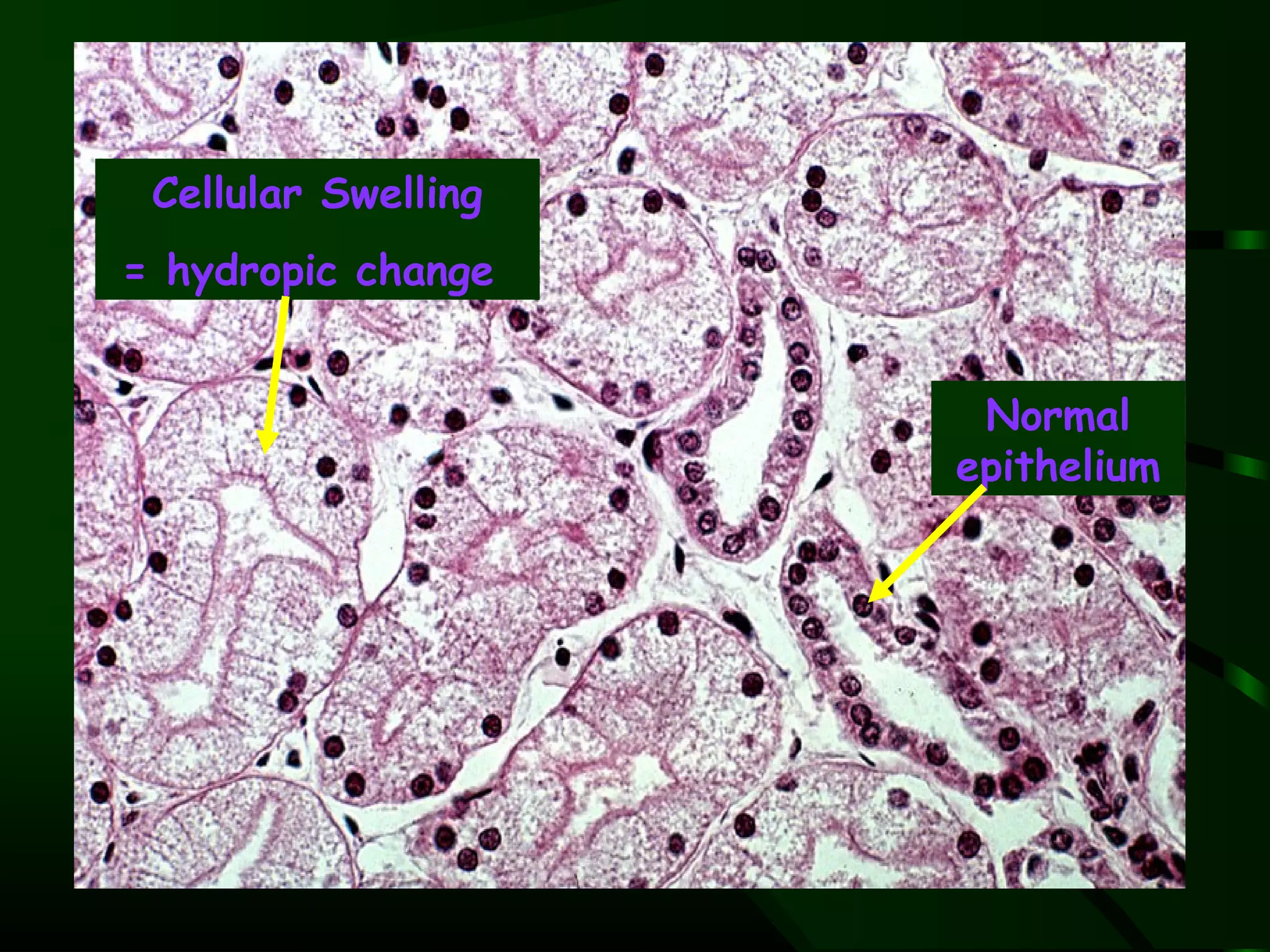
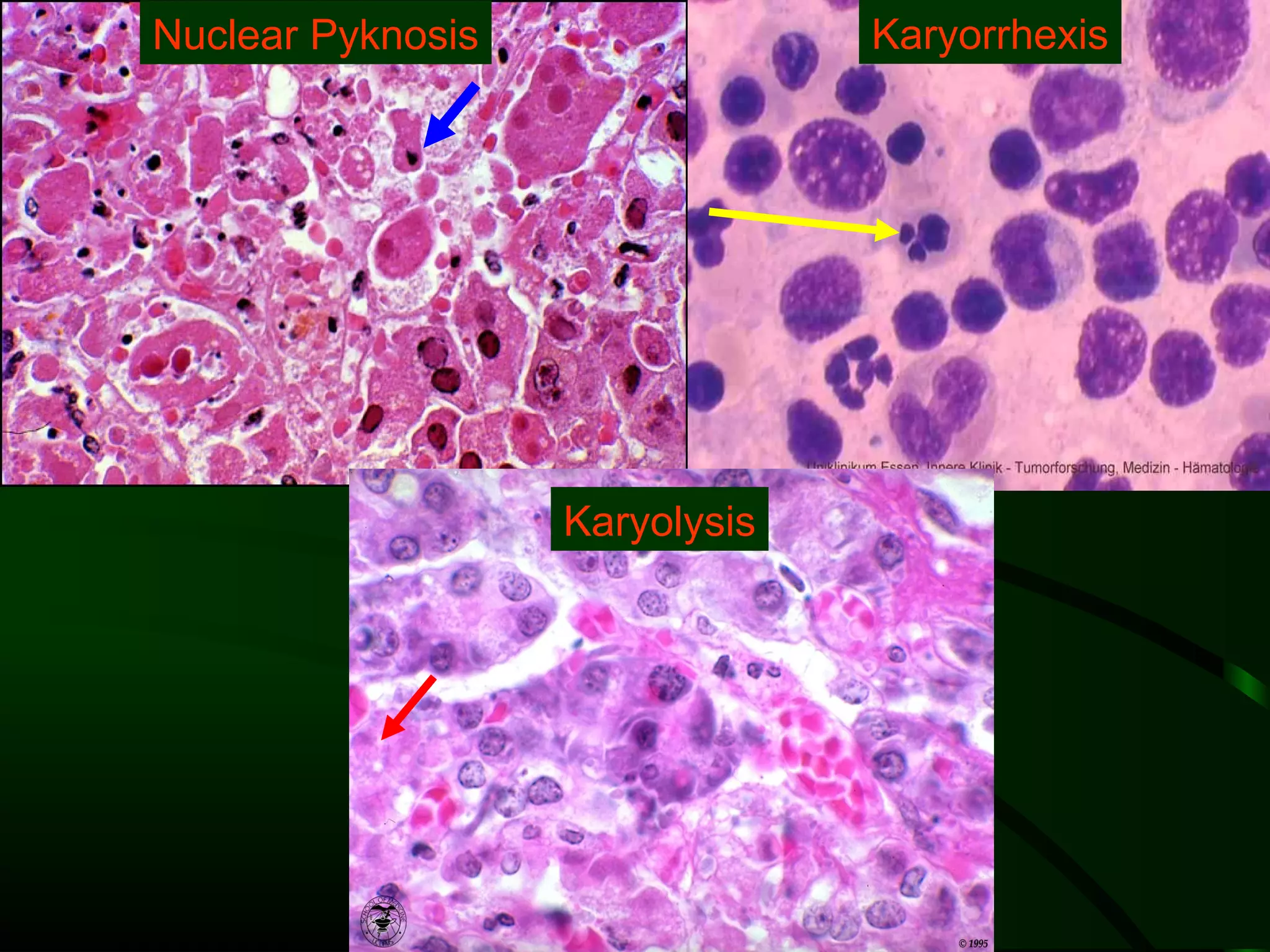
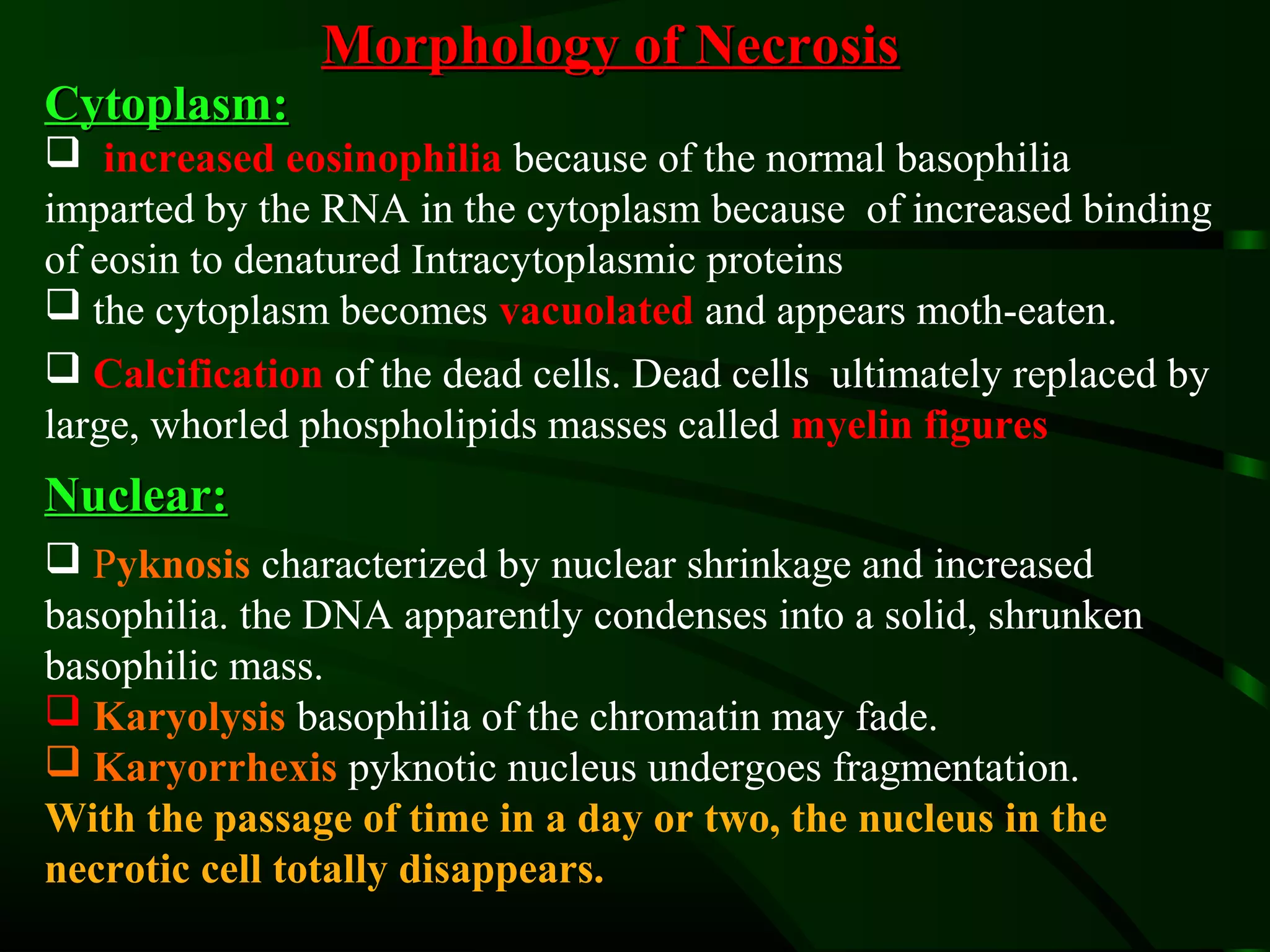
