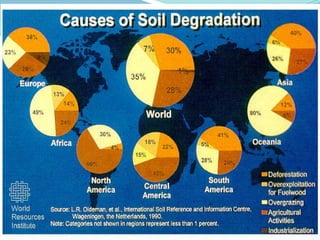
The document discusses the significance of land as a vital natural resource for human society, detailing its uses in agriculture, mineral extraction, and habitat provision. It identifies causes of land degradation, both natural and anthropogenic, including deforestation and urbanization, and explains soil erosion as the wearing away of topsoil by wind and water. Additionally, it describes various soil conservation techniques like no-till farming, mulching, and contour farming aimed at mitigating these issues.