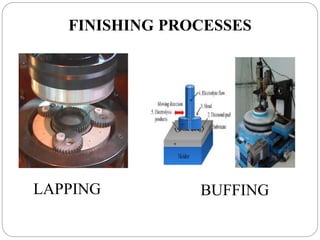
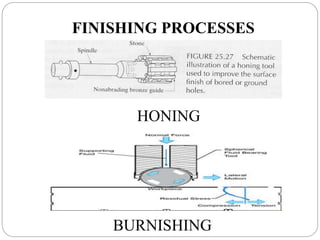
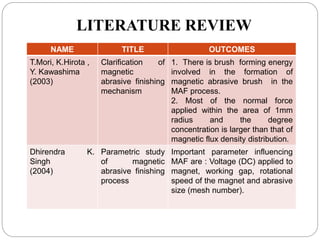
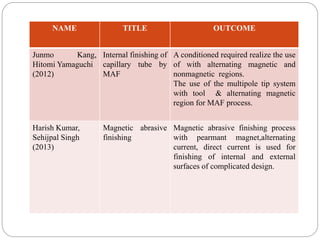
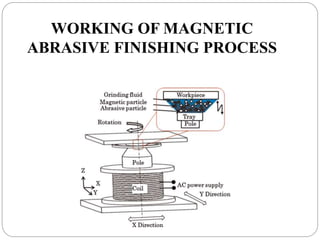
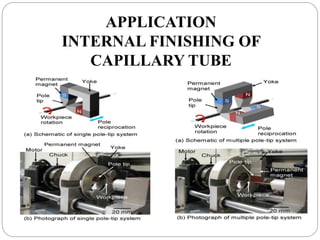
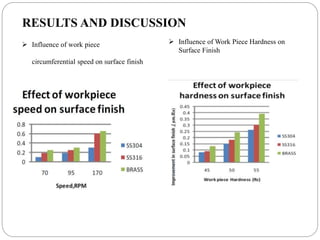
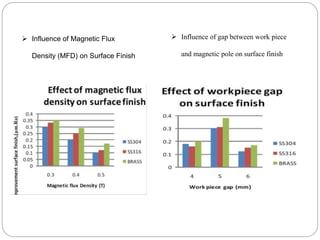
The document discusses the magnetic abrasive finishing (MAF) process, which is an advanced method for achieving high surface finishes on complex materials where traditional techniques may fail. MAF utilizes magnetic fields to energize abrasive particles, allowing precise finishing of internal and external surfaces without direct tool contact, making it suitable for various applications in industries like medical and aerospace. While it provides significant benefits such as adaptability and improved surface characteristics, it also has disadvantages, including high costs and challenges in mass production.