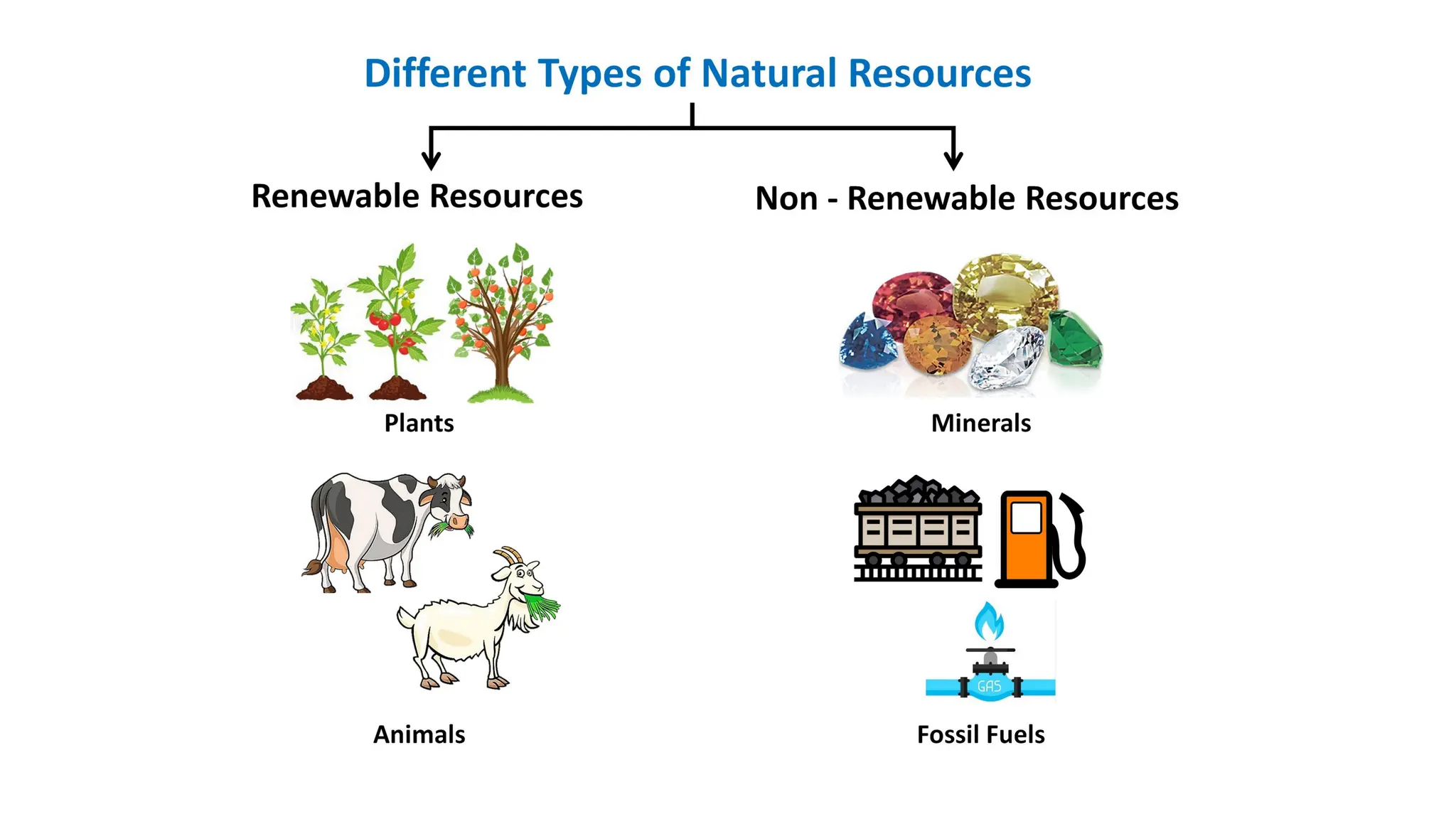
The document discusses natural resources, categorizing them into renewable and non-renewable resources, and detailing the significance of forest, water, mineral, and food resources. It highlights the challenges of resource depletion, including deforestation, pollution, and their adverse environmental impacts. The document emphasizes the importance of conservation efforts and sustainable management practices to mitigate these issues.