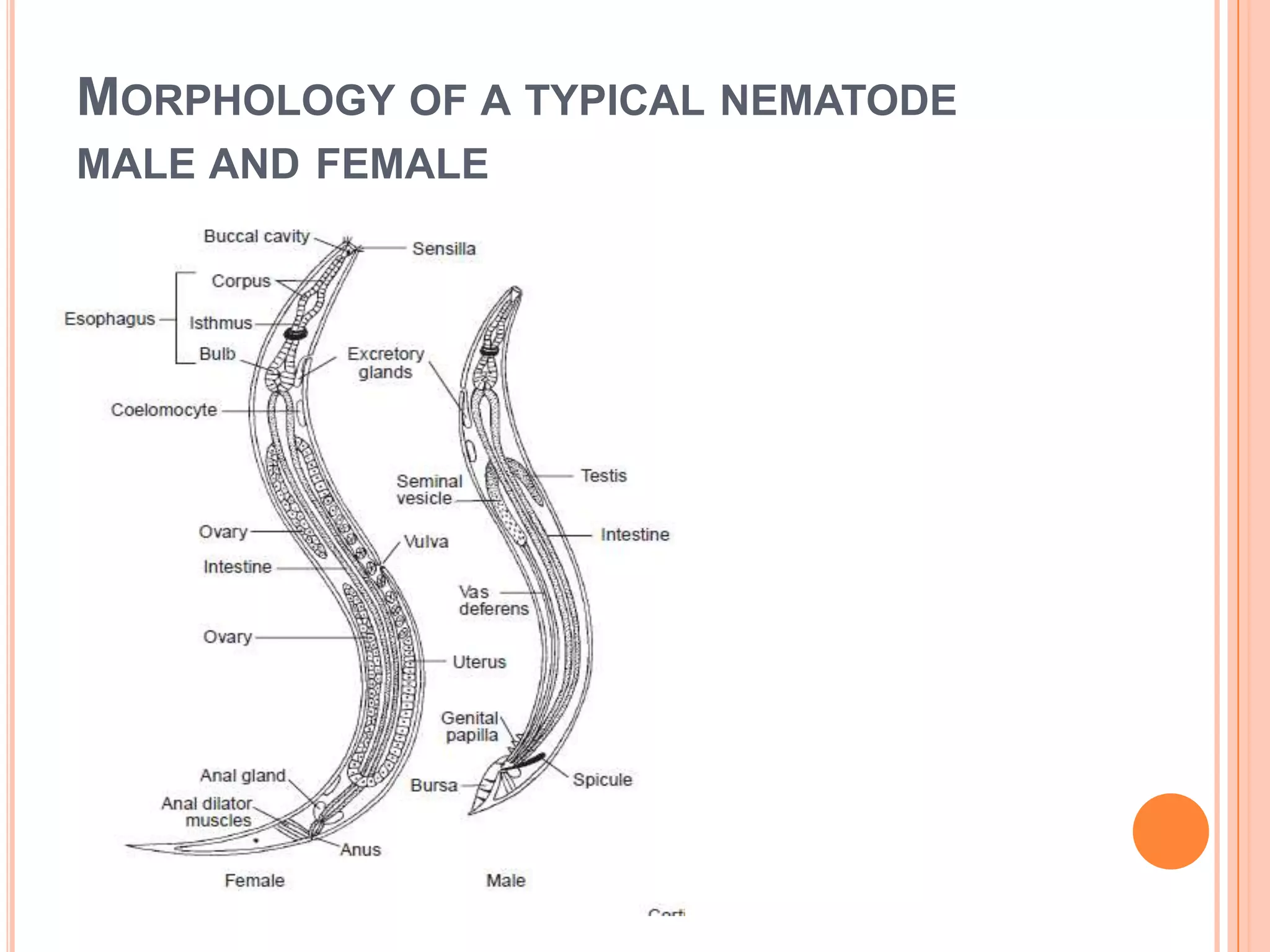
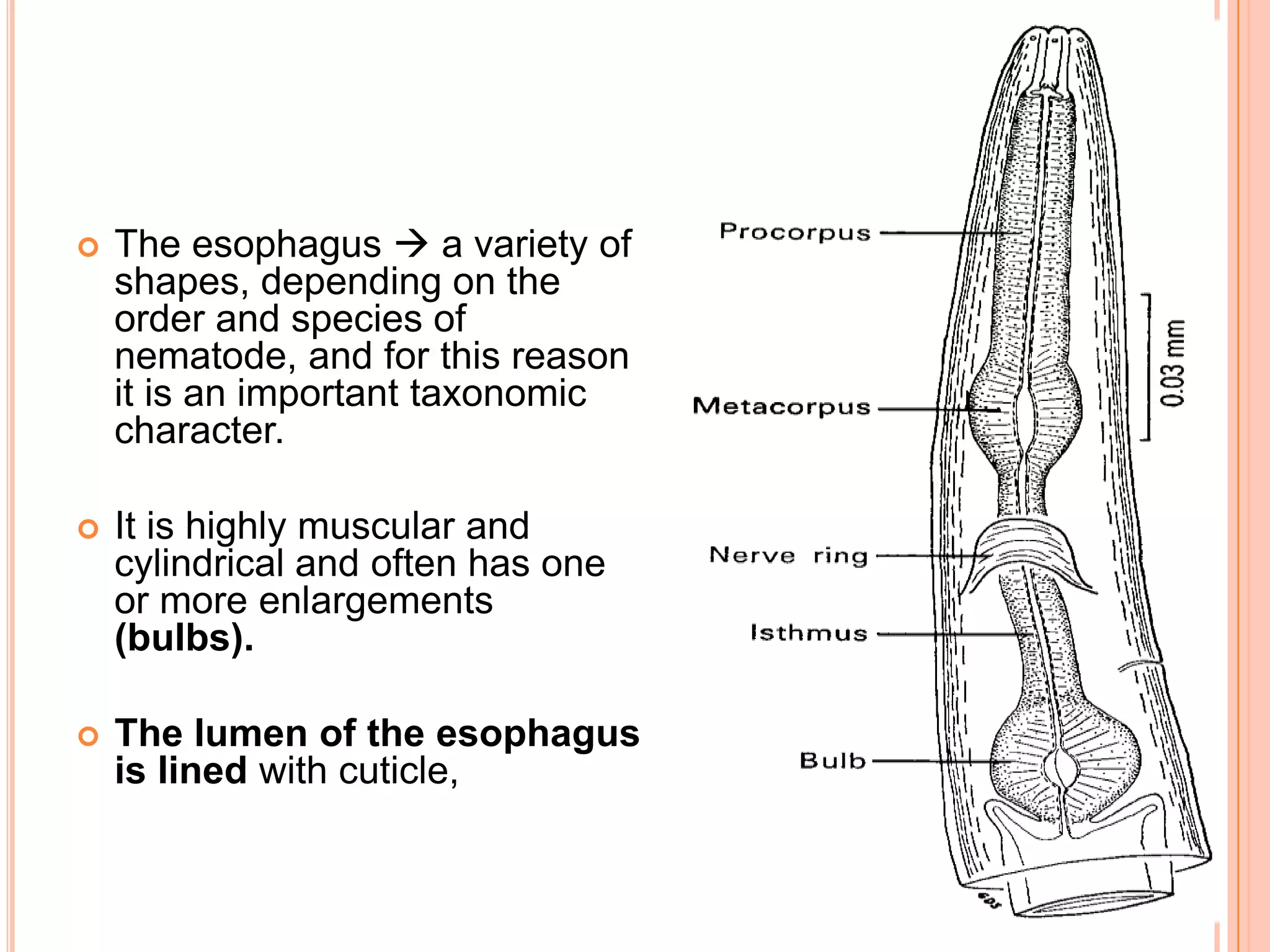
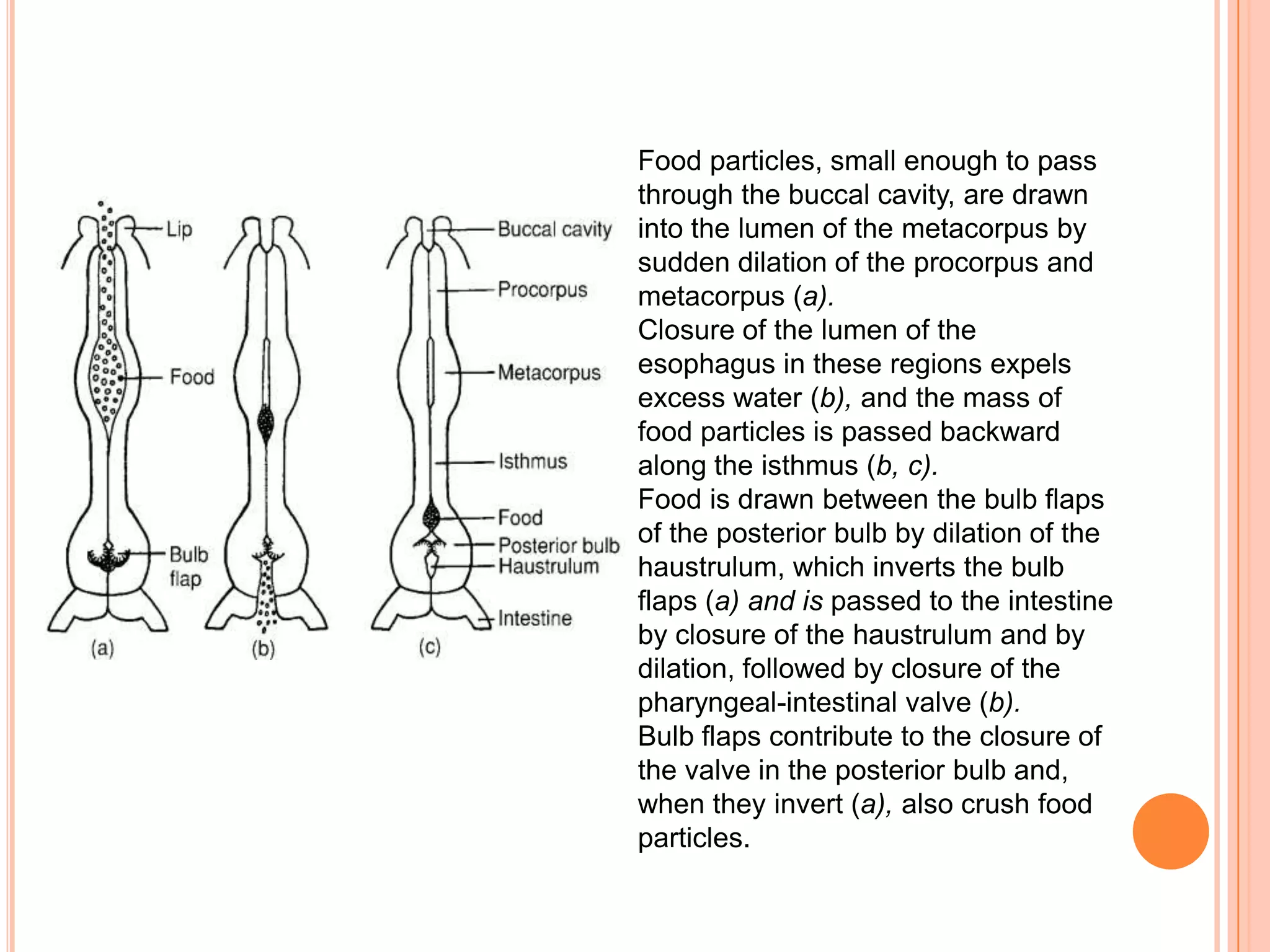
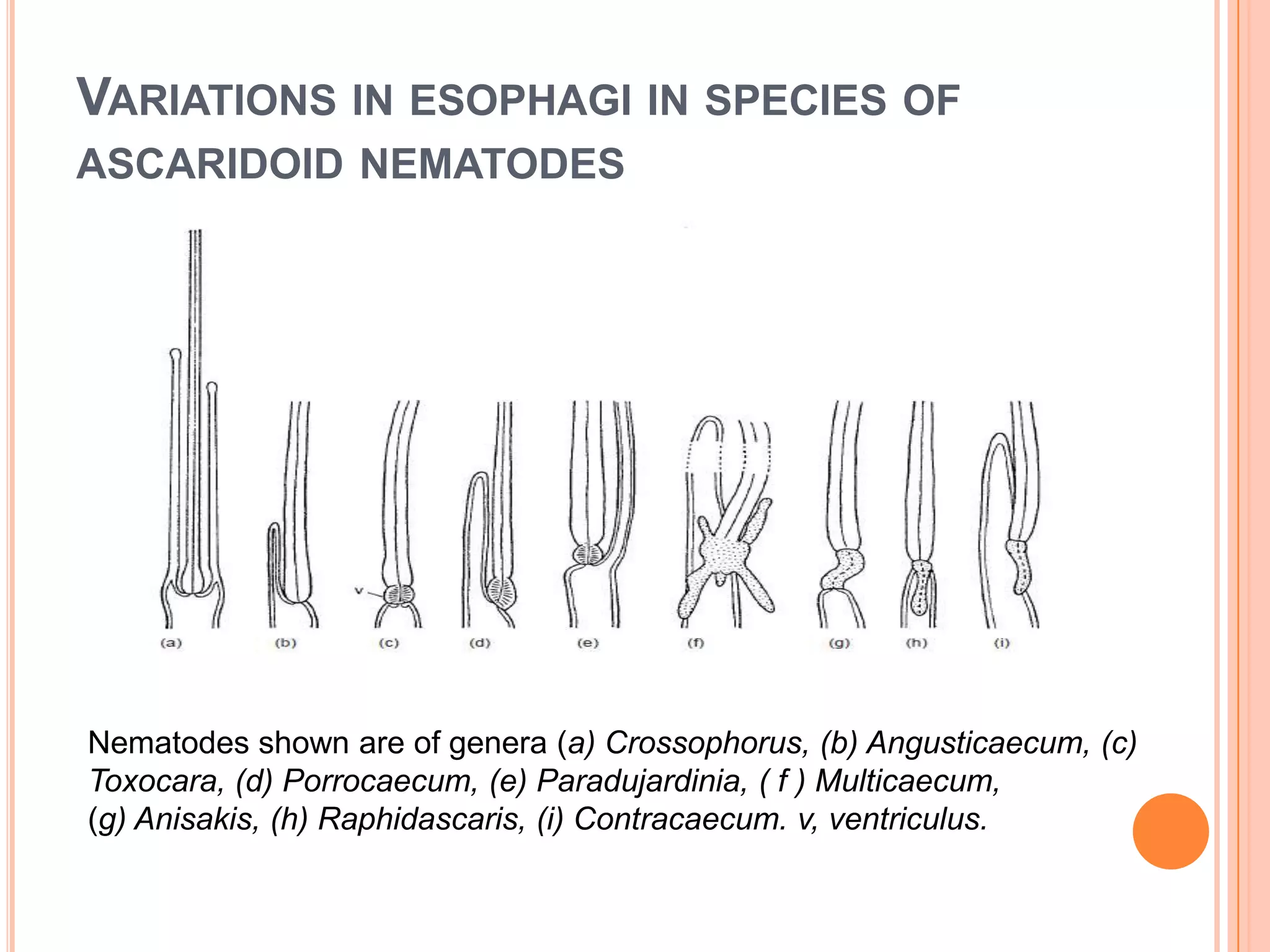
