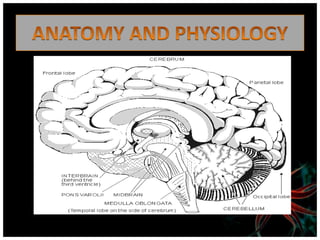
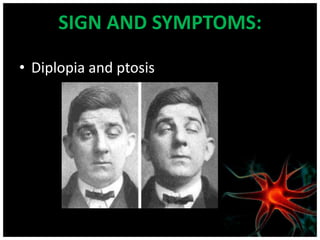
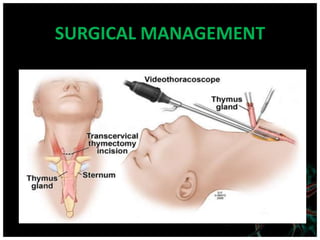
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disorder characterized by varying degrees of weakness in voluntary muscles. It occurs when antibodies block or damage receptors at the neuromuscular junction, preventing normal muscle contraction in response to nerve impulses. Risk factors include female gender under 40, male gender over 60, and other autoimmune disorders. Symptoms include drooping eyelids, blurred or double vision, weakness in the face, and generalized weakness that worsens with activity. Diagnostic tests include the edrophonium test, blood tests for antibodies, repetitive nerve stimulation, and pulmonary function tests. Treatment involves cholinesterase inhibitors, corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and in some cases plasmapher