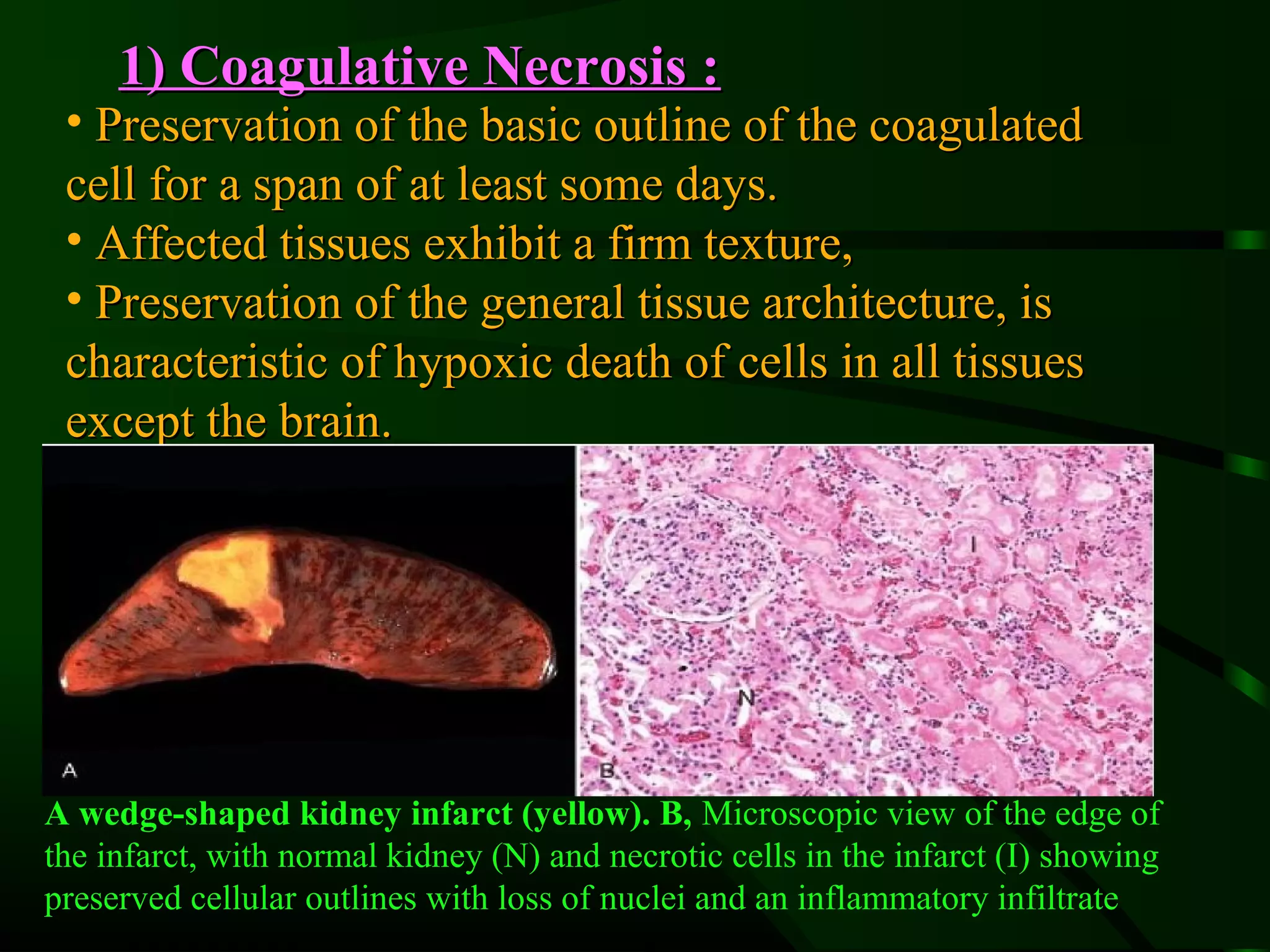
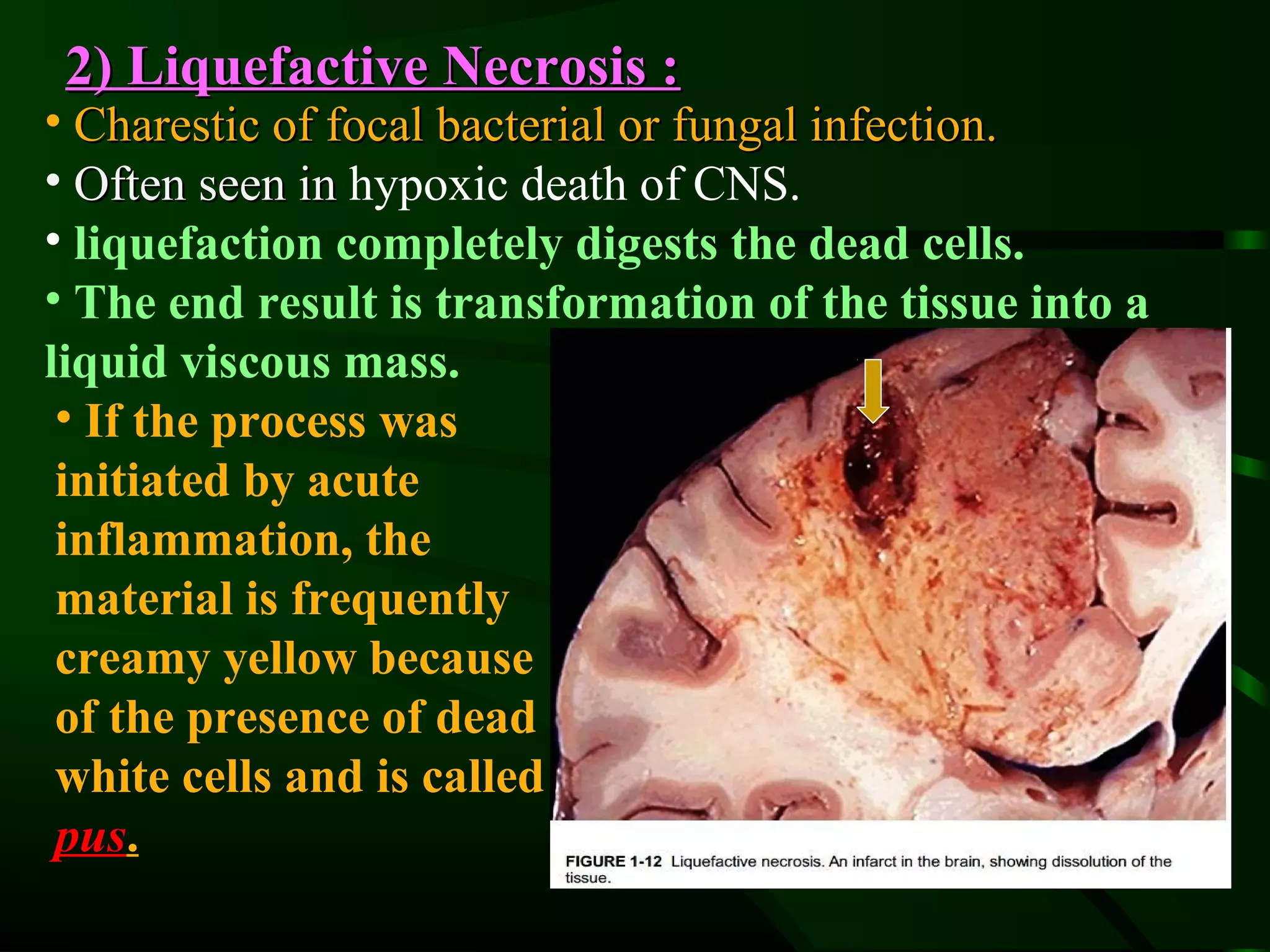
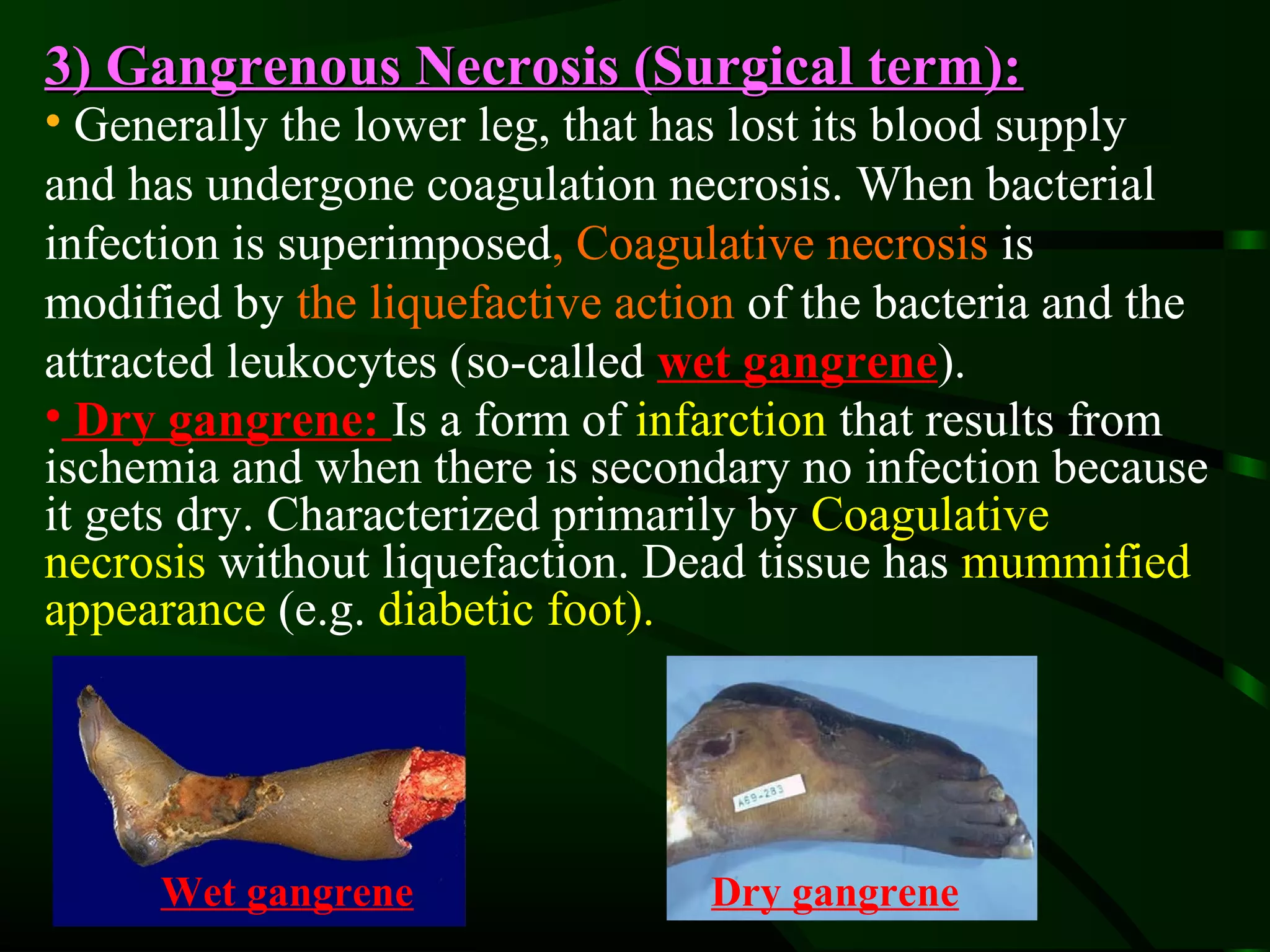
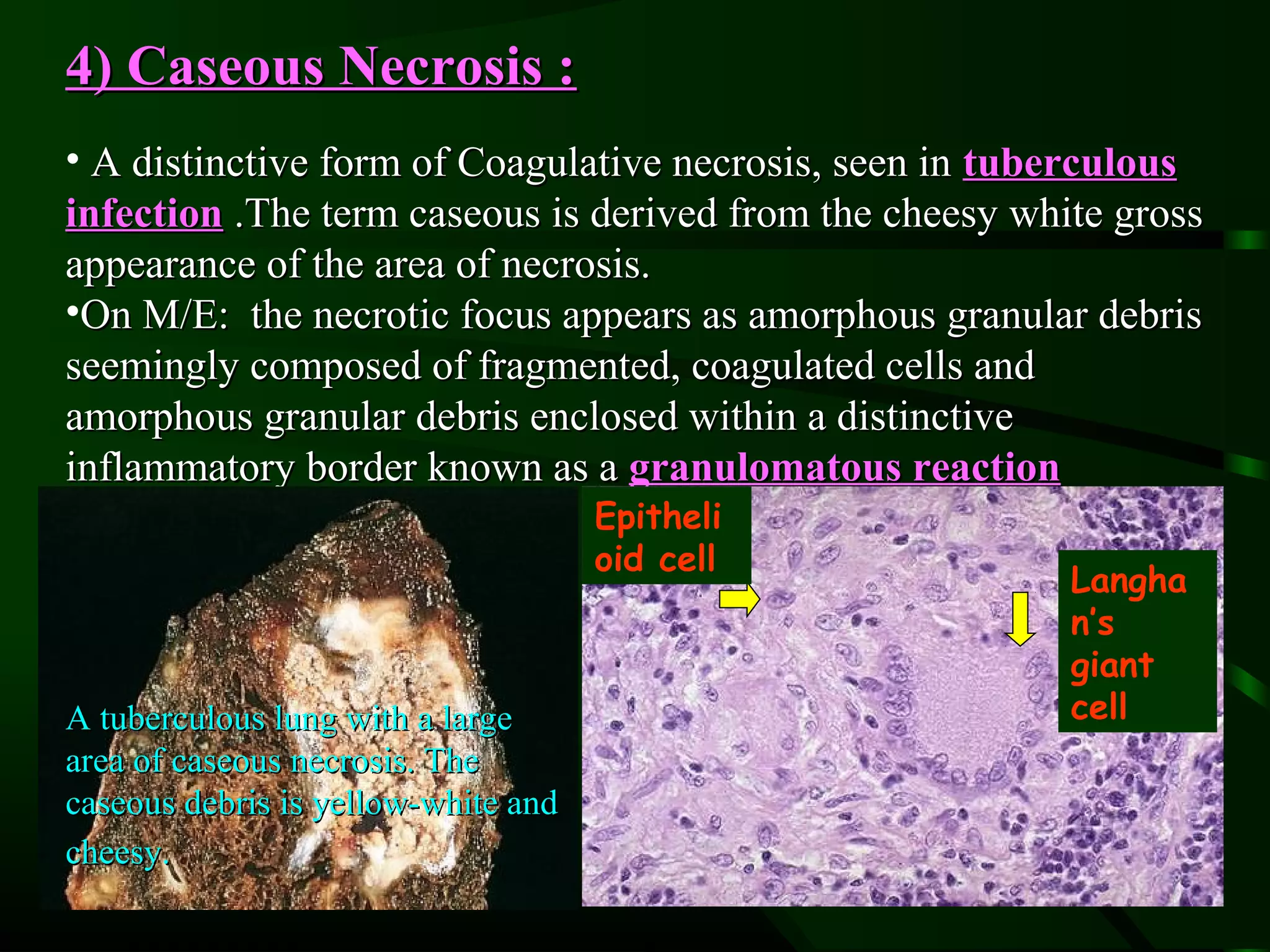