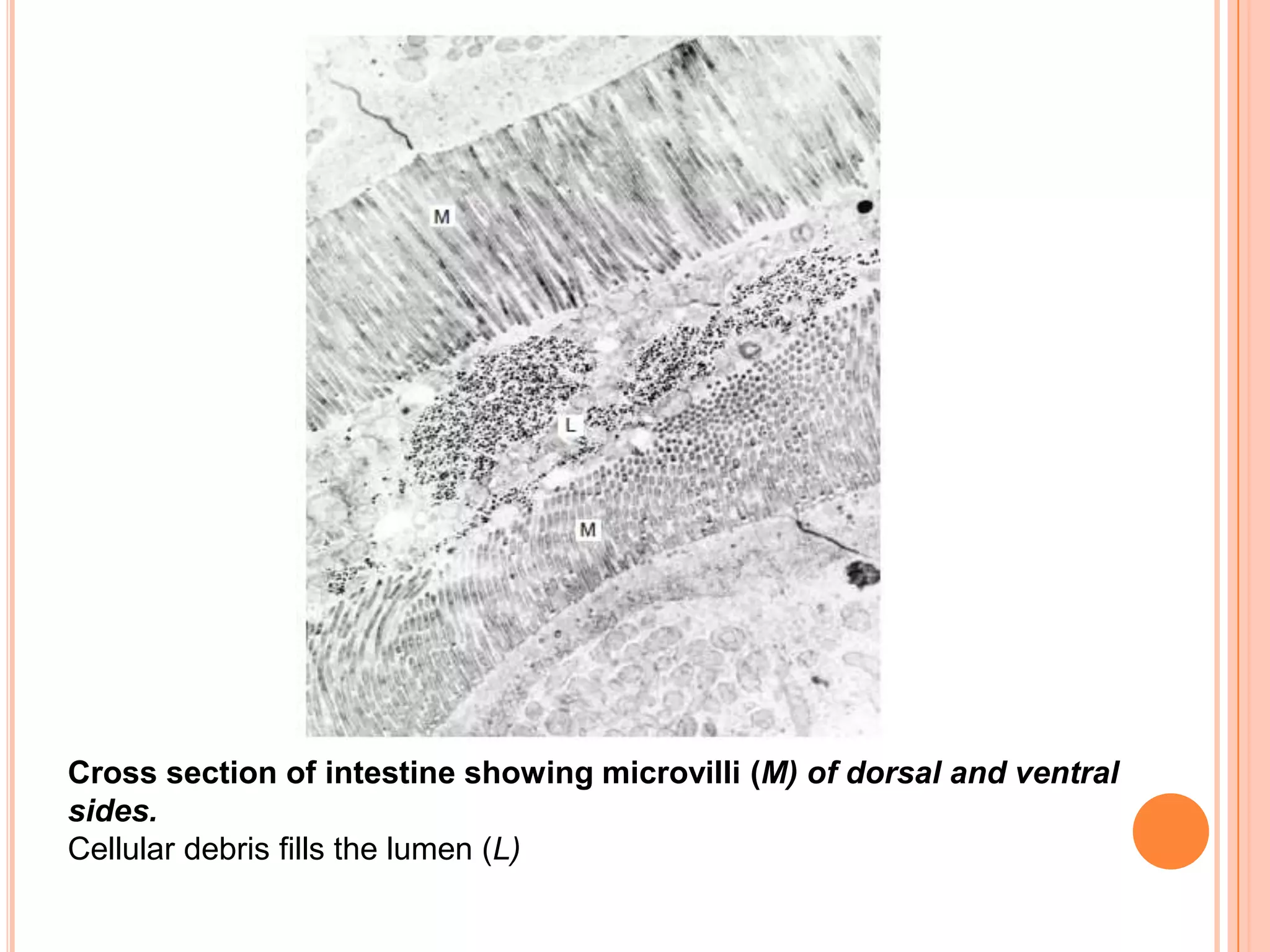
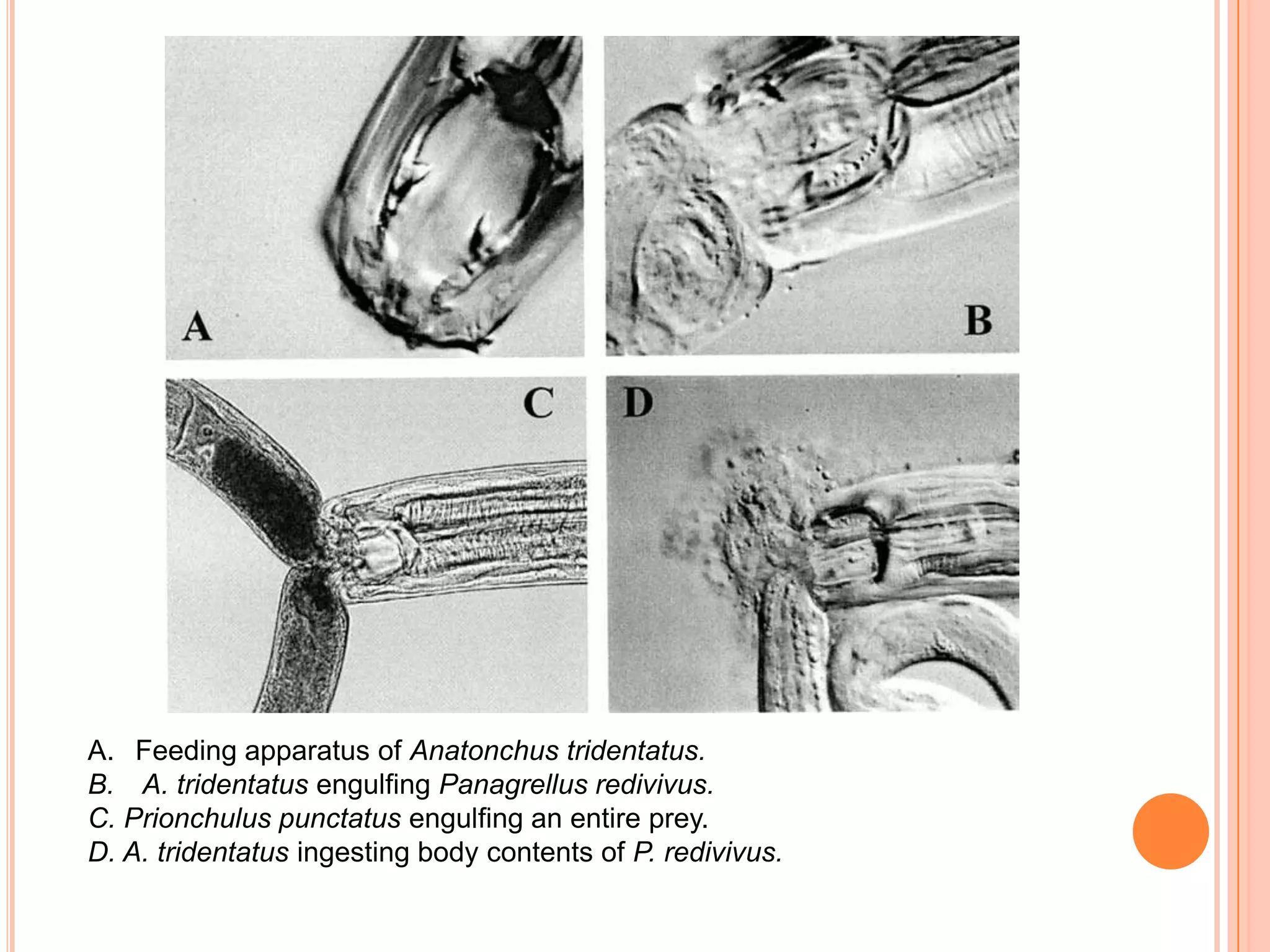
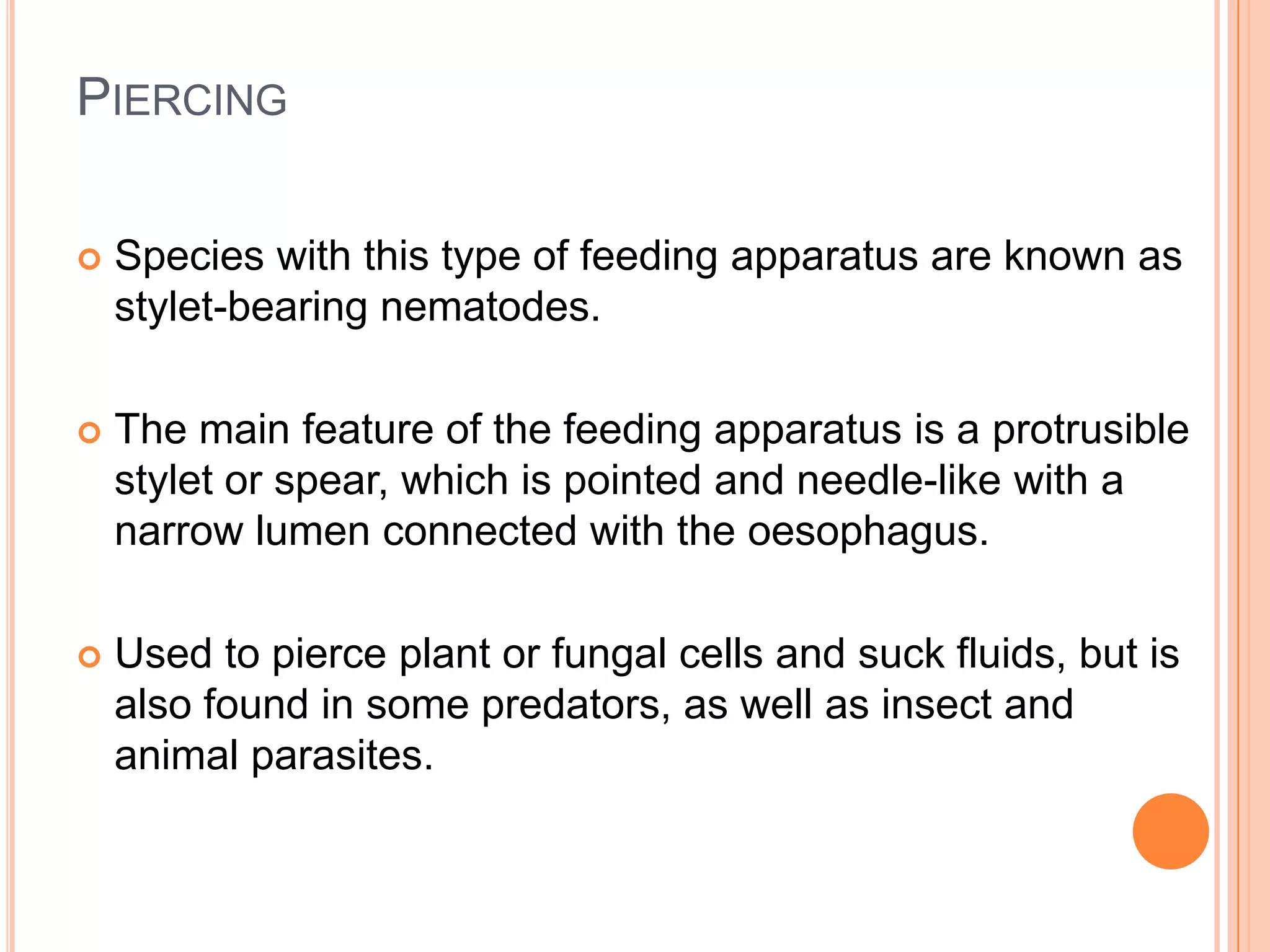
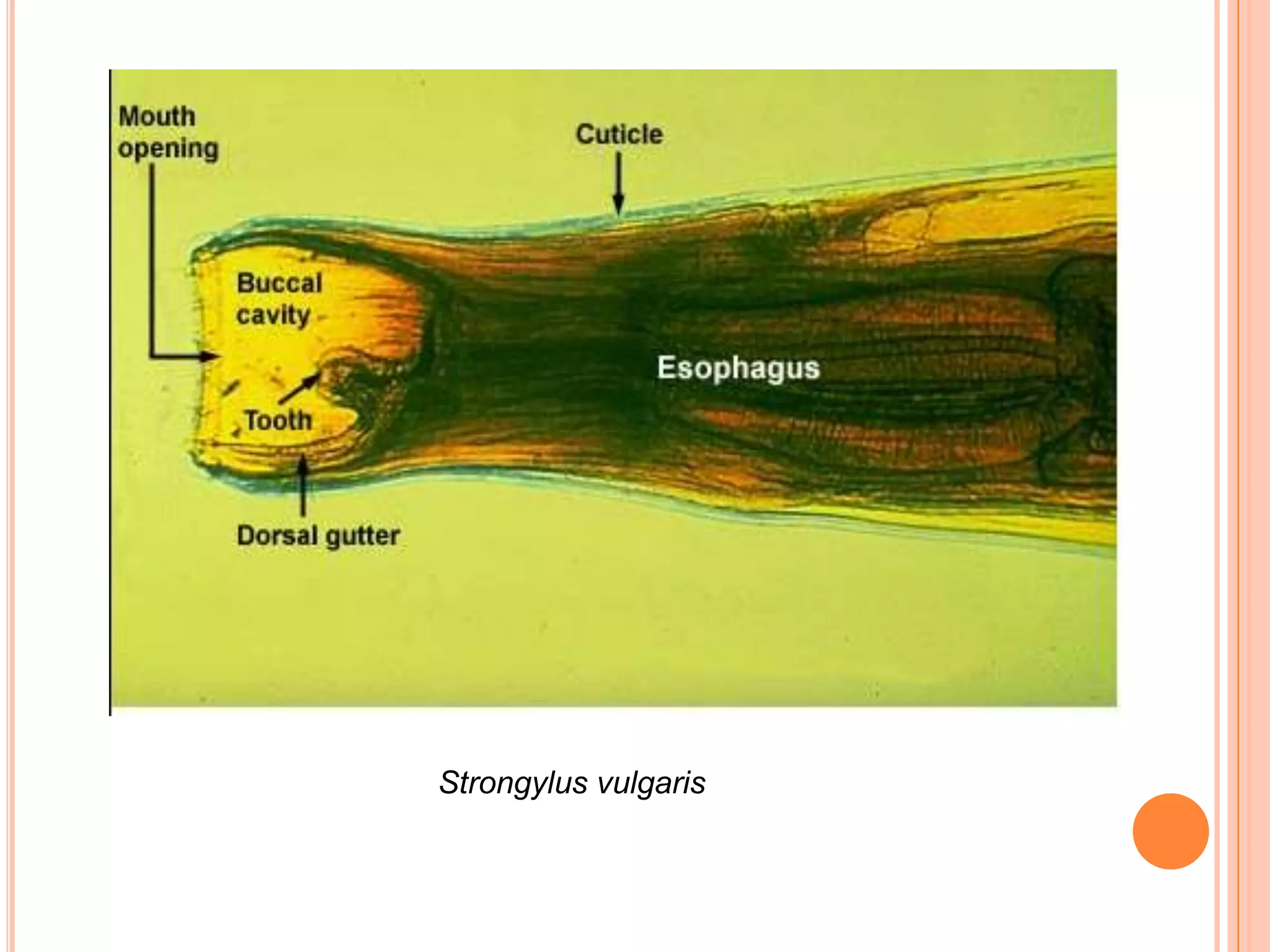
