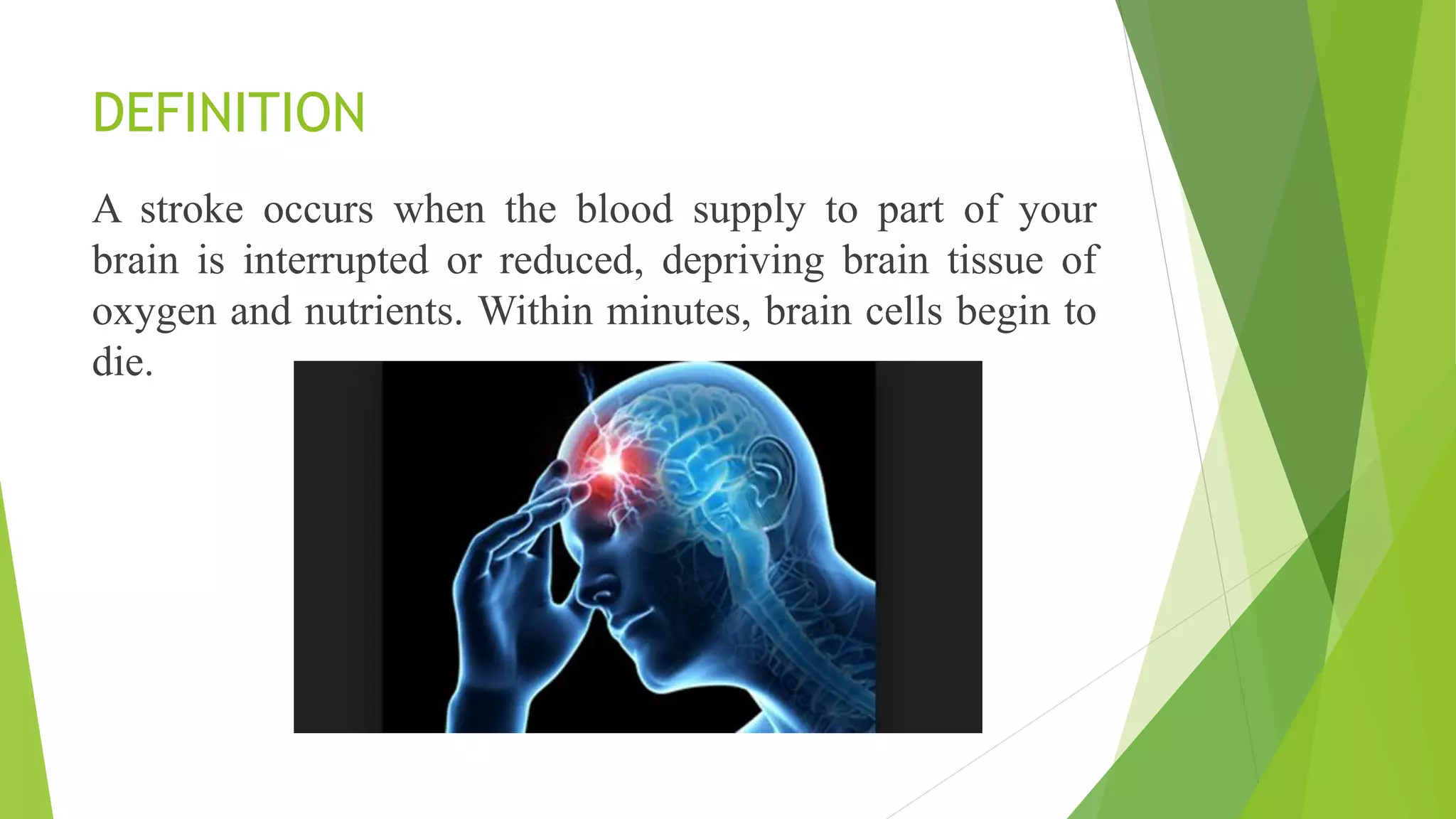
