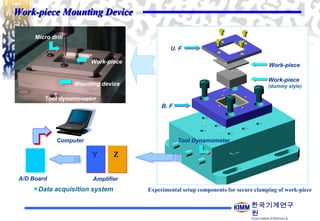
1. The document discusses micro-drilling using a step-forward feeding method to address issues with conventional micro-drilling such as tool breakage.
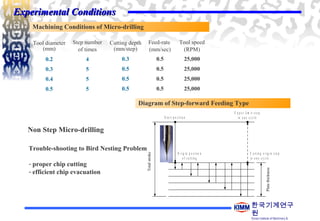
2. An experiment was conducted using different micro-drill diameters and step numbers to drill holes in steel workpieces with and without cutting oil.
3. The results showed that using step-forward feeding and cutting oil reduced cutting forces, burr formation, and tool damage compared to conventional micro-drilling without cutting oil.