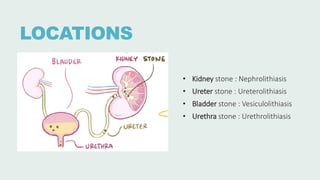
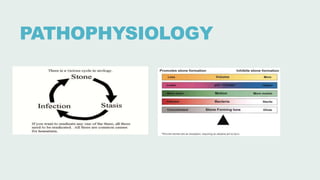
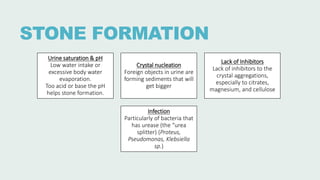
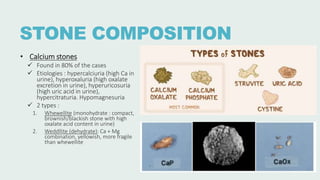
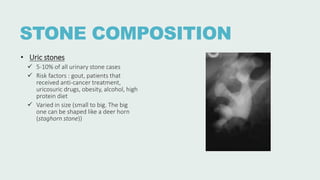
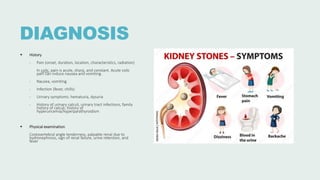
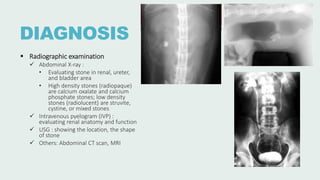
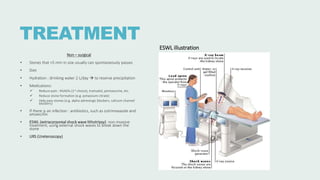
Urolithiasis refers to the formation of stones in the urinary tract. Kidney stones are the most common type and risk factors include male sex, age 30-50 years old, genetic predisposition, diet high in purines/oxalates/calcium, and low water intake. Stones form when urine becomes supersaturated with minerals that precipitate into crystals. The majority are calcium-based, while others contain uric acid, struvite, or cystine. Clinical features range from asymptomatic to severe flank pain. Diagnosis involves urinalysis, radiography, and sometimes urine culture. Treatment depends on stone size but may include increased fluid intake, medications, extracorporeal shockwave lithot











![REFERENCES
• [Guideline] Assimos DG, Krambeck A, Miller NL, et al. Surgical Management of Stones: American Urological Association/Endourological
Society Guideline. American Urological Association. Available at https://www.auanet.org/guidelines-and-quality/guidelines/kidney-
stones-surgical-management-guideline. 2016
• Chirag N Dave, MD. Nephrolithiasis. Medscape. Available at https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/437096-overview. 2023
• Anna Hernández Castillo, MD. Nephrolithiasis. Elsevier. Available at https://www.osmosis.org/answers/nephrolithiasis.
• Gottlieb, M., Long, B., & Koyfman, A. (2018). The evaluation and management of urolithiasis in the ED: A review of the literature. The
American Journal of Emergency Medicine, 36(4): 699–706.
• Han, H., Segal, A. M., Seifter, J. .L, & Dwyer, J. T. (2015). Nutritional Management of Kidney Stones (Nephrolithiasis). Clinical Nutrition
Research, 4(3): 137–152.
• Matlaga, B. R., Shah, O. D., & Assimos, D. G. (2003). Drug-induced urinary calculi. Reviews in Urology, 5(4), 227–231.
• Scales, C. D., Jr, Smith, A. C., Hanley, J. M., & Saigal, C. S. (2012). Prevalence of kidney stones in the United States. European Urology,
62(1): 160–165.
• Semins, M. J. & Matlaga, B. R. (2010). Medical evaluation and management of urolithiasis. Therapeutic Advances in Urology, 2(1):3–9
• Campbell, M.F., Kavoussi, L.R. and Wein, A.J. (2020) Campbell-Walsh Urology. 12th Edition, Elsevier Saunders, Philadelphia, PA..](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/urolithiasis-231015195224-ed47a43a/85/UROLITHIASIS-pptx-22-320.jpg)