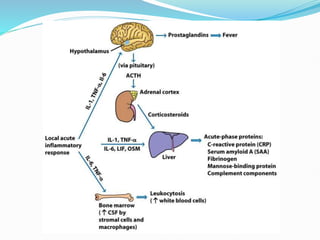
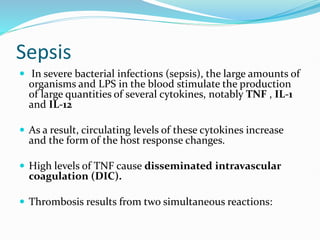
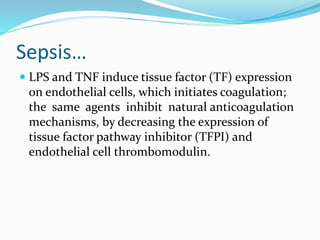
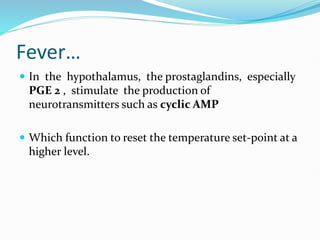
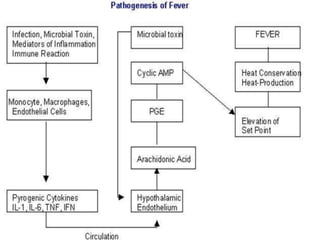
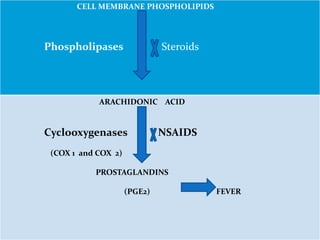
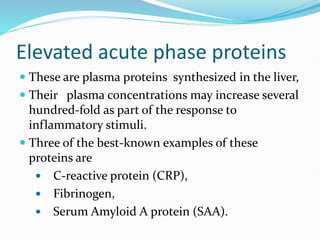
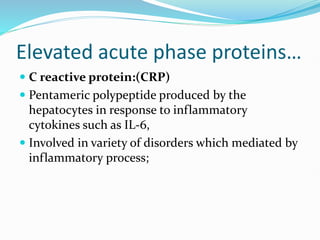
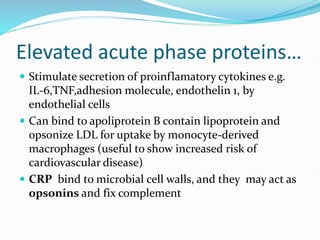
This document outlines the systemic effects of inflammation, including fever, elevated acute phase proteins, anemia, leukocytosis/leukopenia, sepsis, ARDS, and wasting syndrome. It provides details on the mechanisms and clinical presentations of each effect. For example, it explains that fever occurs due to the effects of pyrogens like prostaglandins on the hypothalamus, while elevated acute phase proteins like C-reactive protein and serum amyloid A are produced in the liver in response to cytokines. Sepsis can lead to disseminated intravascular coagulation, hypoglycemia, and cardiac failure.











![Leukocytosis
Leukocytosis is a common feature of inflammatory
reactions, especially those induced by bacterial
infection.
The leukocyte count usually climbs to 15,000 or 20,000
cells/µl, but sometimes it may reach extraordinarily
high levels of 40,000 to 100,000 cells/µl. [normal
4,000-11000 cells/µl]
These extreme elevations are referred to as
leukemoid reactions because they are similar to the
white cell counts obtained in leukemia.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/systemiceffectsofinflammation-231221195451-c77adfa2/85/Systemic-effects-of-inflammation-pptx-21-320.jpg)