical environment through analysis of nuclei absorption frequencies.













![The relative energy of resonance of a particular nucleus resulting
from its local environment is called chemical shift.
NMR spectra show applied field strength increasing from left to
right.
Left part is downfield, the right is upfield.
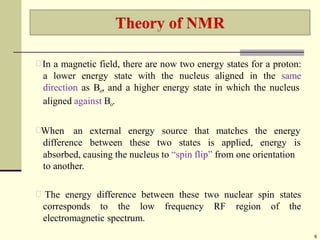
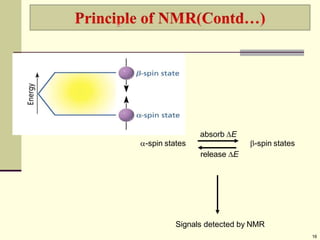
Nuclei that absorb on upfield side are strongly shielded where
nuclei that absorb on downfield side is weakly shielded.
Chart calibrated versus a reference point, set as 0, tetramethylsilane
[TMS].
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmr-171129145034/85/NMR-17-320.jpg)