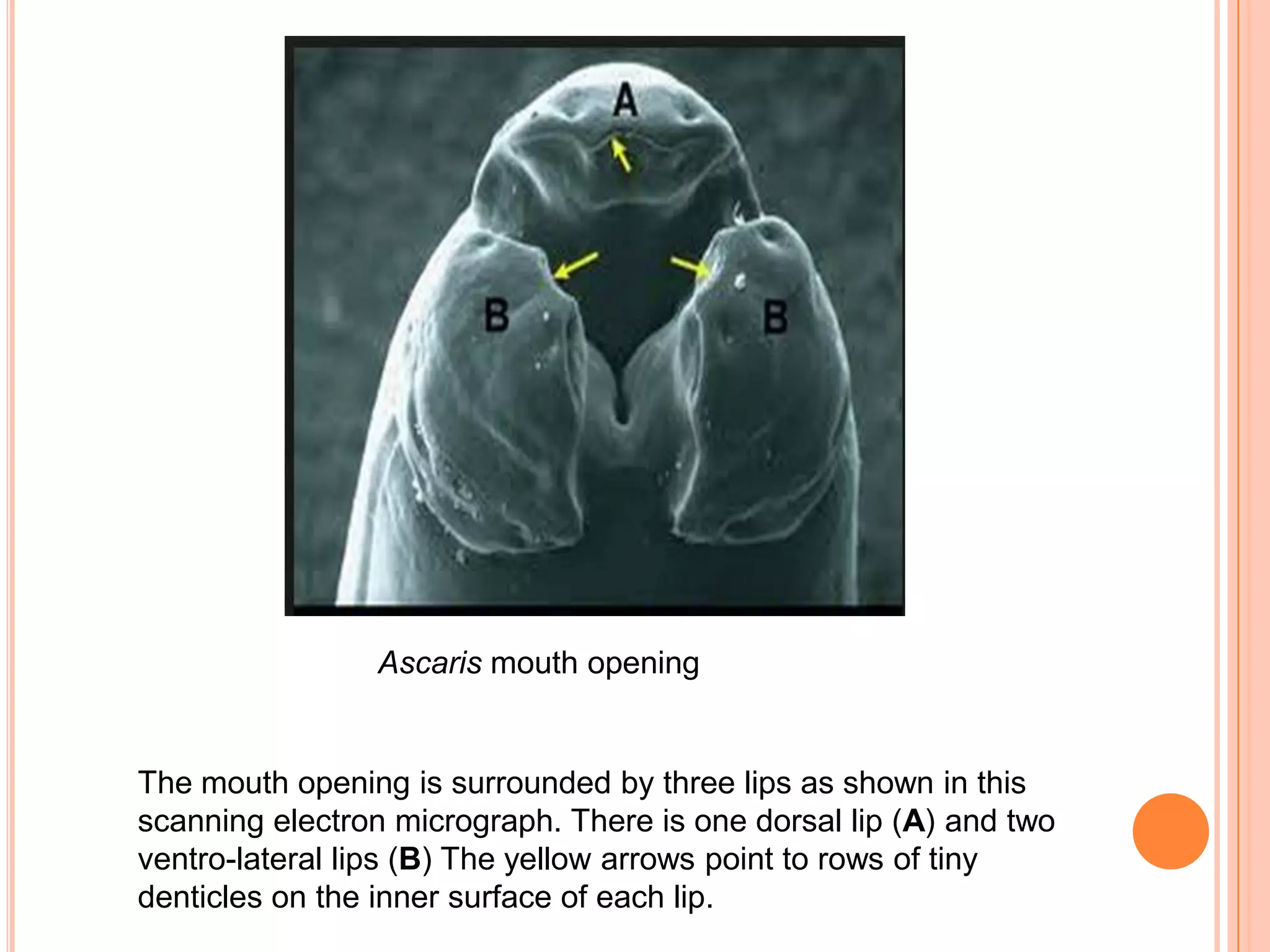
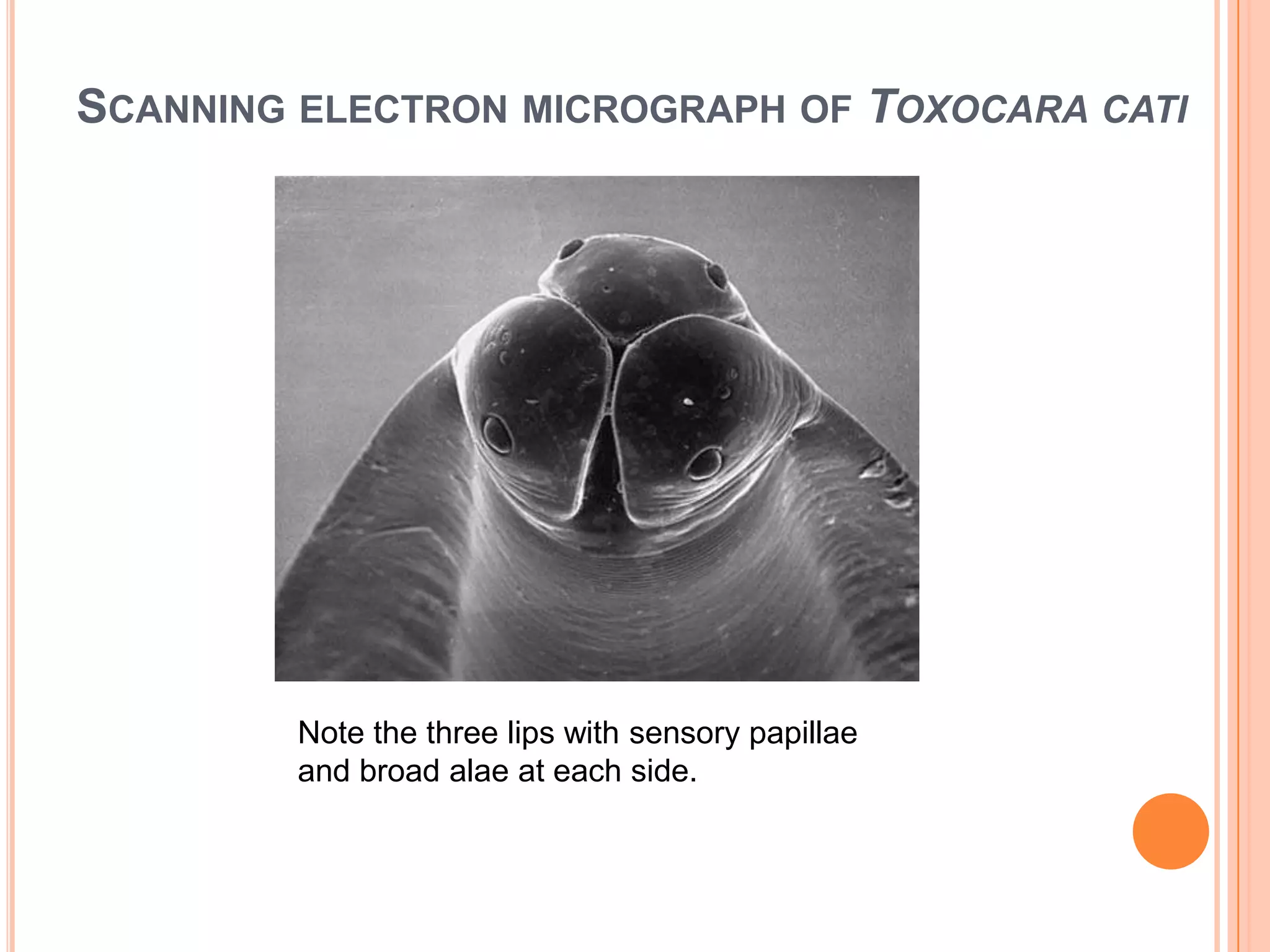
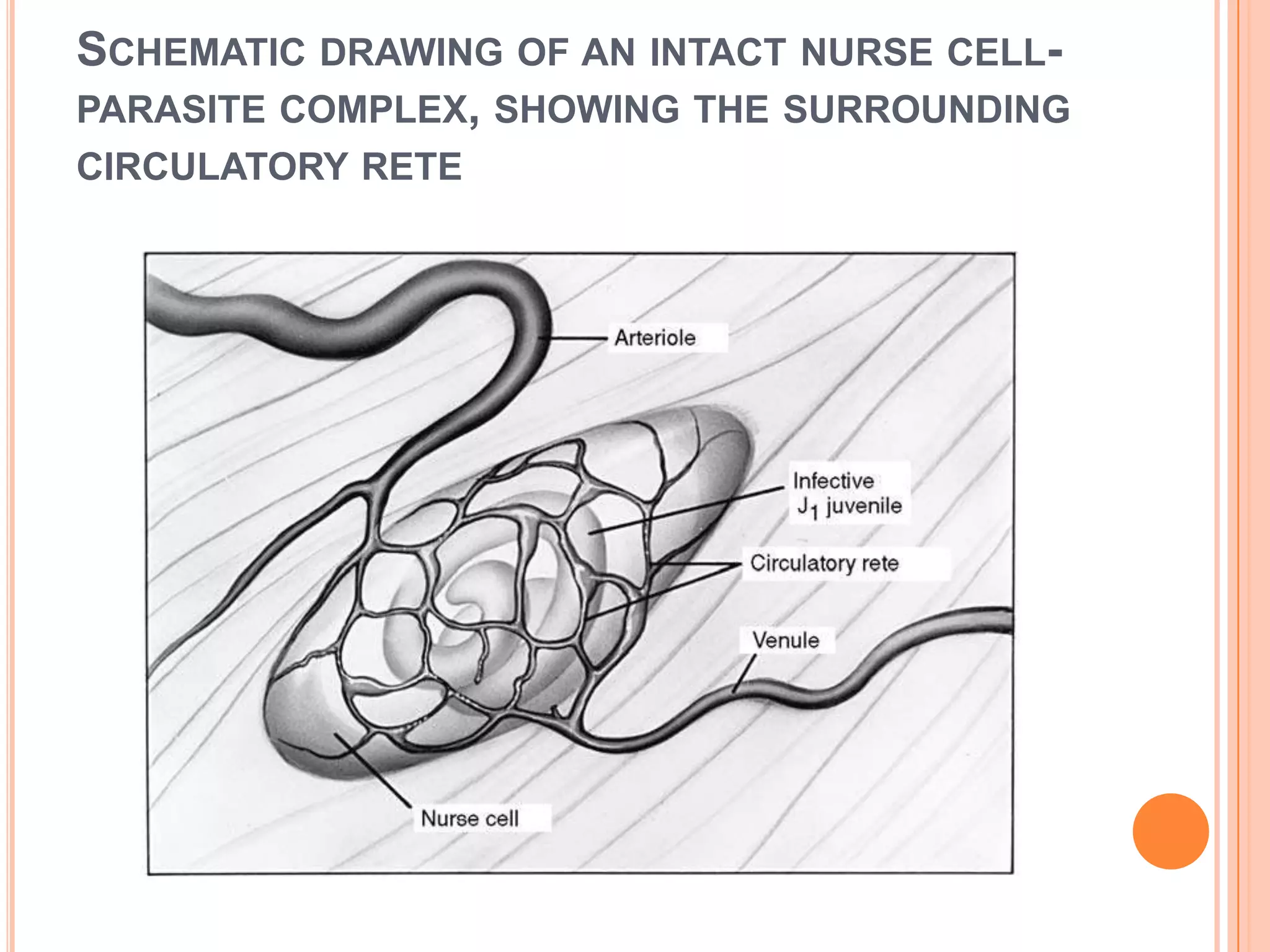
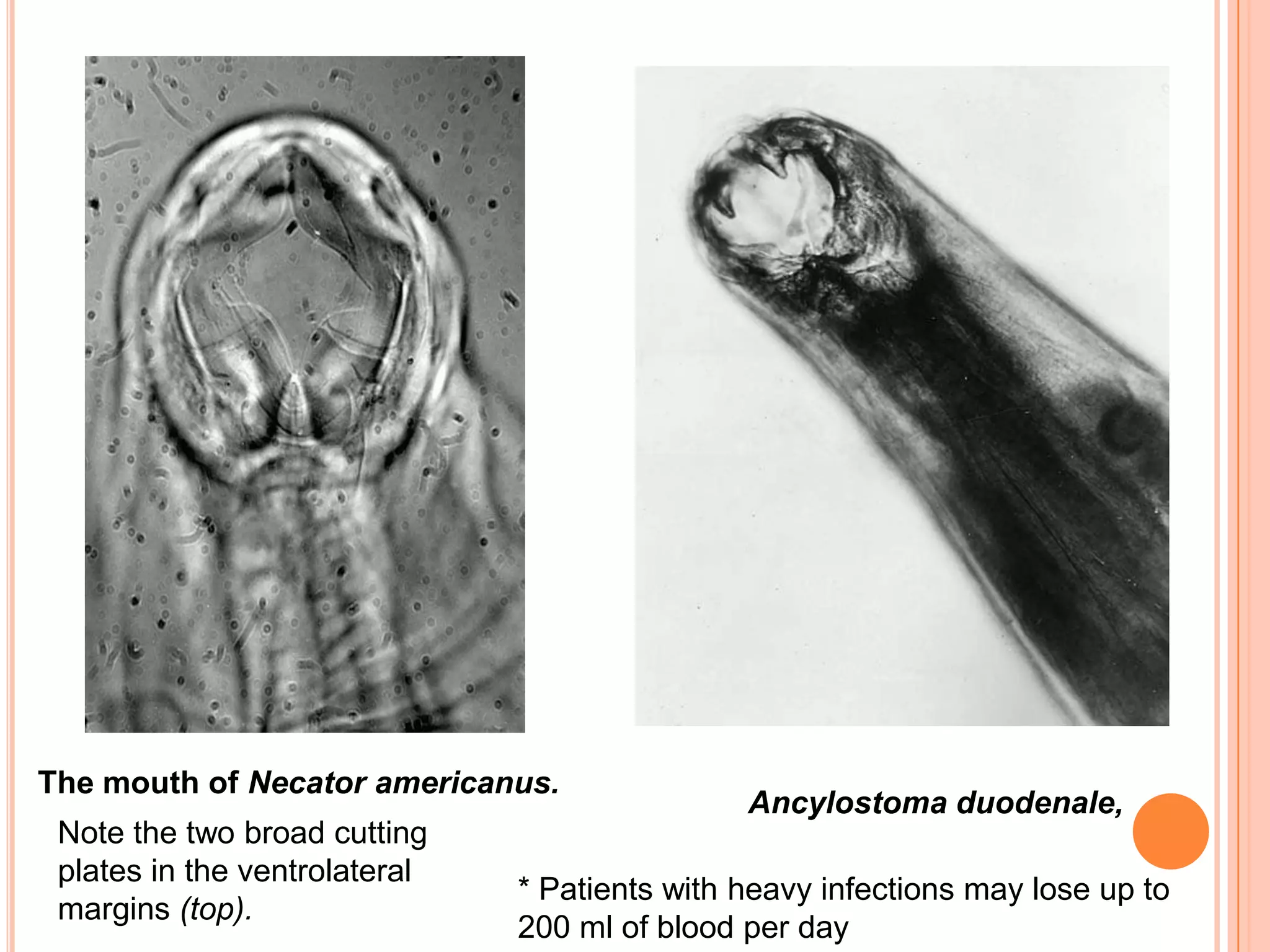
