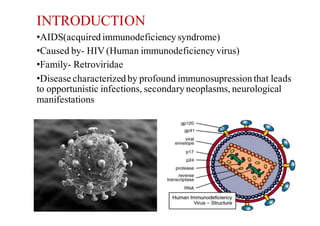
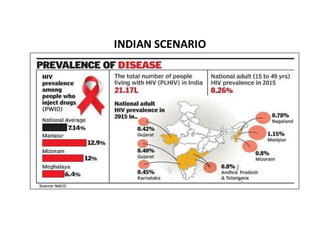
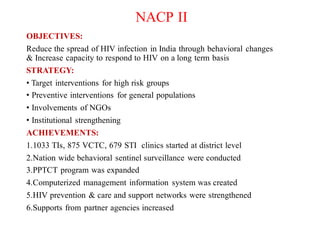
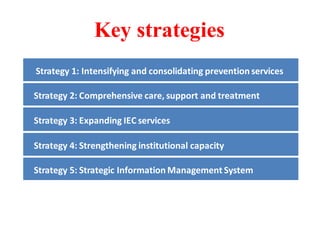
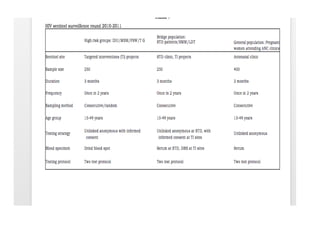
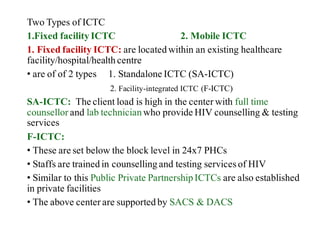
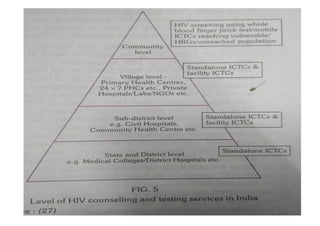
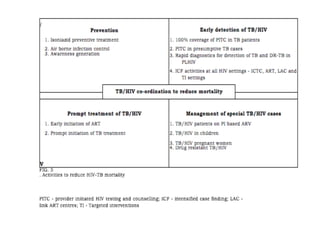
The National AIDS Control Programme in India aims to address and reduce the impact of HIV/AIDS through a series of strategic phases, starting from its inception in 1986. It outlines various objectives, achievements, and strategies focusing on prevention, treatment, and care for high-risk populations and the general public, including the introduction of antiretroviral treatment (ART) and prevention of mother-to-child transmission (PMTCT) initiatives. The document emphasizes a comprehensive approach by integrating surveillance, targeted interventions, and strengthening healthcare capacities across the nation.