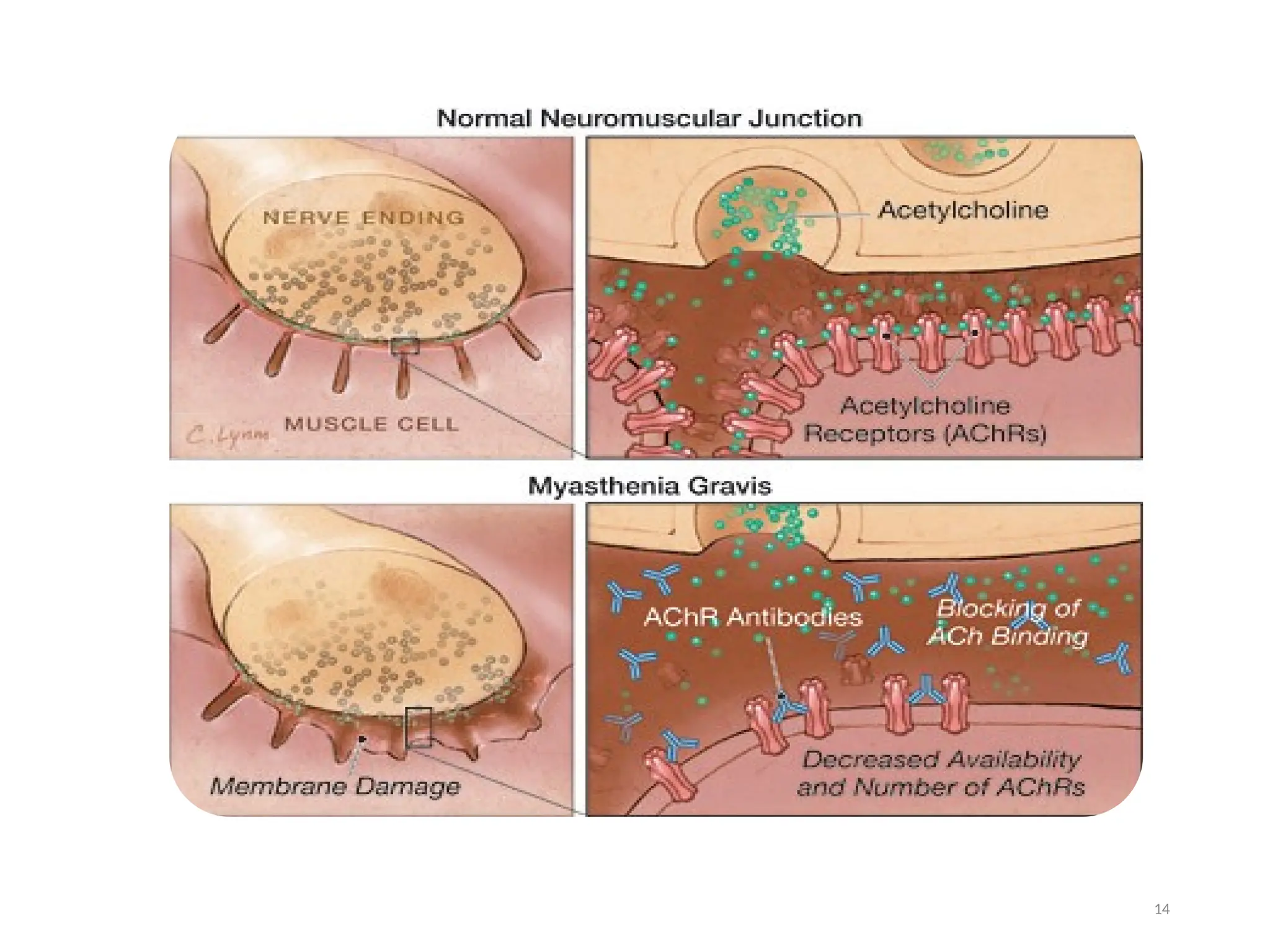
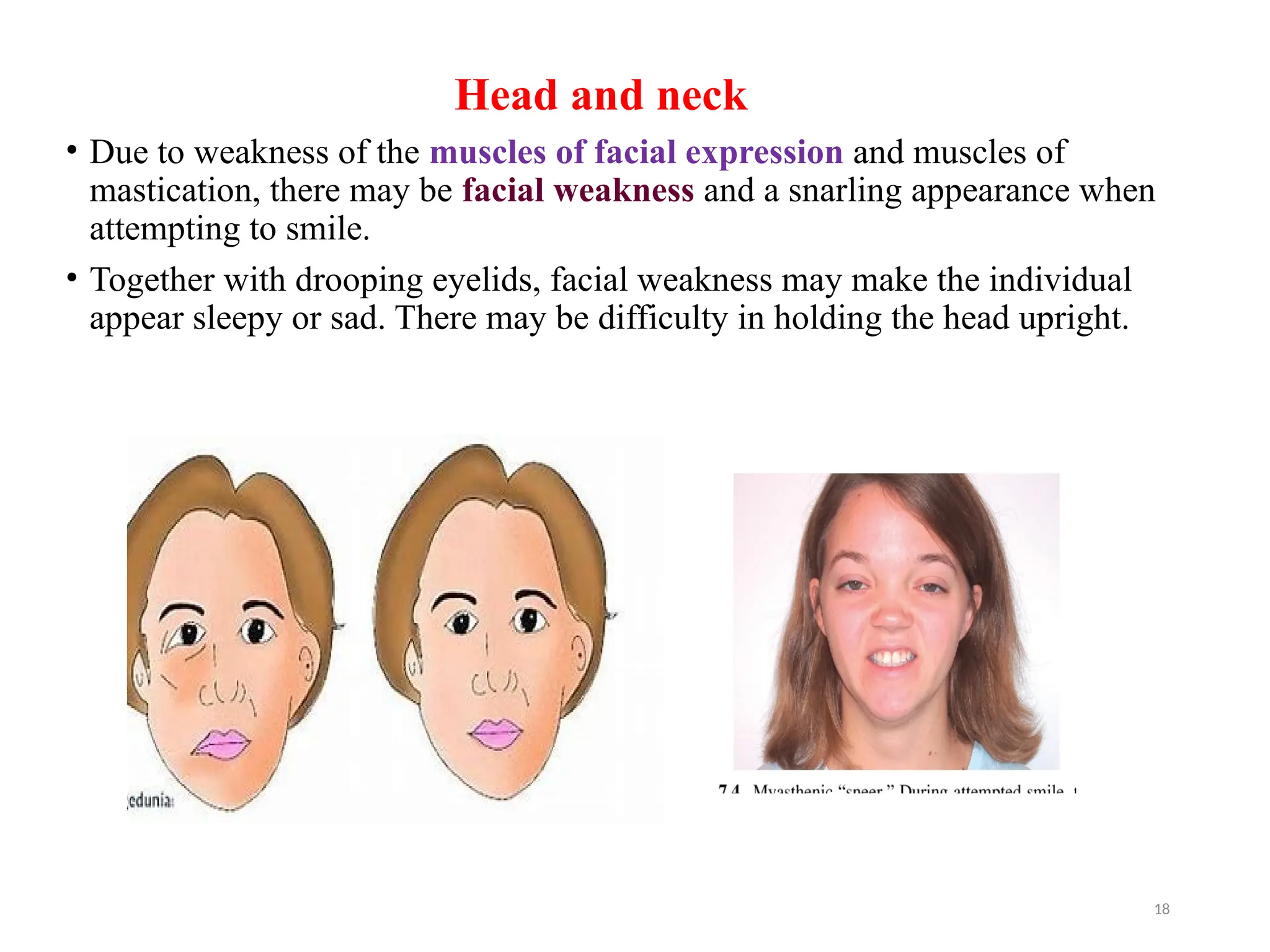
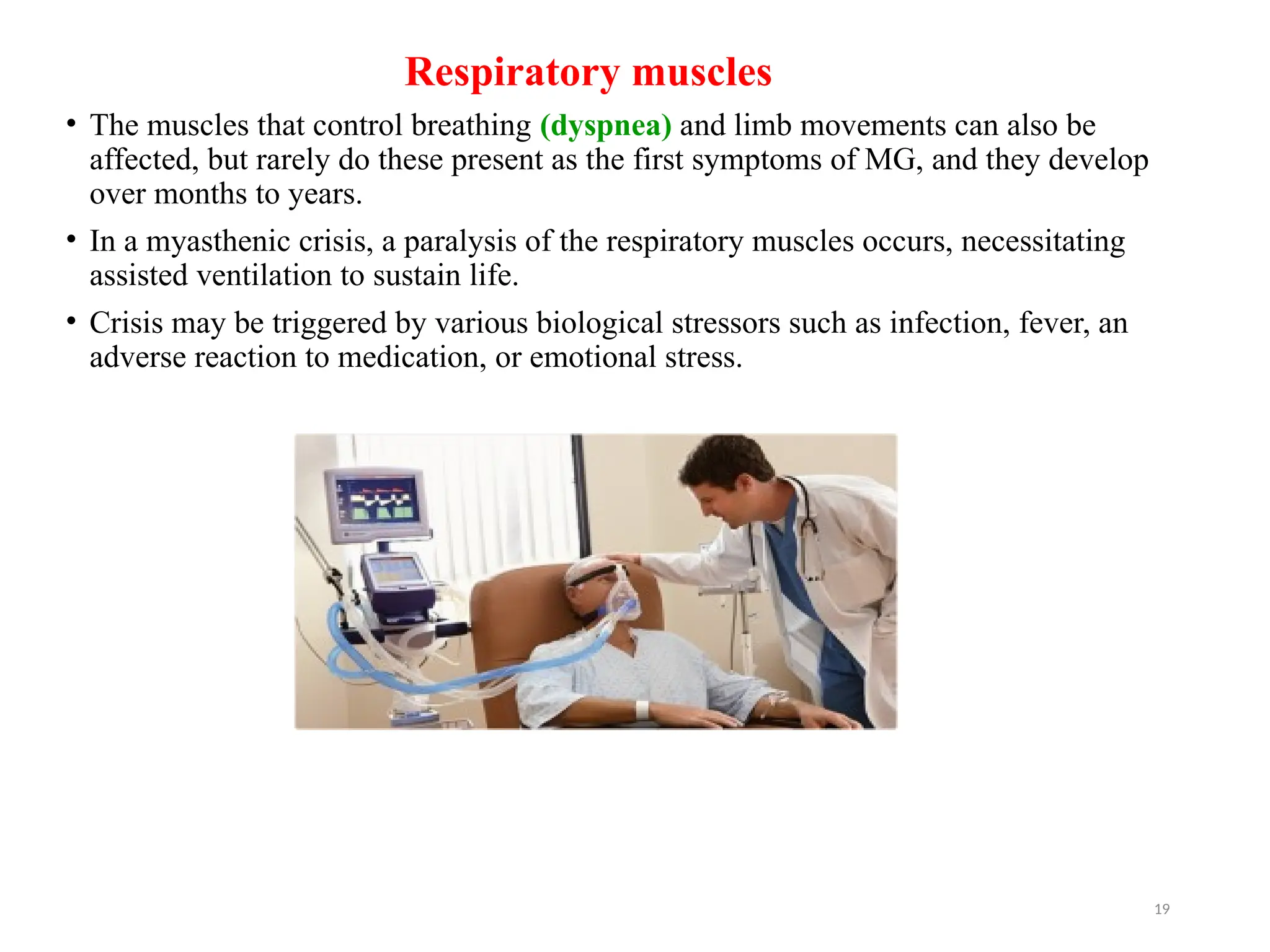
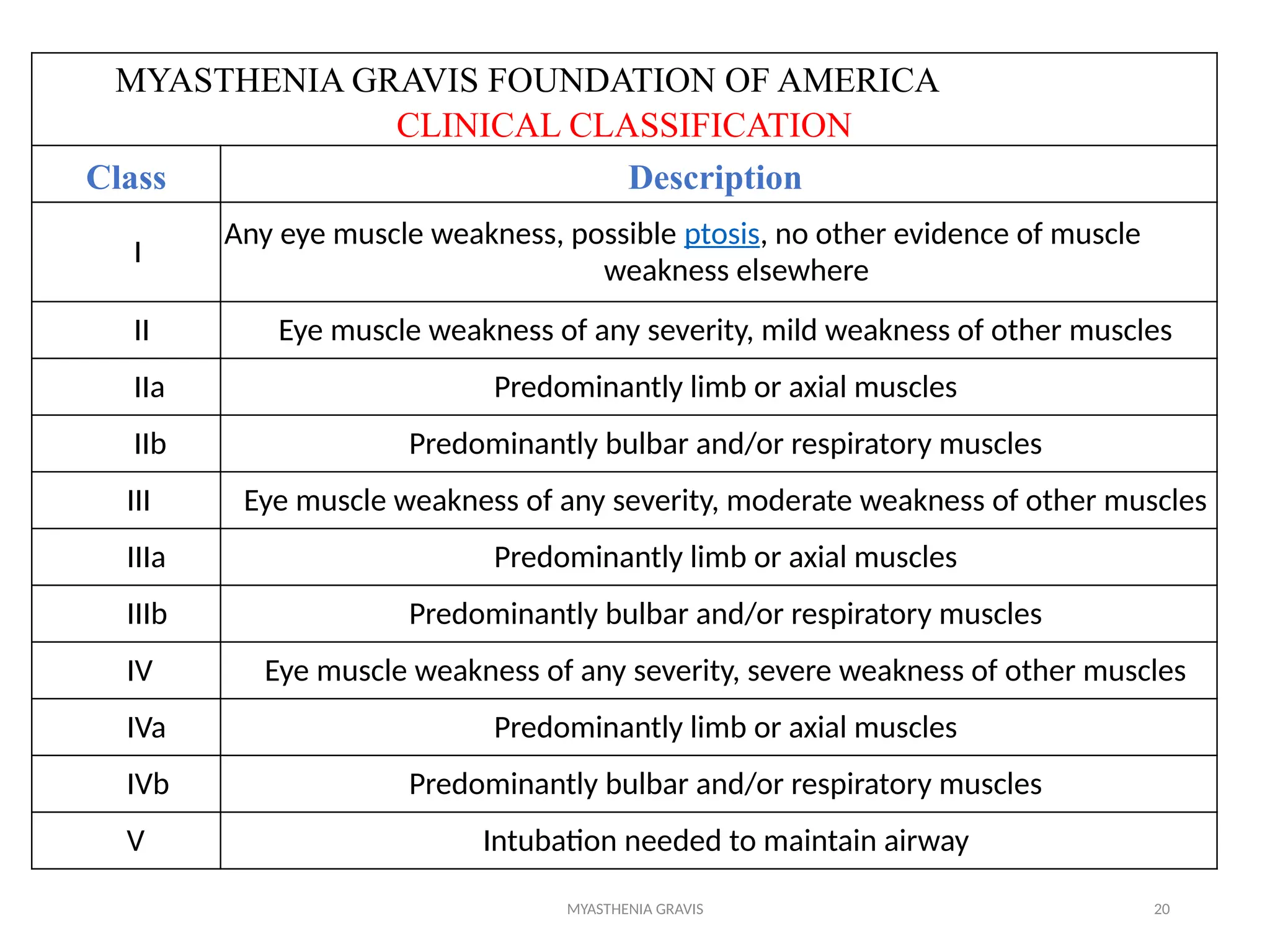
