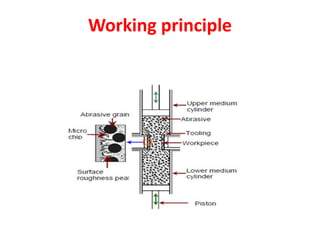
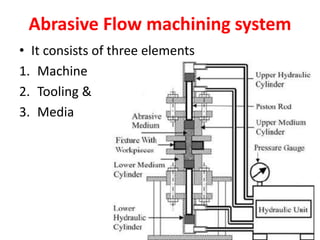
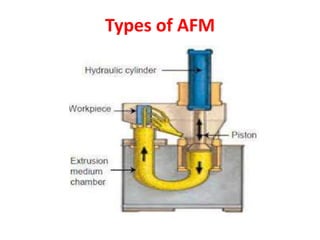
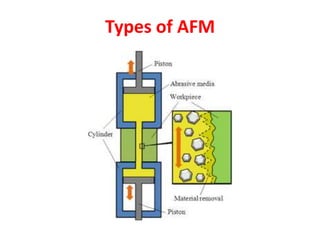
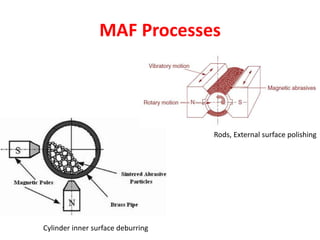
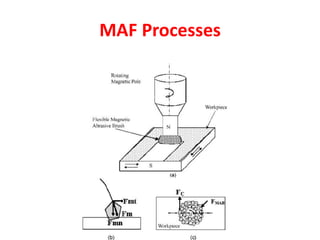
This document discusses two abrasive finishing processes: abrasive flow machining (AFM) and magnetic abrasive finishing (MAF). AFM involves extruding an abrasive-laden putty between a workpiece and tooling to remove material, allowing for burr removal, radiusing, and polishing of complex shapes. MAF uses magnetic iron particles coated with abrasive grains to polish rod and flat surfaces. Both processes allow for close tolerances, intricate surface features, and machining of hard materials with minimal material removal due to thin chip formation.