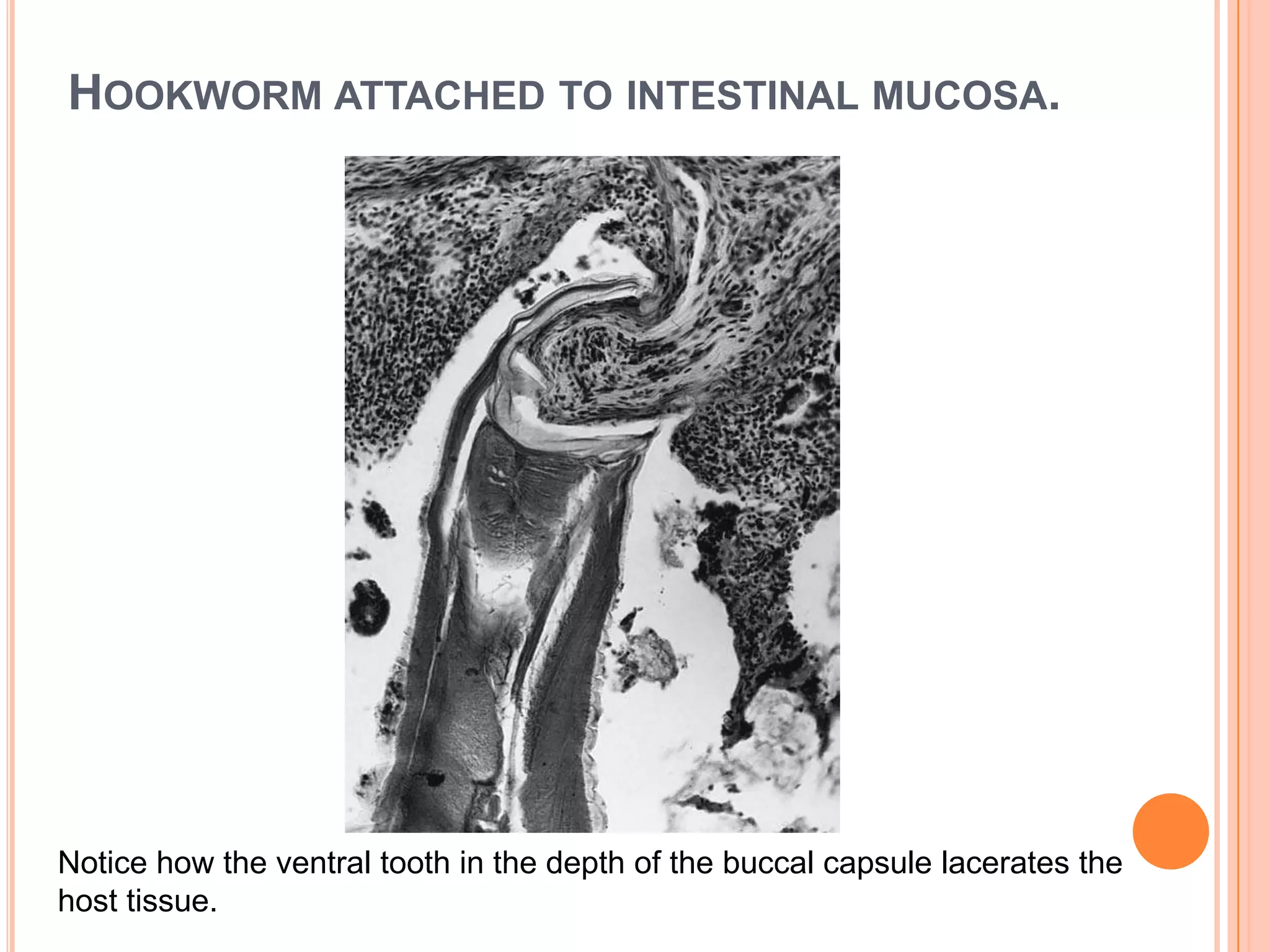
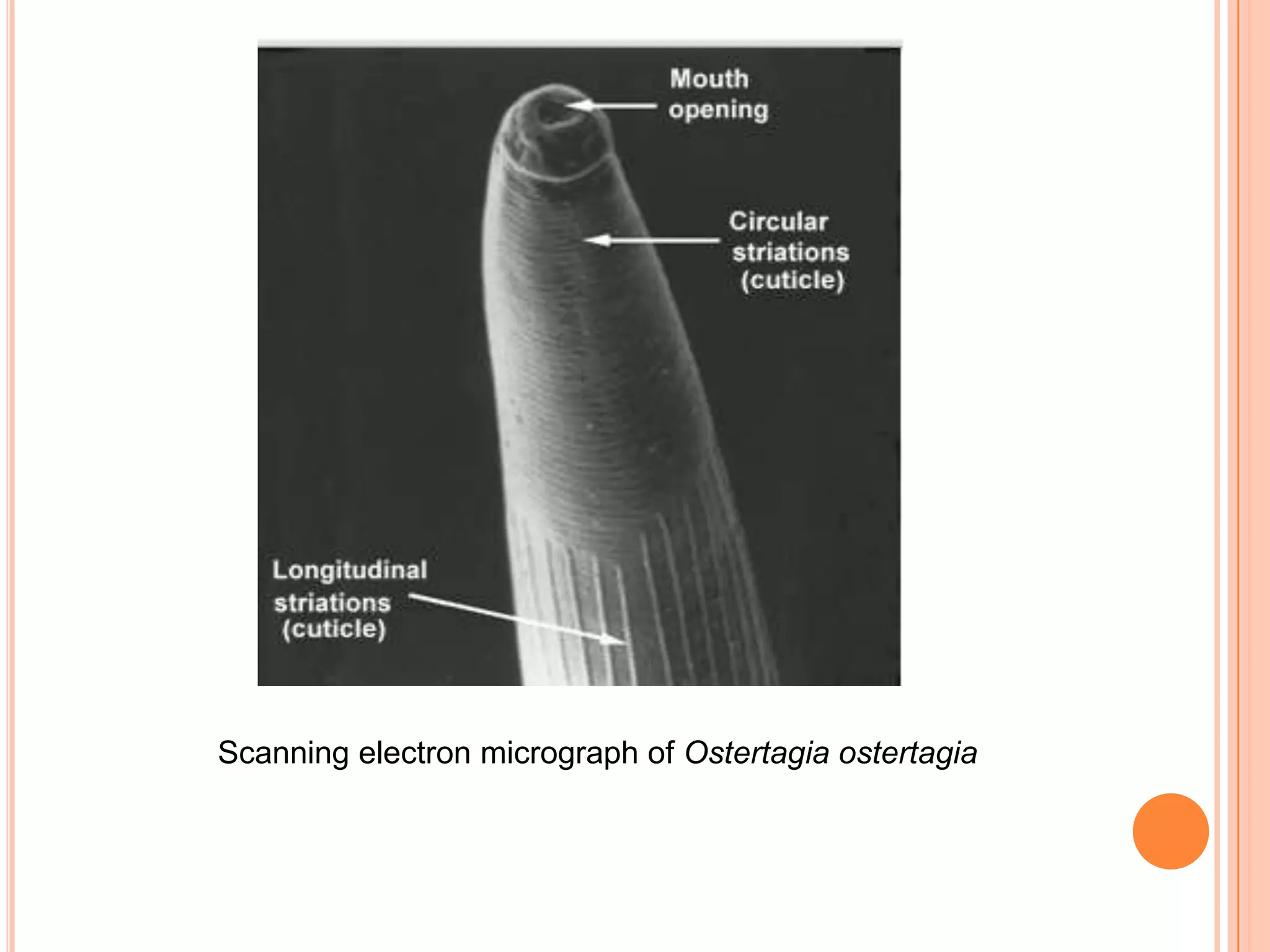
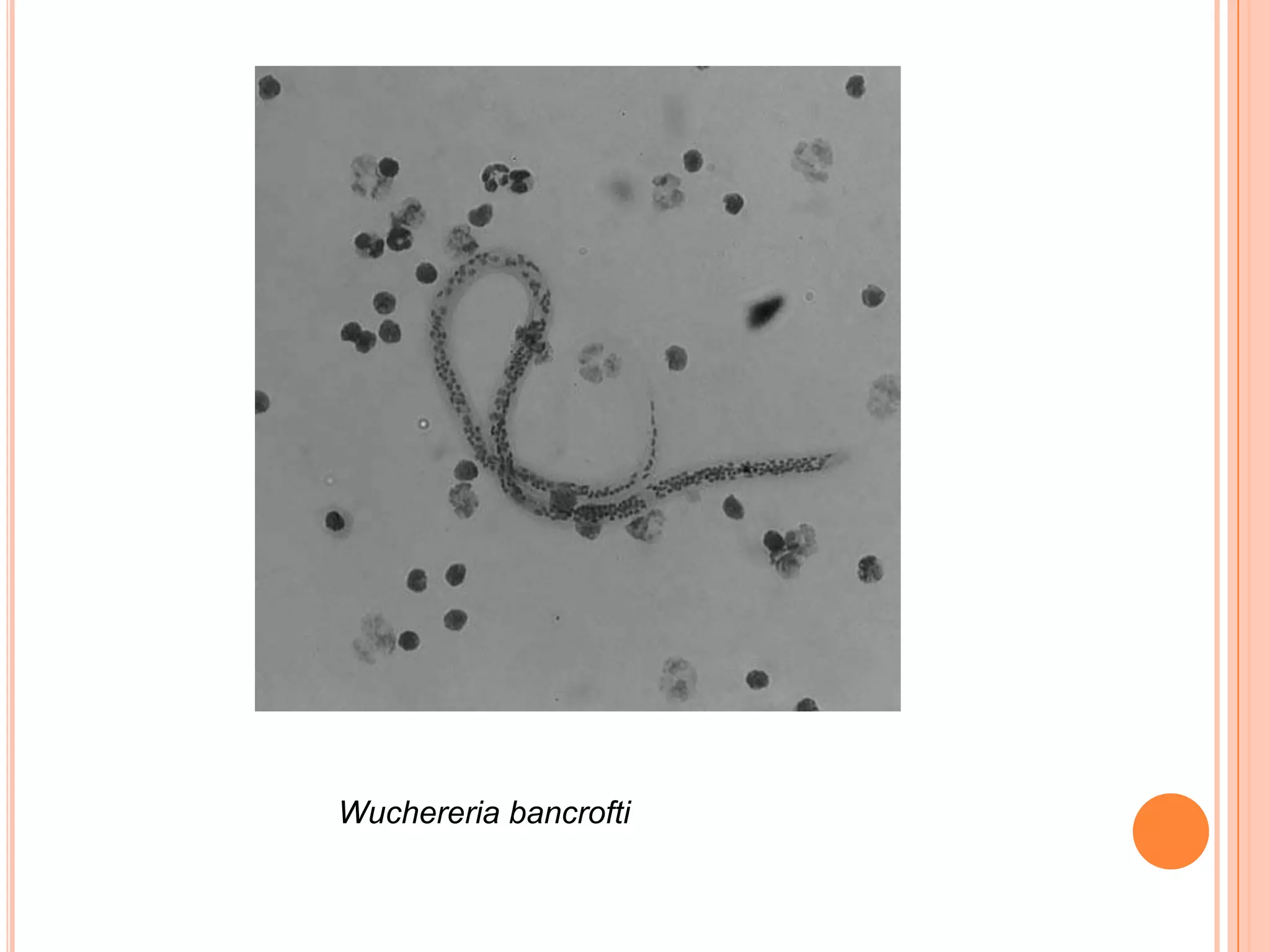
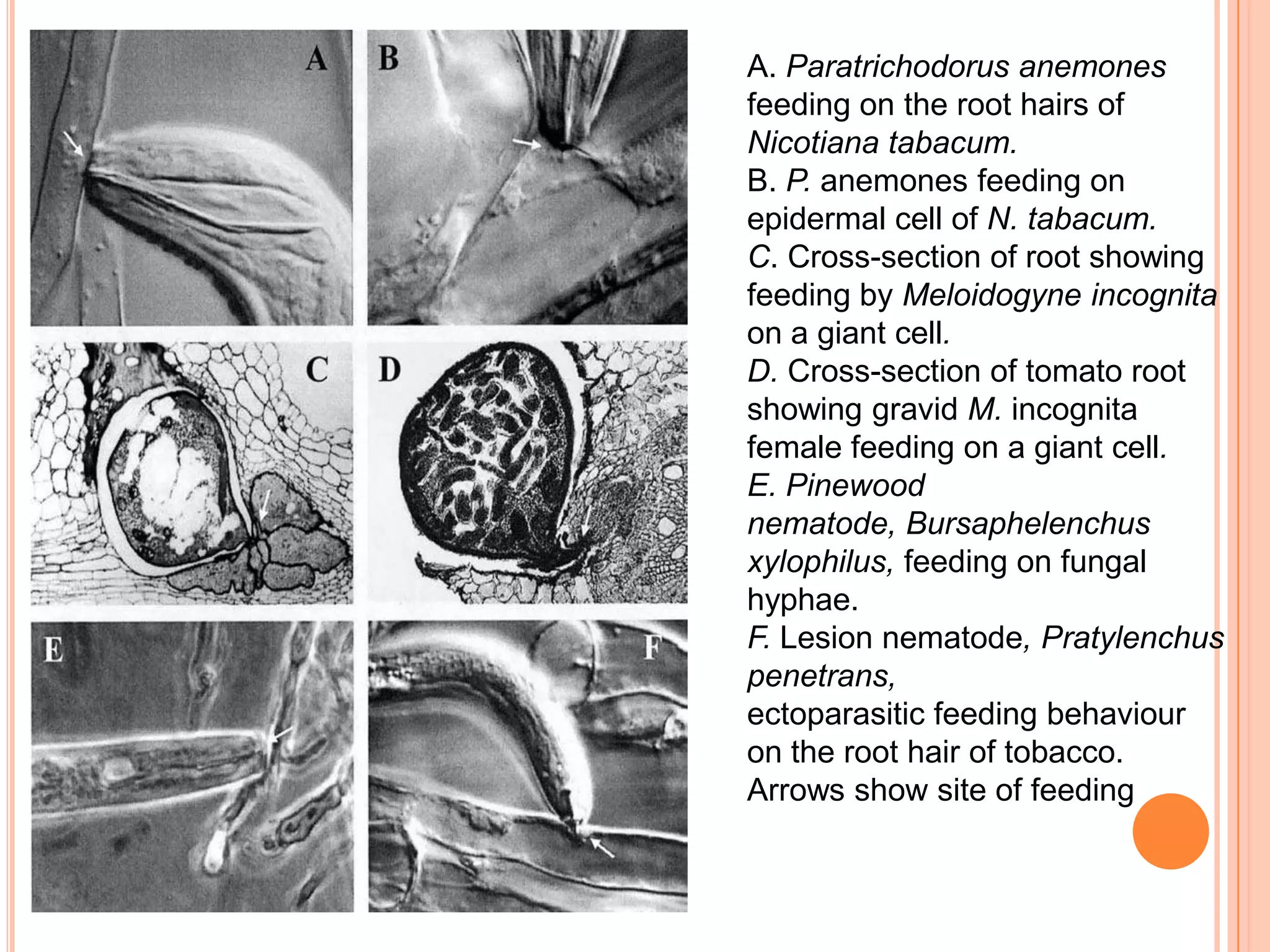
