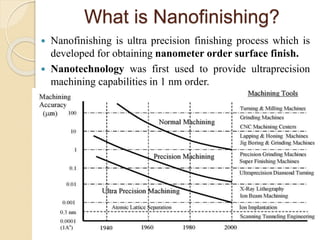
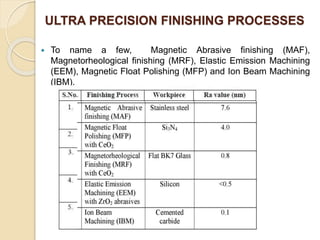
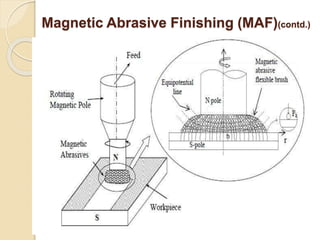
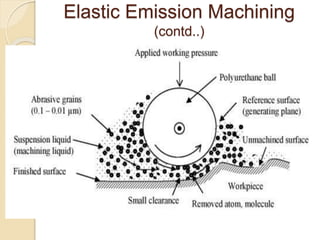
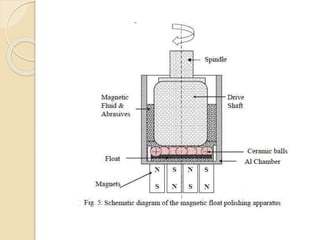
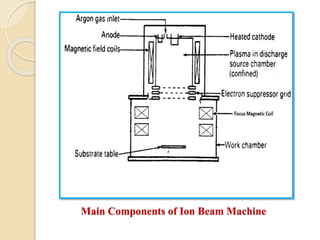
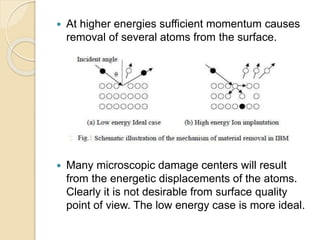
Nanofinishing is an ultra-precision finishing process aimed at achieving nanometer-order surface finishes, essential for the demands of modern electronics and computer industries. Various techniques such as Magnetic Abrasive Finishing, Magnetorheological Finishing, Elastic Emission Machining, Magnetic Float Polishing, and Ion Beam Machining are employed to produce high precision surface finishes. These methods enable the machining of advanced materials while overcoming limitations of traditional finishing processes.