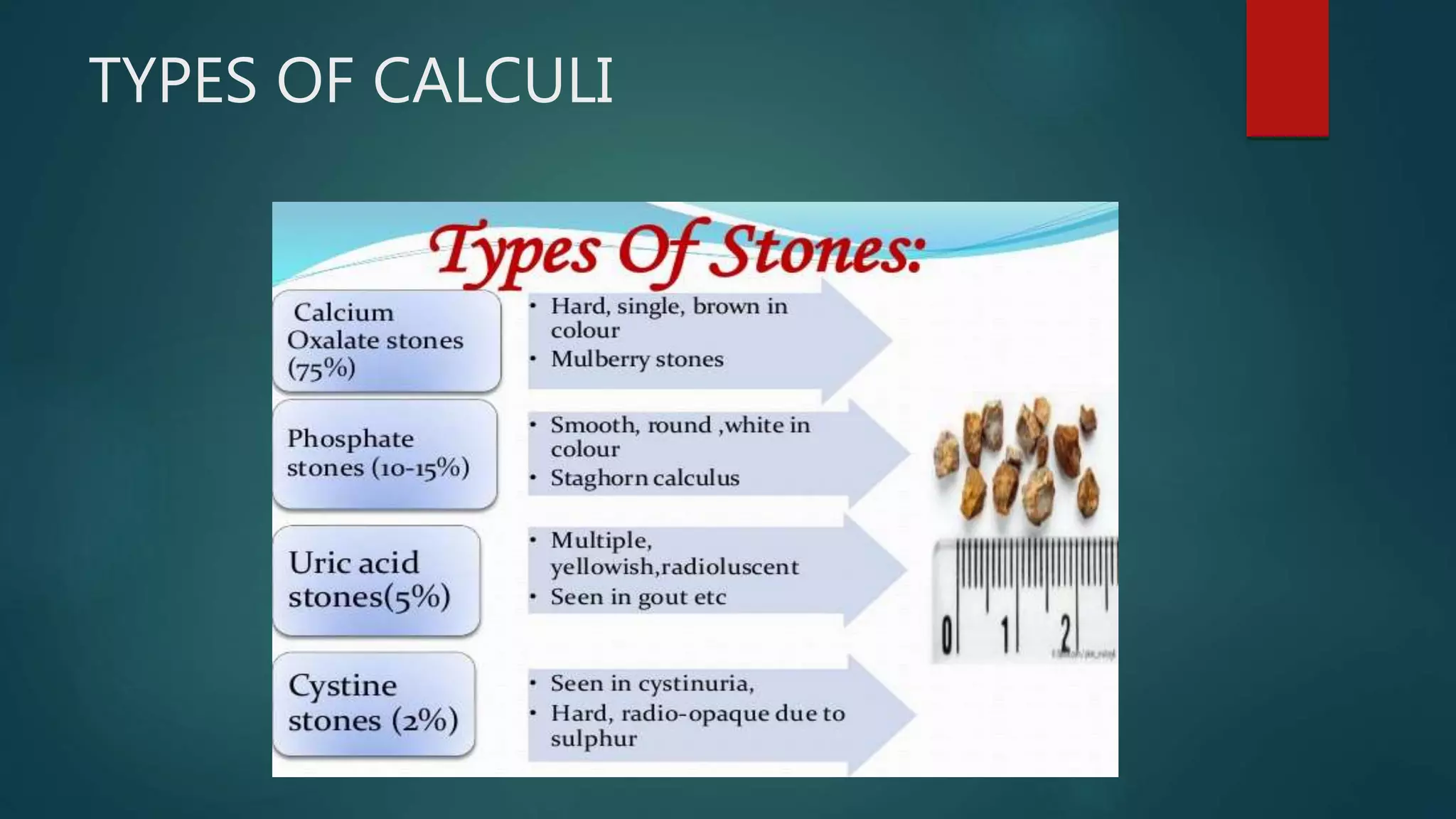
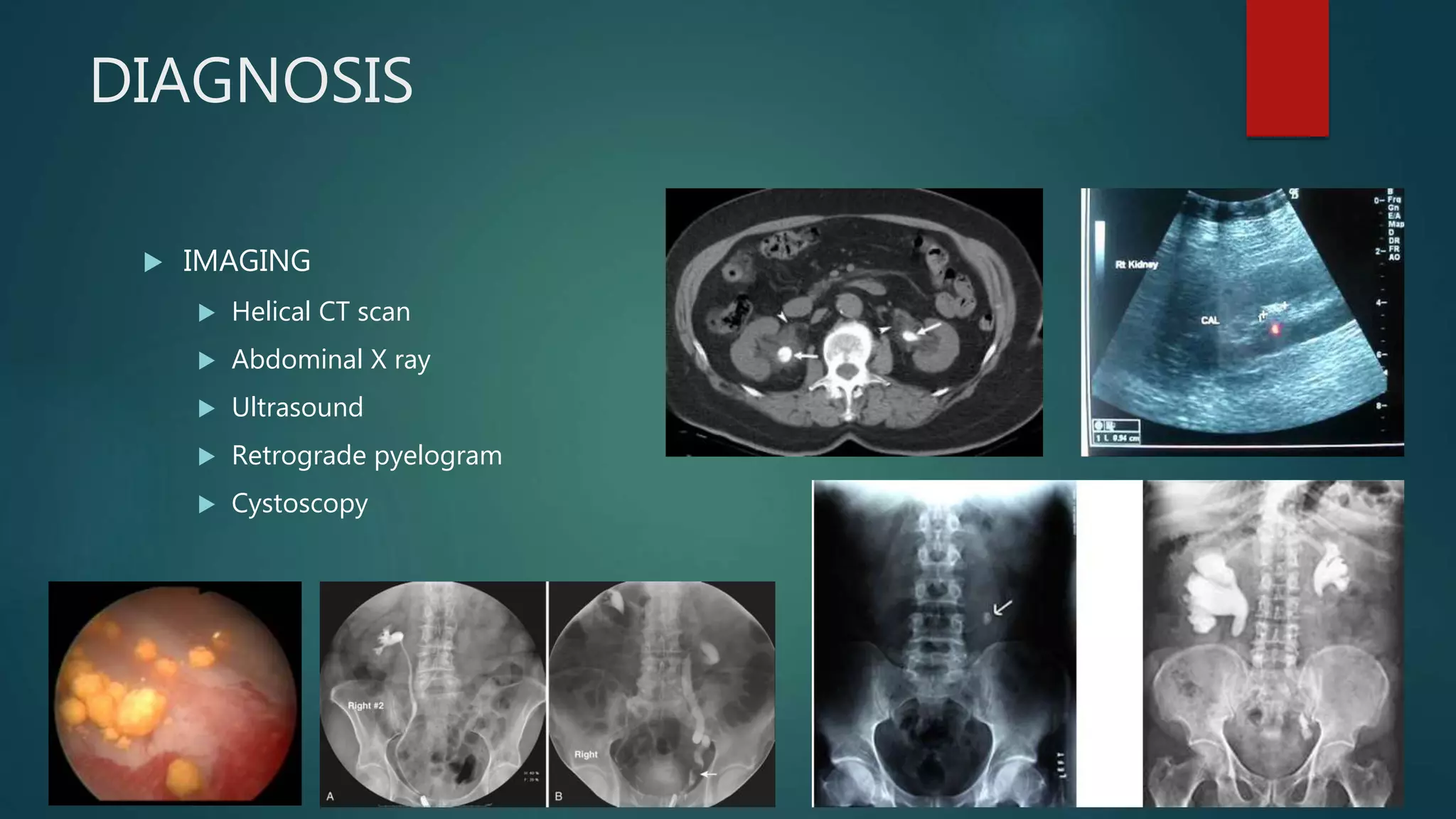
The document discusses nephrolithiasis (kidney stones) and pyelonephritis (kidney infection). It covers the types, risk factors, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnosis and treatment of both conditions. Calcium oxalate stones are the most common type of kidney stones. Risk factors for stone formation include dietary factors like calcium intake as well as urinary abnormalities. Pyelonephritis is commonly caused by gram-negative bacteria ascending from the bladder. It can cause kidney swelling and damage if left untreated.