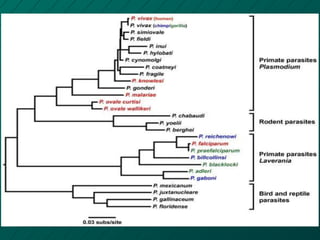
Parasitism has evolved over time as parasites adapt to their hosts. Parasites like malaria originated in primates in Africa and later transferred to humans. Malaria is caused by Plasmodium parasites transmitted via mosquito bites and Plasmodium falciparum is thought to have evolved from gorillas to infect humans around 50,000 years ago. Parasites continue evolving in response to hosts and their environments.