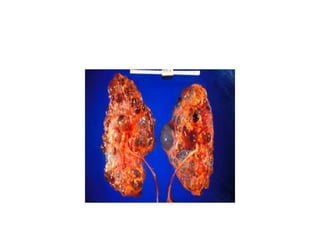
Upper urinary tract disorders encompass conditions affecting the kidneys and ureters, which can be congenital or acquired, including infections, obstructions, and neoplasms. Congenital disorders such as renal agenesis and horseshoe kidney are noted for their varying clinical implications, while acquired disorders often present through infections or calculi leading to significant symptoms and complications. Management strategies include surgical intervention, medical treatment, and proactive monitoring, depending on the specific condition and its severity.