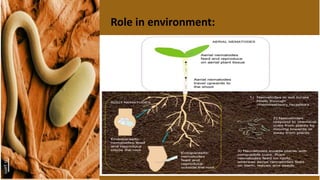
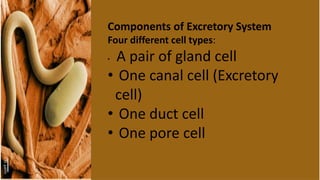
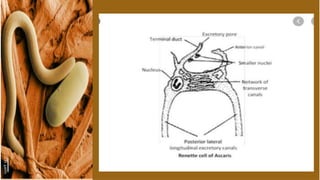
Nematodes have a simple excretory system for osmoregulation and excretion. Ammonia is the main nitrogenous waste product that is secreted through the body wall. There are two main types of excretory systems - glandular and tubular. The glandular type features a single renette cell that leads to a duct and pore, while the tubular type has a H-shaped structure with longitudinal and transverse ducts connecting to an excretory pore. Specialized renette cells and other structures help regulate salts, remove waste, and control osmotic pressure in nematodes inhabiting different environments.