Embed presentation


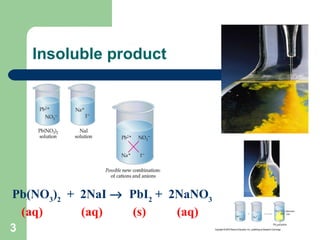



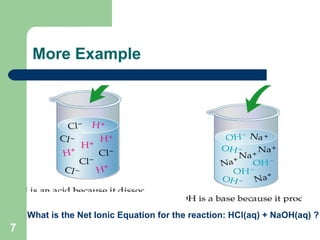
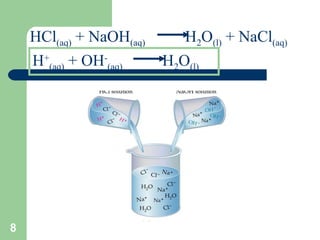
The document discusses solubility and writing ionic equations. It defines a soluble substance as one that dissociates into ions in aqueous solution. It provides a 5-step process for writing ionic equations: 1) Write the balanced molecular equation, 2) Add state symbols, 3) Write out aqueous ions, 4) Cancel spectator ions on both sides, 5) Write the net ionic equation with only reactants and products. An example uses this process to derive the net ionic equation for the reaction of lead nitrate and potassium iodide.







