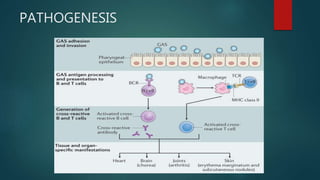
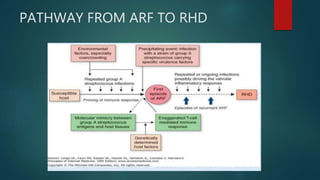
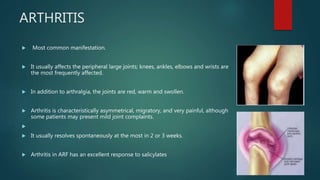
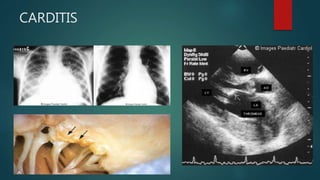
Rheumatic fever is an inflammatory disease that occurs as a delayed reaction to a Group A streptococcal throat infection. It most commonly affects children between 5-18 years old. The main manifestations include arthritis, carditis, chorea, and less commonly subcutaneous nodules and erythema marginatum. It is diagnosed using the revised Jones criteria which requires evidence of a preceding streptococcal infection and either two major manifestations or one major and two minor manifestations. Treatment involves primary prevention through antibiotic treatment of streptococcal infections, anti-inflammatory treatment such as aspirin for arthritis and steroids for carditis, supportive management of complications, and long-term secondary prevention through antibiotic prophylaxis.


















![REFERENCE
Stollerman GH. Rheumatic fever. Lancet. 1997;349:935–942. [PubMed]
Pomerance A. Cardiac involvement in rheumatic and ‘collagen’ diseases. In: Pomerance A, Davies MJ,
editors. The pathology of the heart. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications; 1975. pp. 279–306.
Denny FW, Wannamaker LW, Brink WR, Rammelkamp CH, Jr, Custer E. A Prevention of rheumatic fever;
treatment of the preceding streptococcic infection. J Am Med Assoc. 1950;143:151–153. [PubMed]
Carapetis JR. The stark reality of rheumatic heart disease. Eur Heart J. 2015;36:1070–1073. [PubMed]
Longo DL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Jameson J, Loscalzo J. eds.Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine,
18e. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2012.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rheumaticfever-181117115345/85/Rheumatic-fever-25-320.jpg)