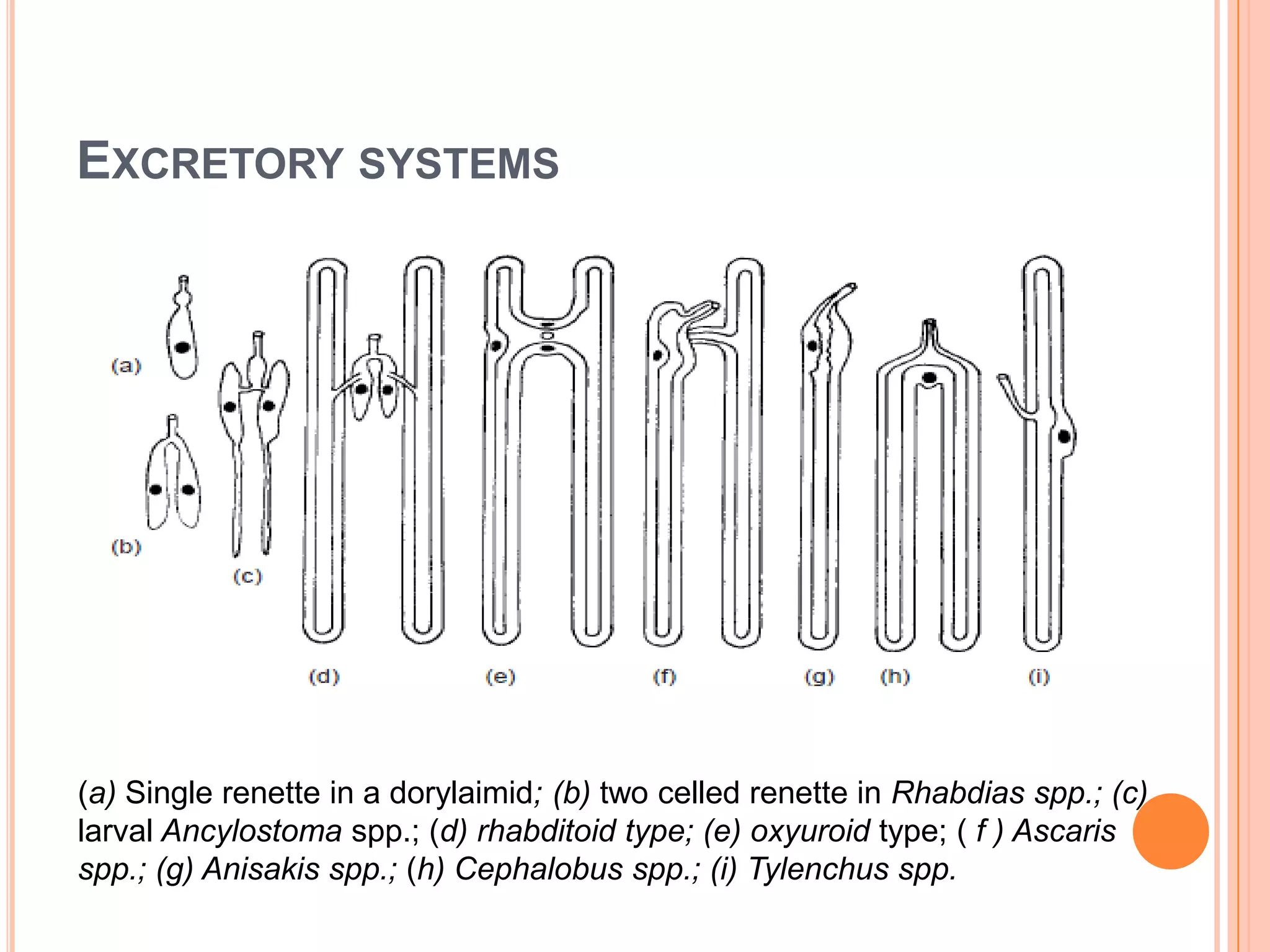
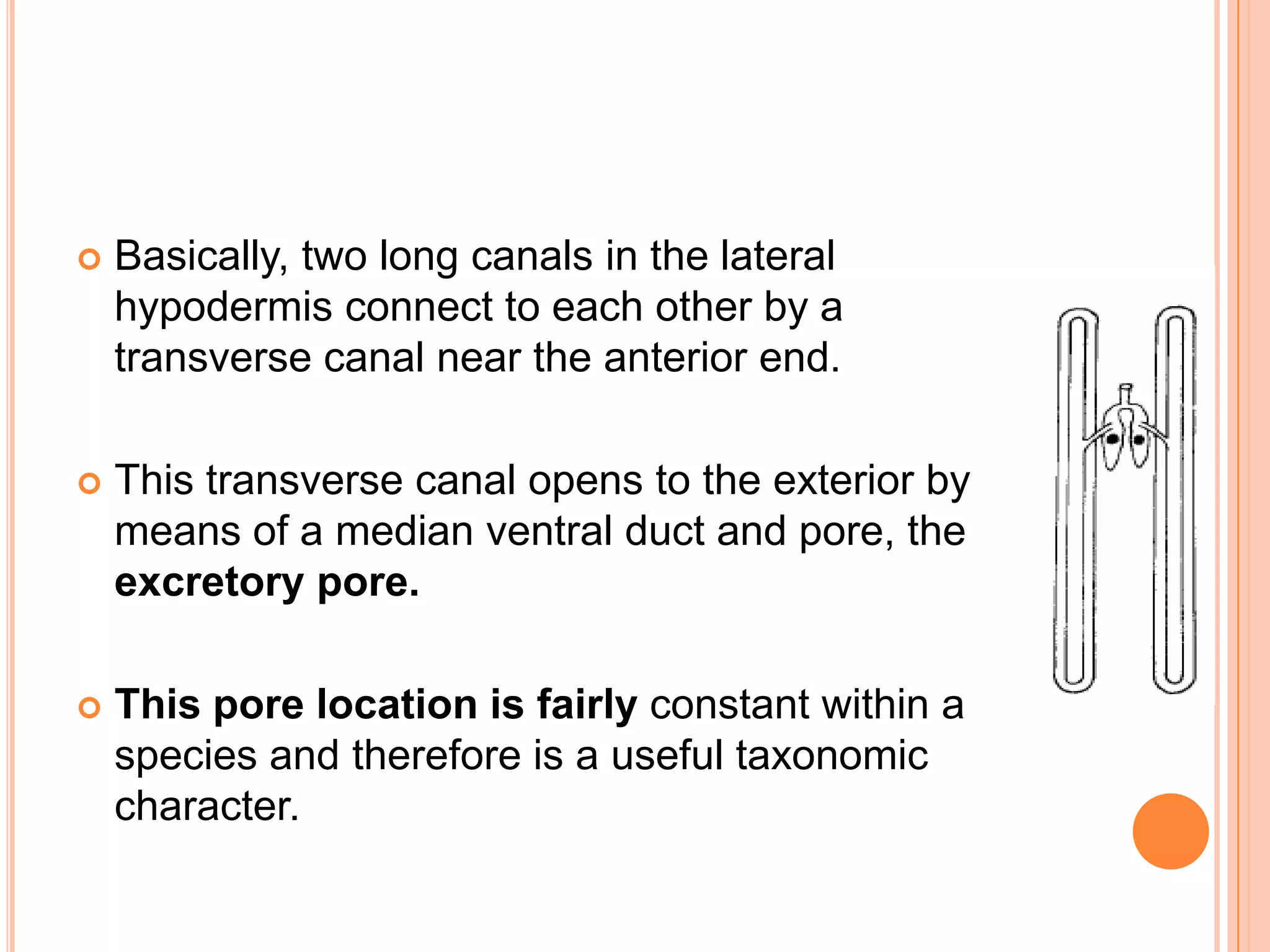
Nematodes have a complete digestive system comprised of three main parts - the stomodaeum, intestine, and proctodaeum. The stomodaeum includes structures like the mouth, pharynx, and esophagus. The esophagus pumps food into the simple tubular intestine, where digestion and absorption occurs. Undigested waste is expelled through the proctodaeum and anus. Nematodes have different feeding apparatus depending on their lifestyle, such as styles for piercing plant cells or teeth for cutting animal tissues. Their secretory-excretory systems also vary in structure between free-living and parasitic forms.