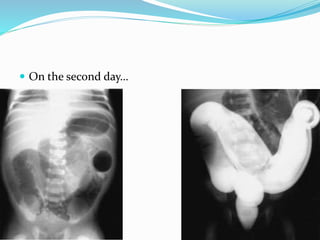
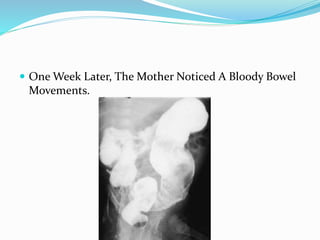
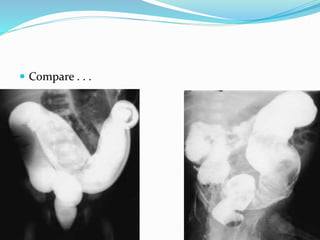
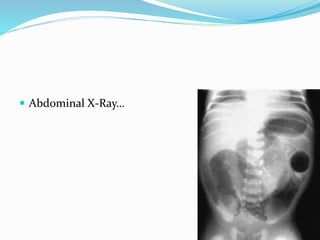
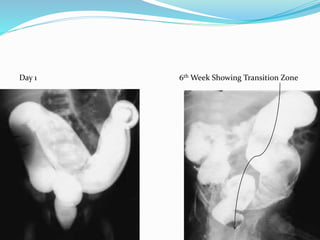
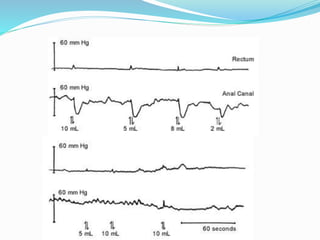
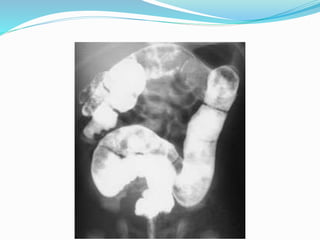
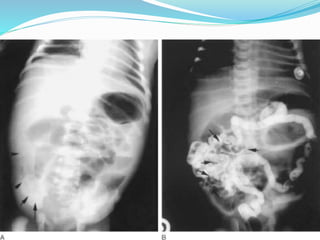
The document discusses various causes of neonatal intestinal obstruction including meconium ileus, meconium plug syndrome, Hirschsprung's disease, and anal atresia. It provides details on the presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of each condition. For example, it notes that meconium ileus presents at birth with abdominal distension and vomiting and is often associated with cystic fibrosis. Diagnosis is typically made through contrast enema and treatment may involve gastrografin enema or surgery to evacuate the obstructing meconium.