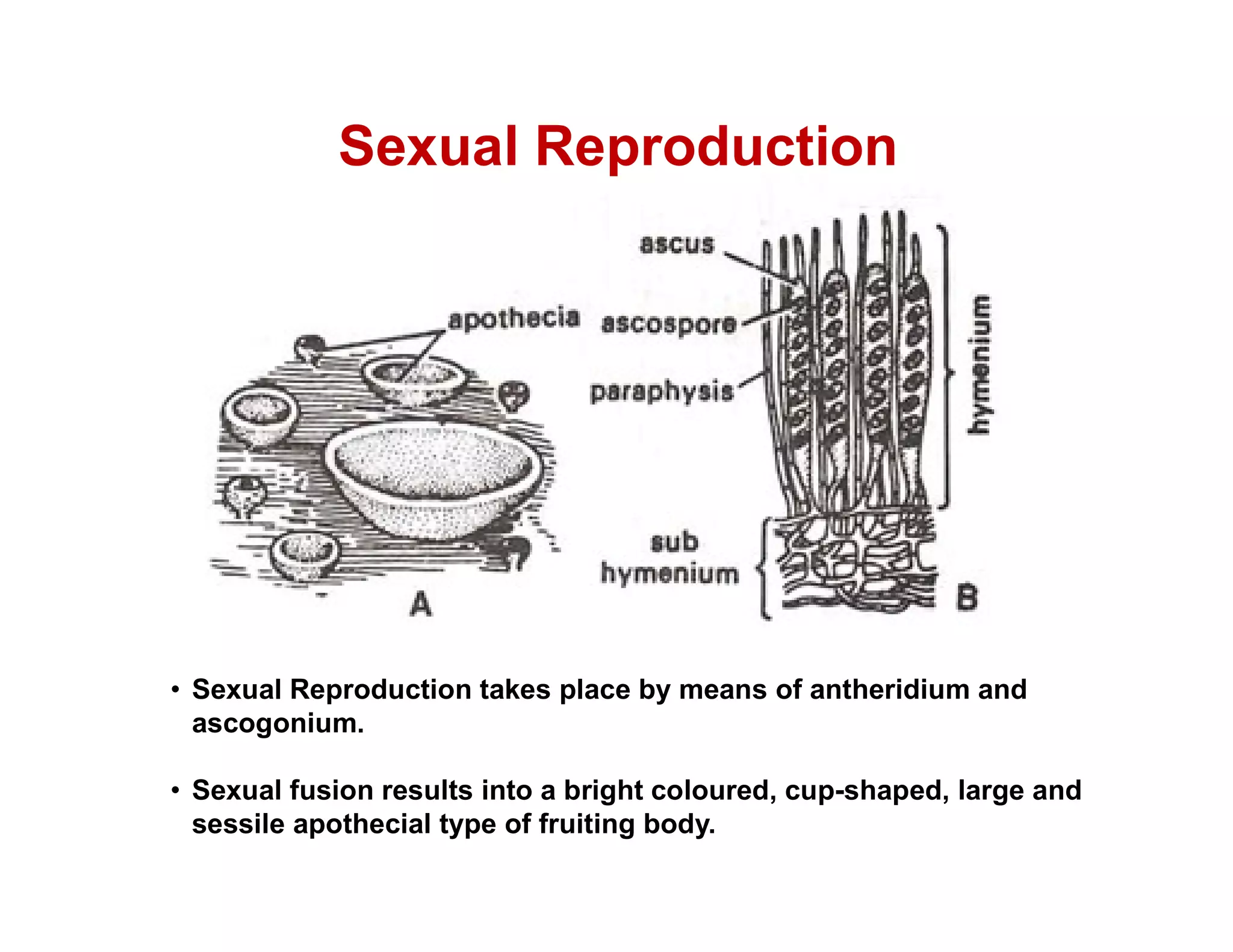
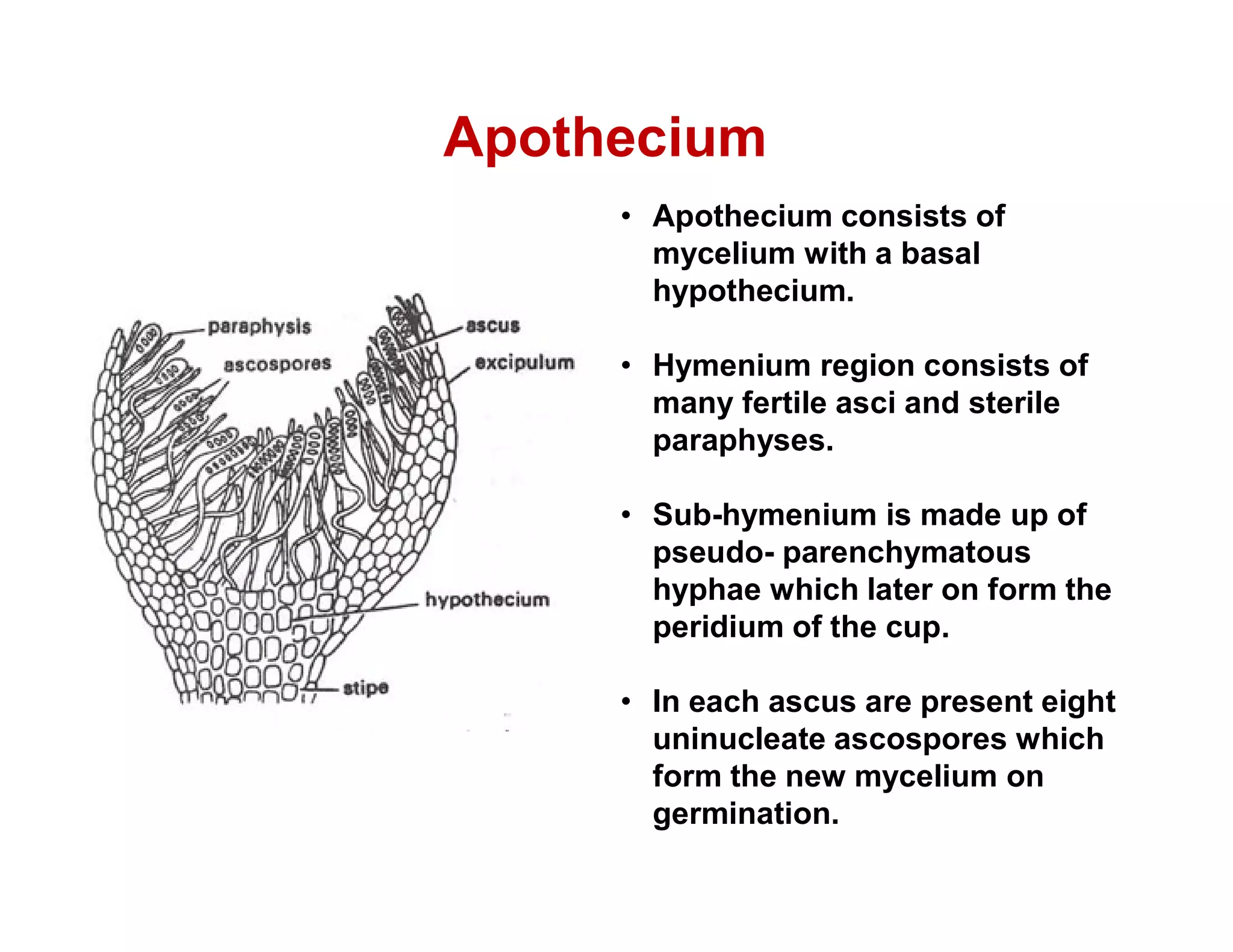
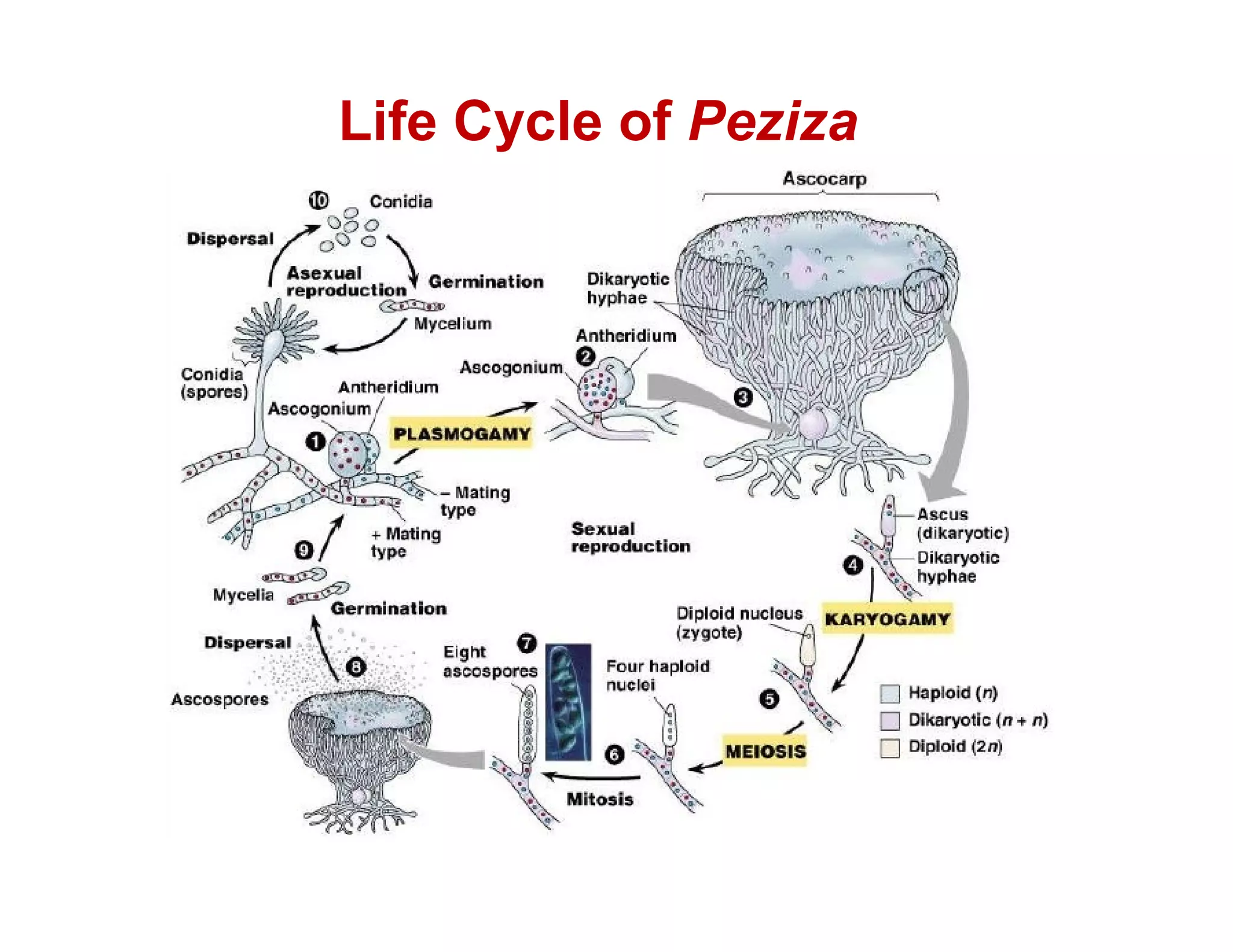
Peziza is a genus of cup fungi that grows on the ground, rotting wood, or dung. It produces cup or disc-shaped fruiting bodies called apothecia that can be sessile or stalked, and range in size from 0.5-10 cm in diameter. Peziza contains over 100 species and reproduces both sexually through antheridia and ascogonia fusion or asexually by producing conidia or chlamydospores.