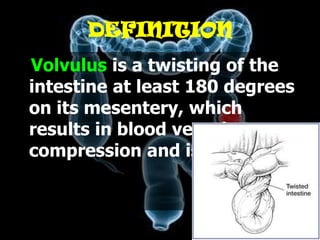
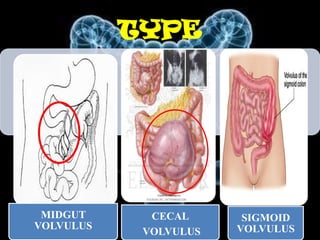
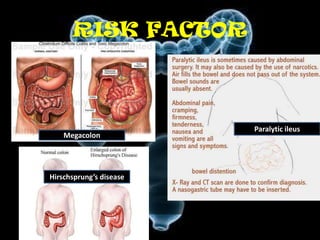
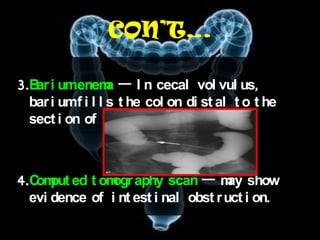
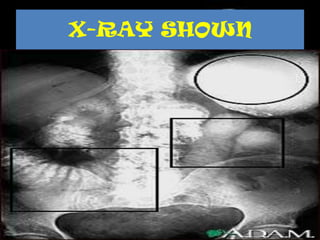
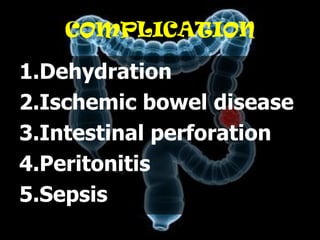
Volvulus is a twisting of the intestine resulting in blood vessel compression and ischemia. There are three main types: midgut, cecal, and sigmoid volvulus. Risk factors include chronic constipation, abnormal intestinal contents, and congenital malrotation. Signs include abdominal distension, pain, vomiting, and rapid heart rate. Diagnostic tests include abdominal x-rays, blood work, barium enema, and CT scan. Treatment depends on the type but may include surgery, sigmoidoscopy, or monitoring for signs of ischemia. Complications can be dehydration, ischemic bowel disease, perforation, peritonitis, and sepsis.