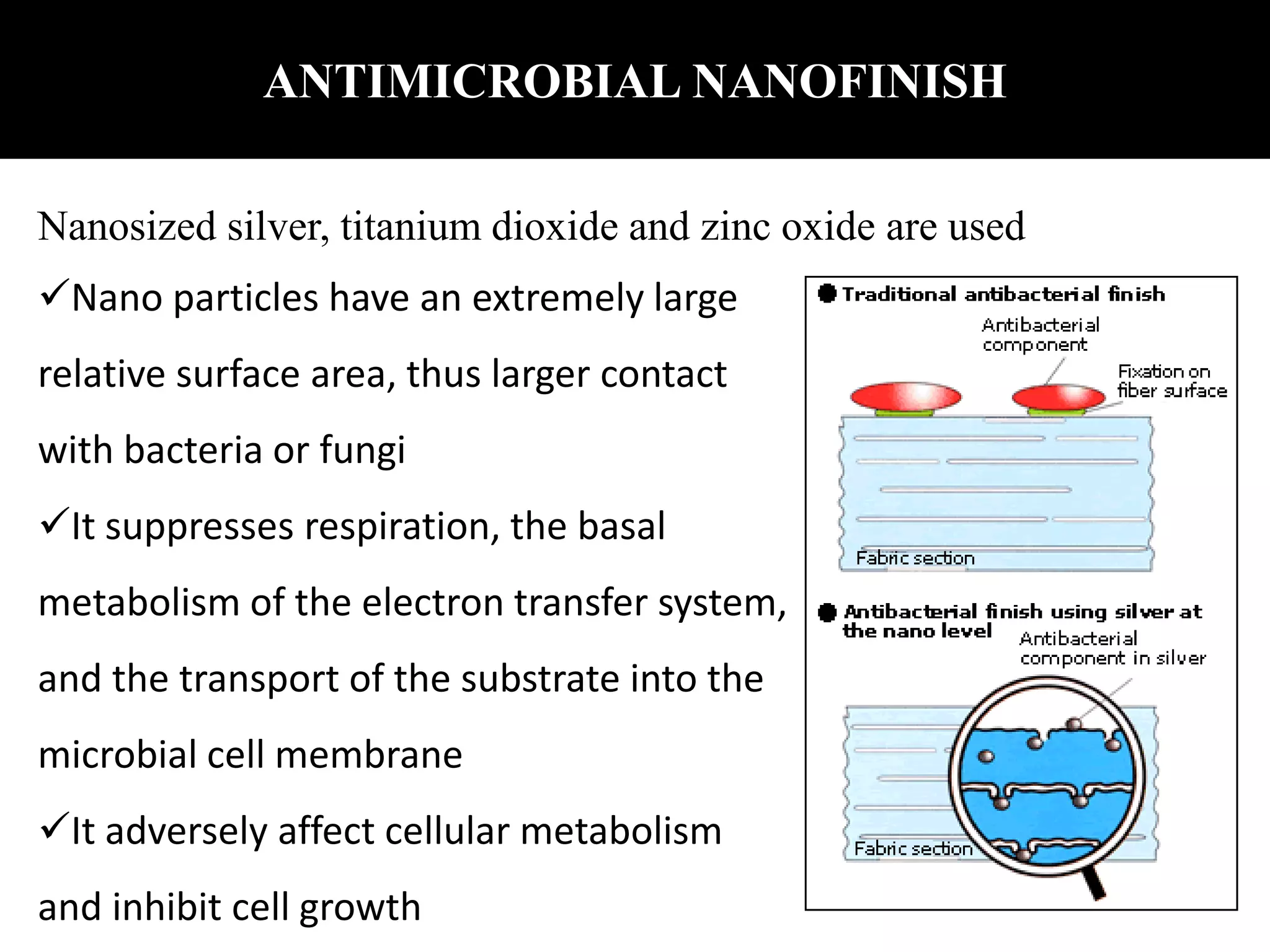
The document discusses the application of nanotechnology in textile finishing, highlighting the synthesis of nanophase materials, their functional properties, and various applications such as water repellency and antimicrobial finishes. It outlines the benefits of using nanotechnology in textiles, including enhanced durability and functionality, while also addressing potential disadvantages like strength loss and toxicity. Future developments in this field aim at creating multifunctional finishes and sustainable nanofinishing processes.