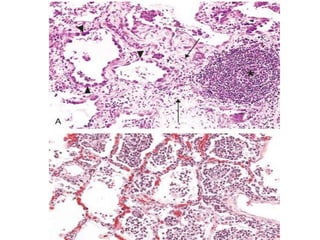
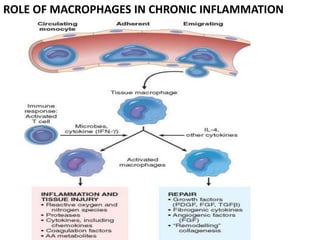
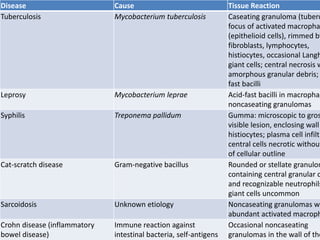
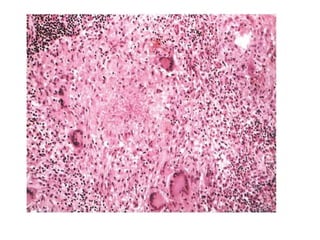
Chronic inflammation is inflammation that lasts for weeks or months, where inflammation, tissue damage, and attempts at repair occur simultaneously. It can be caused by persistent infections, autoimmune diseases, or prolonged exposure to toxic agents. Chronic inflammation is characterized by infiltration of mononuclear cells like macrophages, lymphocytes, and plasma cells. It also involves ongoing tissue destruction and attempts at healing through fibrosis and new blood vessel formation. Macrophages and lymphocytes play major roles, and granulomatous inflammation forms distinctive clusters of immune cells around certain infectious agents or foreign materials.