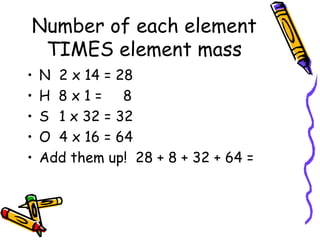This document provides an overview of basic chemistry concepts related to naming and writing formulas for ionic compounds. It discusses:
1) How to name ionic compounds by writing the cation first followed by the anion with "-ide" ending, except for polyatomic ions.
2) How to write formulas for ionic compounds by ensuring charges are balanced between cations and anions using subscripts.
3) Special rules for writing formulas involving polyatomic ions and d-block metal cations, which can have multiple oxidation states requiring specifying the oxidation number.
4) How to calculate formula masses of compounds by multiplying the number of atoms of each element by the atomic mass and summing the products.