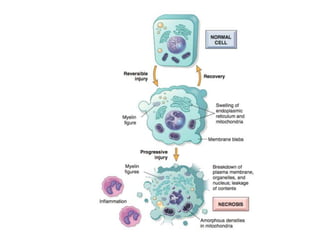
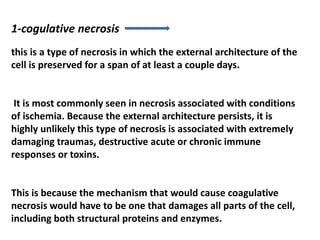
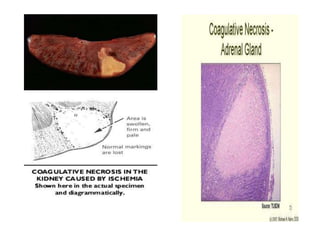
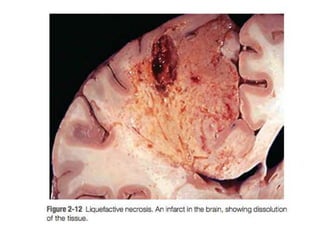
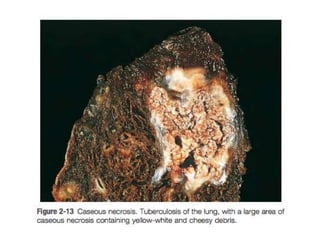
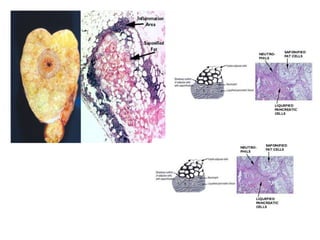
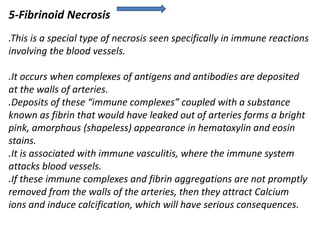
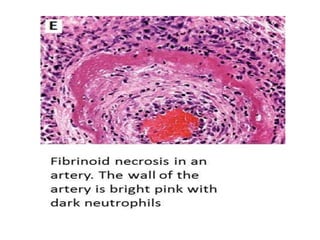
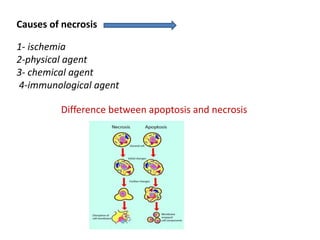
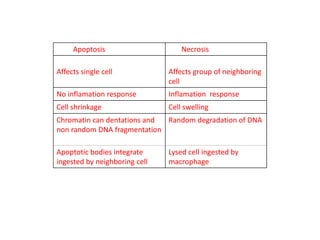
Necrosis is the premature death of cells in living tissue due to factors like lack of blood flow, radiation, chemicals, or physical trauma. There are several types of necrosis including coagulative, liquefactive, caseous, fat, and fibrinoid necrosis. Coagulative necrosis preserves cell structure, while liquefactive necrosis completely breaks cells down. Caseous necrosis is seen in tuberculosis and forms cheesy deposits. Fat necrosis destroys lipid deposits. Fibrinoid necrosis involves immune complex deposition in blood vessels. Necrosis causes inflammation and cannot be reversed, unlike apoptosis which is programmed cell death.