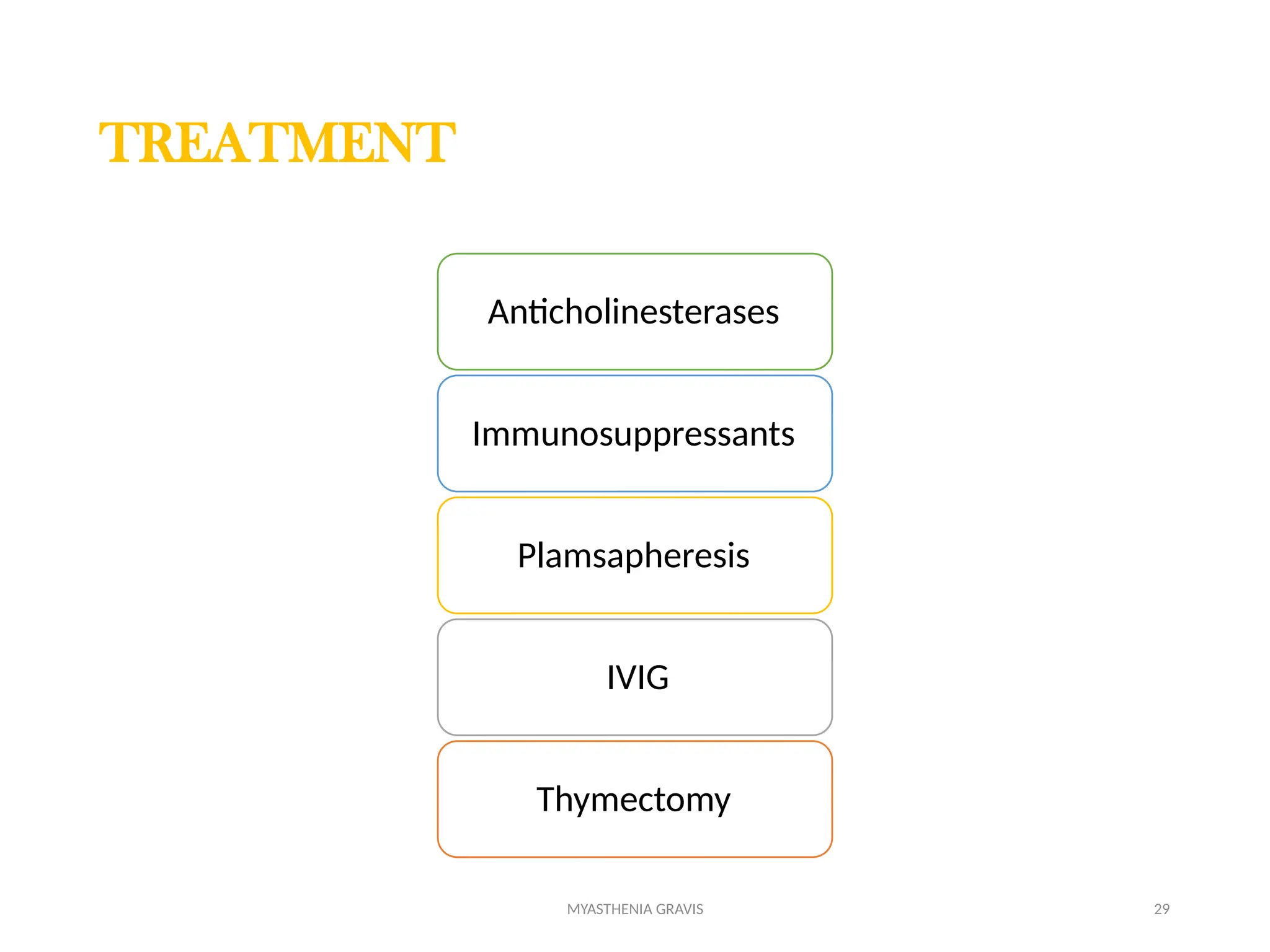
The document outlines a case study of a 55-year-old male patient presenting with symptoms indicative of myasthenia gravis, including left eye ptosis, double vision, and loss of balance. It details the diagnostic methods, pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and treatment options for myasthenia gravis, an autoimmune disorder characterized by muscle weakness that worsens with activity. The document emphasizes the importance of timely diagnosis and management to improve patient outcomes, including potential treatments like anticholinesterases and thymectomy.