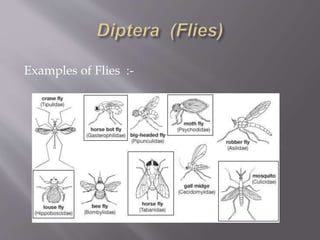
The document discusses the order Diptera, or true flies. It notes that Diptera are characterized by having one pair of wings, with the hind wings reduced to knob-like structures called halteres. Flies range in size from less than 1mm to over 7cm. There are over 125,000 known fly species worldwide. Flies can be found in most habitats and play both beneficial and harmful roles in ecosystems.