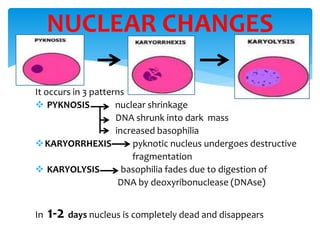
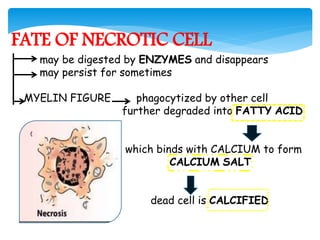
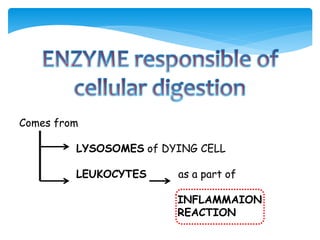
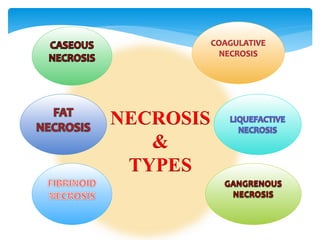
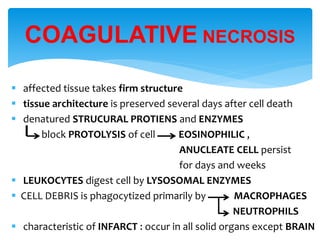
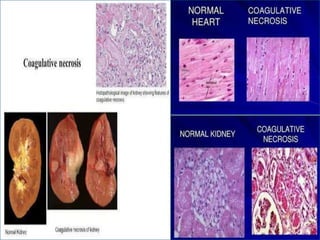
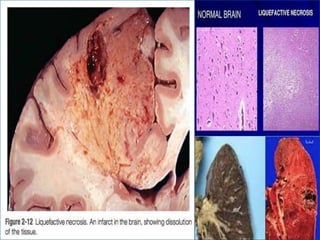
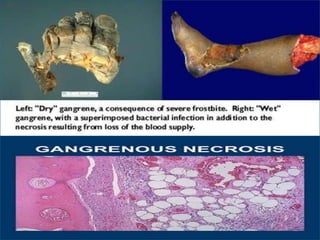
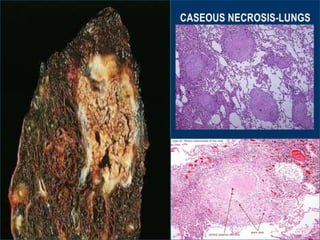
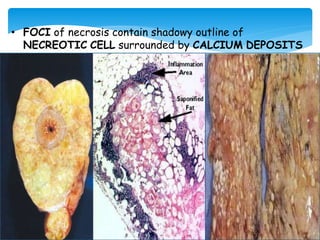
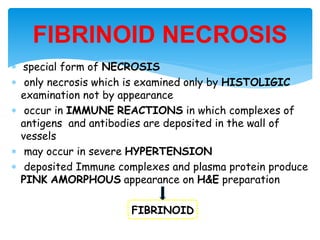
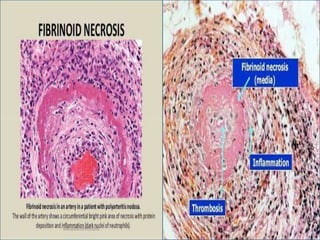
This document discusses different types of cell death known as necrosis. It defines necrosis as irreversible damage to cells that cannot be corrected and involves failure of ATP generation, membrane damage, and damage from reactive oxygen species. The document outlines several patterns of necrosis including coagulative necrosis where tissue architecture is preserved, liquefactive necrosis where tissue turns into a viscous liquid, and caseous necrosis where tissue has a cheesy, yellow-white appearance. It also discusses specific forms of necrosis that can occur in conditions like infections, gangrene, acute pancreatitis, and immune reactions.