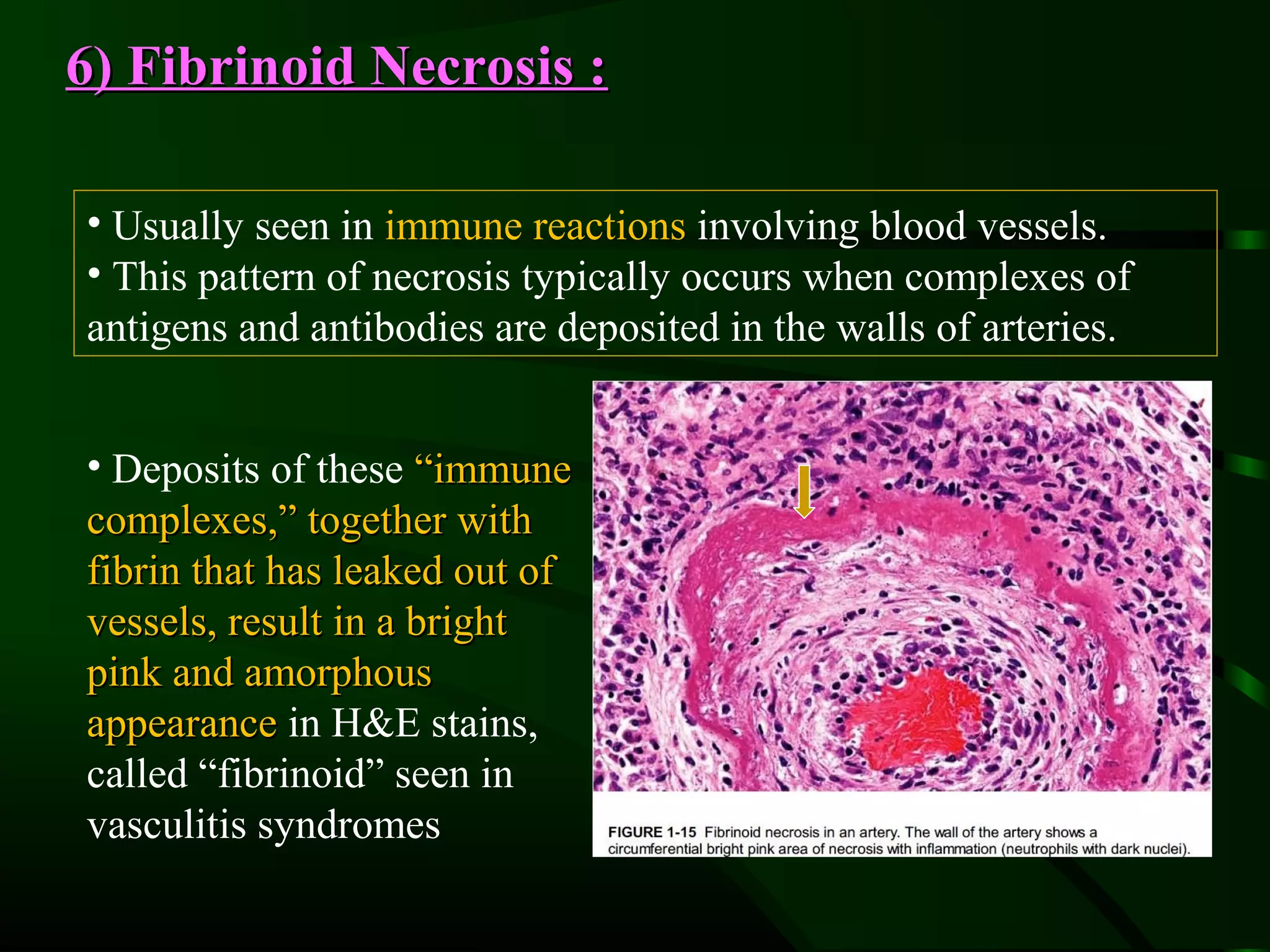
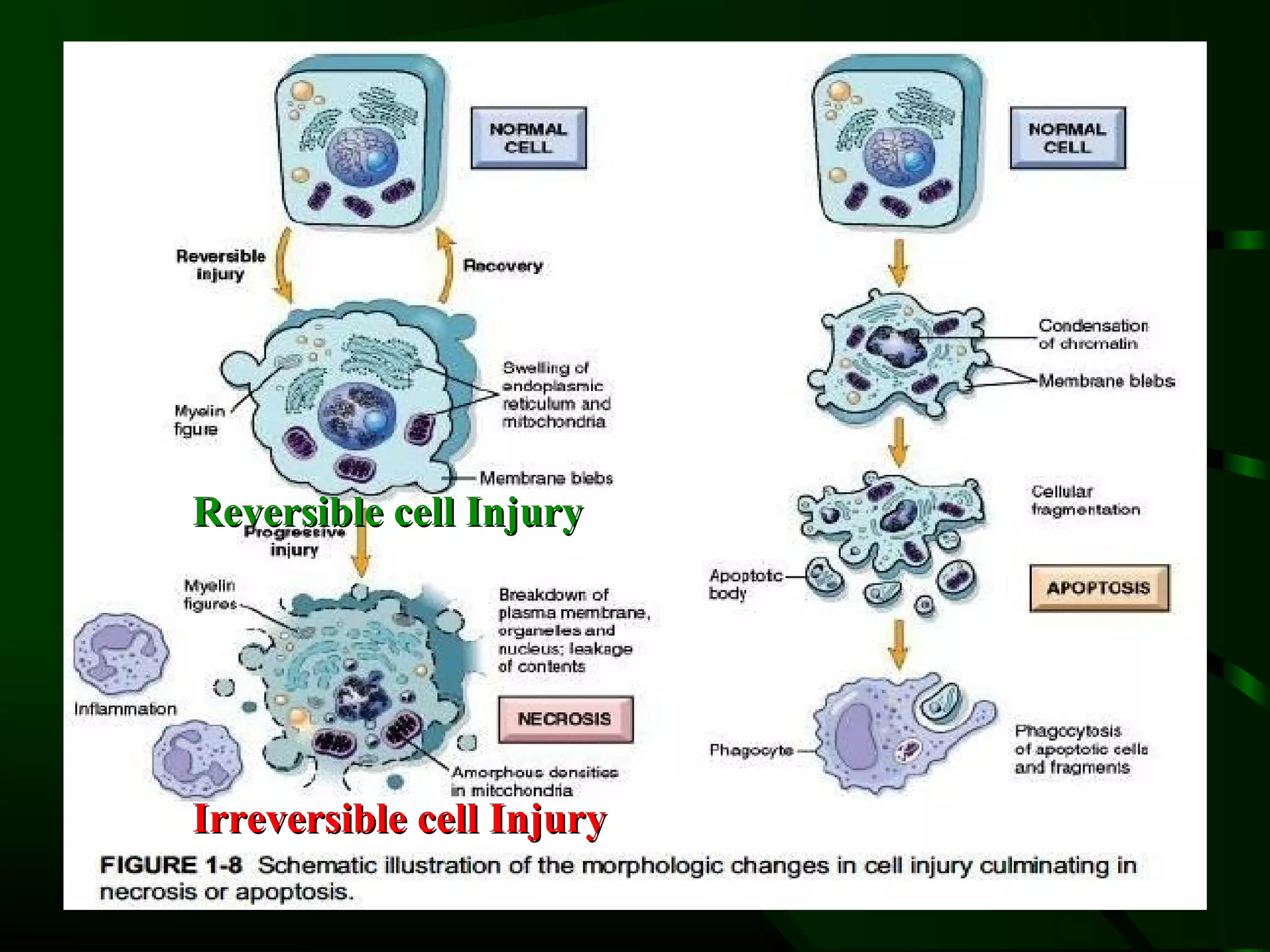
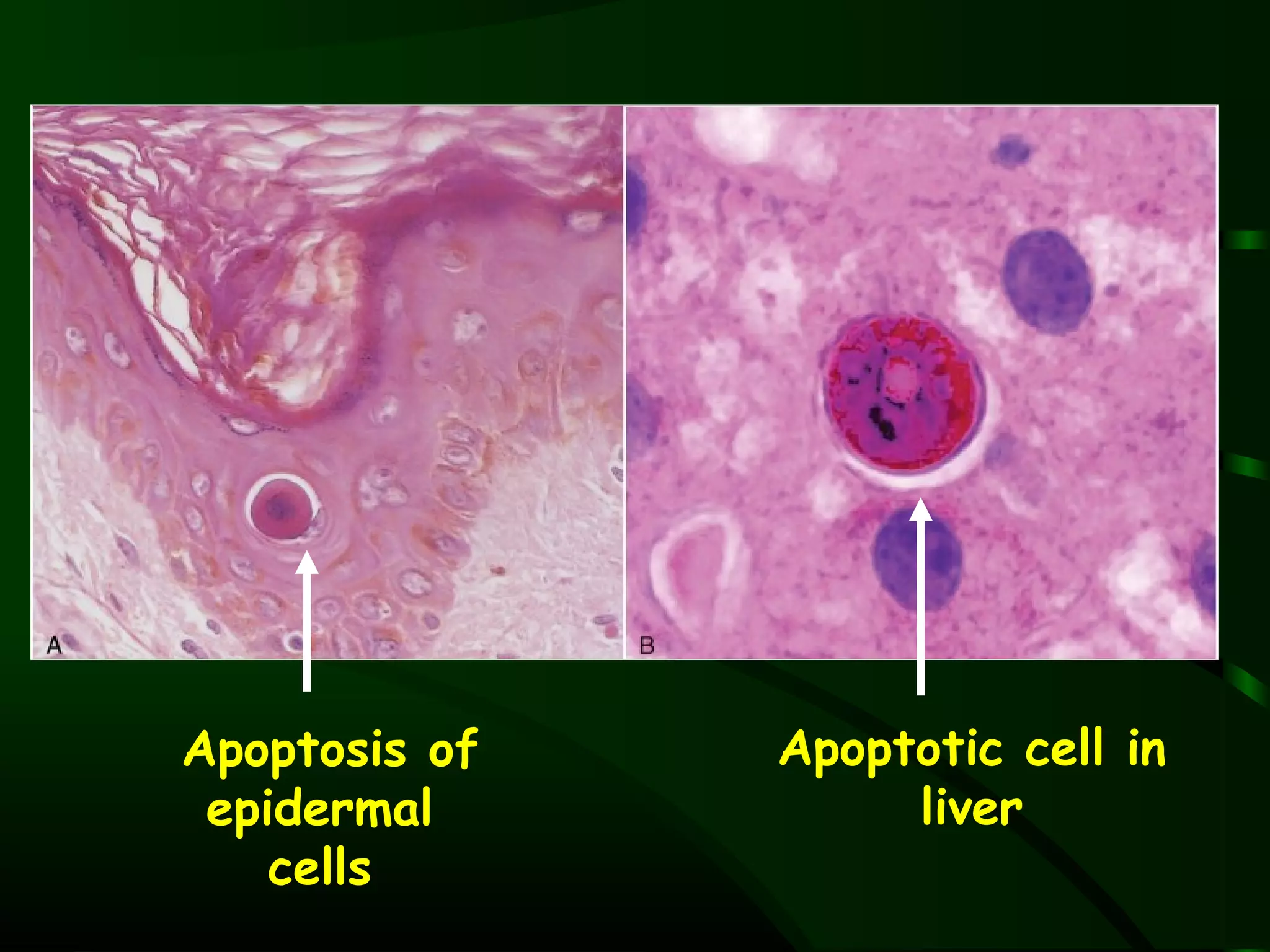
1. The document describes the morphological changes that occur in cells undergoing reversible injury, irreversible injury, necrosis, and apoptosis as observed by light and electron microscopy.
2. Key differences are noted between necrosis, which involves the uncontrolled digestion of cells and release of cellular contents, versus apoptosis, which is a tightly regulated form of programmed cell death where cells break into fragments that are phagocytosed without inflammation.
3. Examples are provided of physiological apoptosis during development and tissue remodeling, as well as pathological apoptosis resulting from DNA damage, misfolded proteins, viral infections, and organ atrophy.