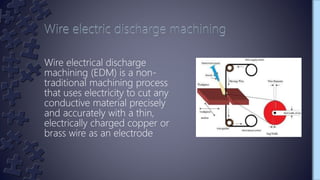
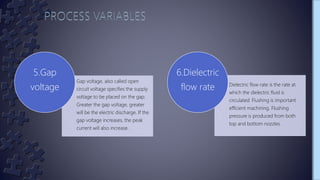
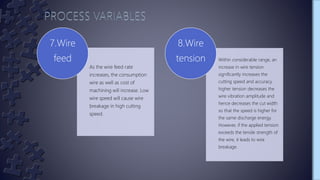
Wire electrical discharge machining (EDM) is a non-traditional machining process that uses electricity to cut conductive materials with a thin copper or brass wire electrode. It works by producing a series of electric sparks between the accurately positioned moving wire and the workpiece, eroding away tiny amounts of material. Key variables that control the process include pulse duration and interval, servo voltage, peak current, and dielectric fluid flow rate. Stratified wires with layered materials can improve cutting speeds and surface quality. EDM is used in aerospace, medical, and other industries for cutting hard metals and shaping complex tooling.