1. The document describes a scientist working to transport a zombie virus cure from their lab to the CDC for mass distribution.
2. With zombies already walking the earth, the scientist must devise a plan to get the cure to where it's needed before it's too late.
3. The scientist is asked to write a journal entry describing their plan or encounter with zombies during the transport of the cure.









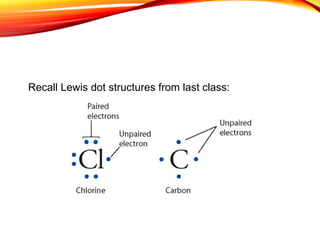
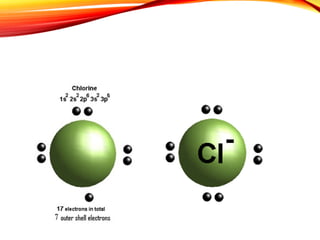





![Sodium chloride is an ionic compound formed by the reaction
between the metal sodium and the non-metal chlorine.
Sodium has 1 electron in its
outer shell.
Chlorine has 7 electrons in its
outer shell.
2.8.7 [2.8.8]-
+
Cl Cl
-
2.8.1 [2.8]+
Na Na
o By losing this electron, it
has a filled outer shell and
forms a positive ion.
o By gaining an electron from
sodium, it has a filled outer
shell and forms a negative
ion.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ionsandionicbonding-181031181132/85/Ions-and-ionic-bonding-19-320.jpg)