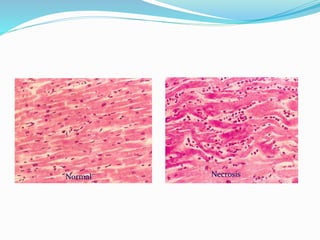
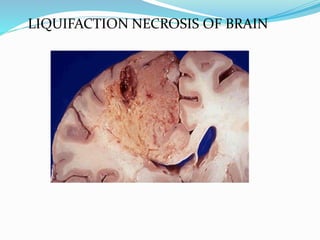
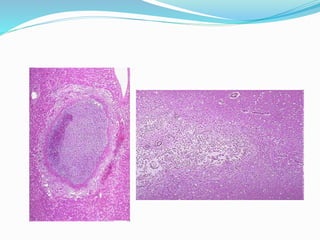
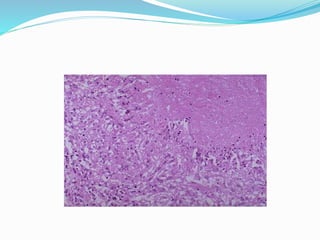
Necrosis is the death of cells and living tissue. There are several types of necrosis based on etiology and appearance:
1. Coagulative necrosis occurs when cells die but retain their shape. The dead cells may be replaced by regeneration or fibrosis.
2. Liquefactive necrosis involves tissue degradation by hydrolytic enzymes, forming a soft area containing debris.
3. Caseous necrosis is seen in tuberculosis, appearing like dry cheese and containing structureless debris amid granulomatous inflammation.
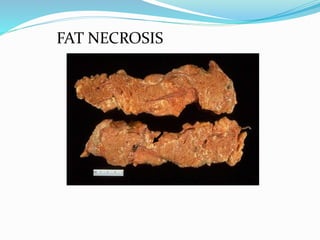
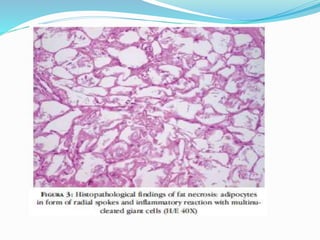
4. Fat necrosis results from lipase action in adipose tissue, appearing as yellowish deposits of calcium soaps.
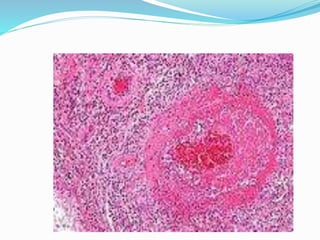
5. Fibrinoid necrosis involves deposition of fibrin-like