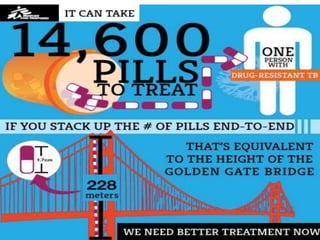
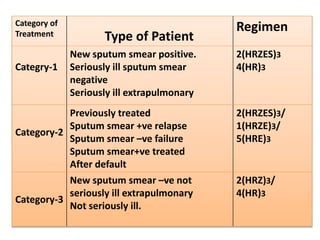
The National Tuberculosis Control Programme and Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programme were implemented in India to deal with the tuberculosis problem. The objectives are to reduce infection rates through case detection, treatment, and BCG vaccination. In the 1990s, the programmes suffered from management issues and inadequate funding. The RNTCP adopted the DOTS strategy recommended by the WHO to improve cure rates and case detection through direct observation of treatment. Treatment involves a two-phase regimen administered under direct observation at least initially. Nurses play an important role in treating TB patients through home visits, education, and contact screening.