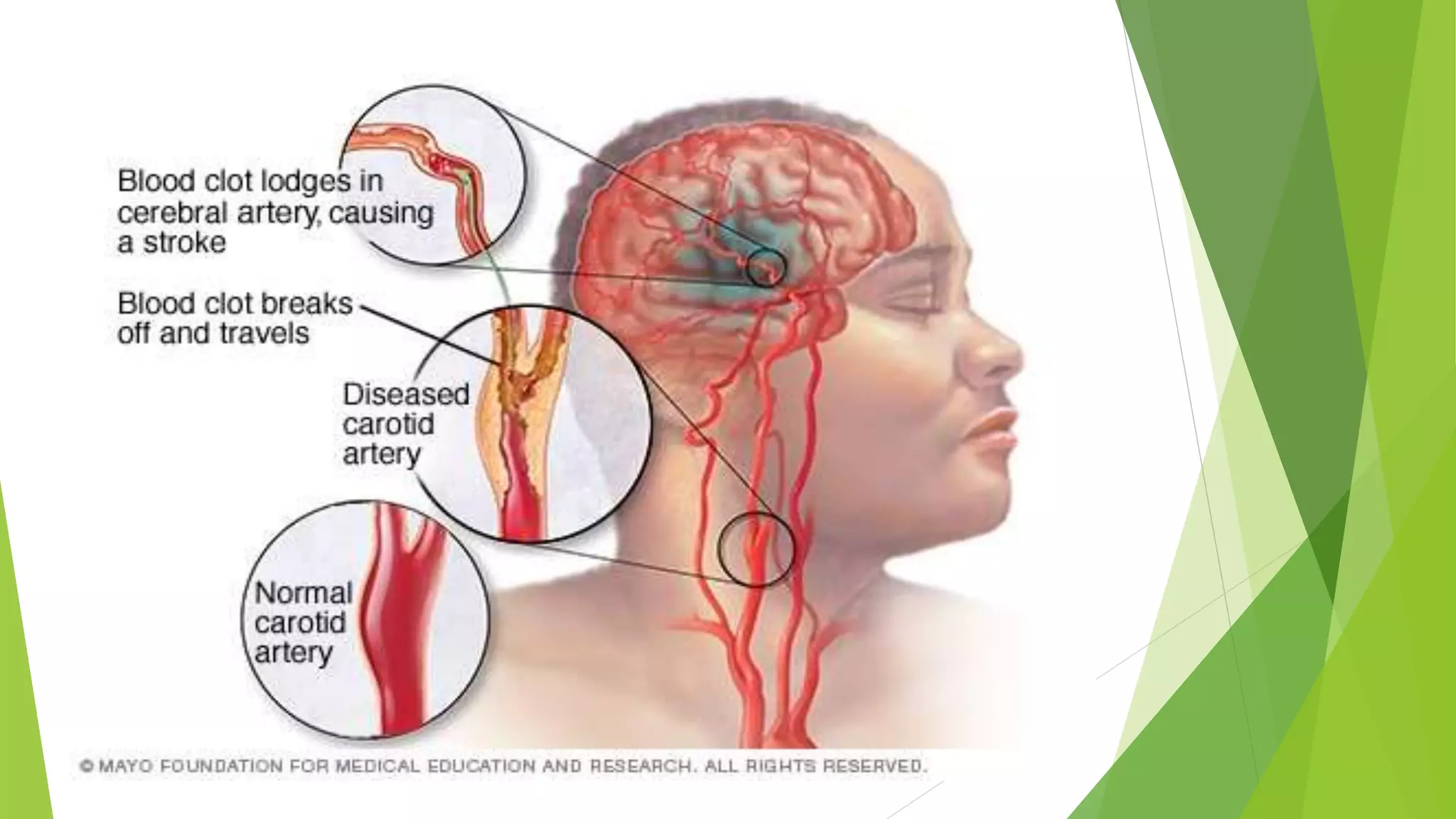
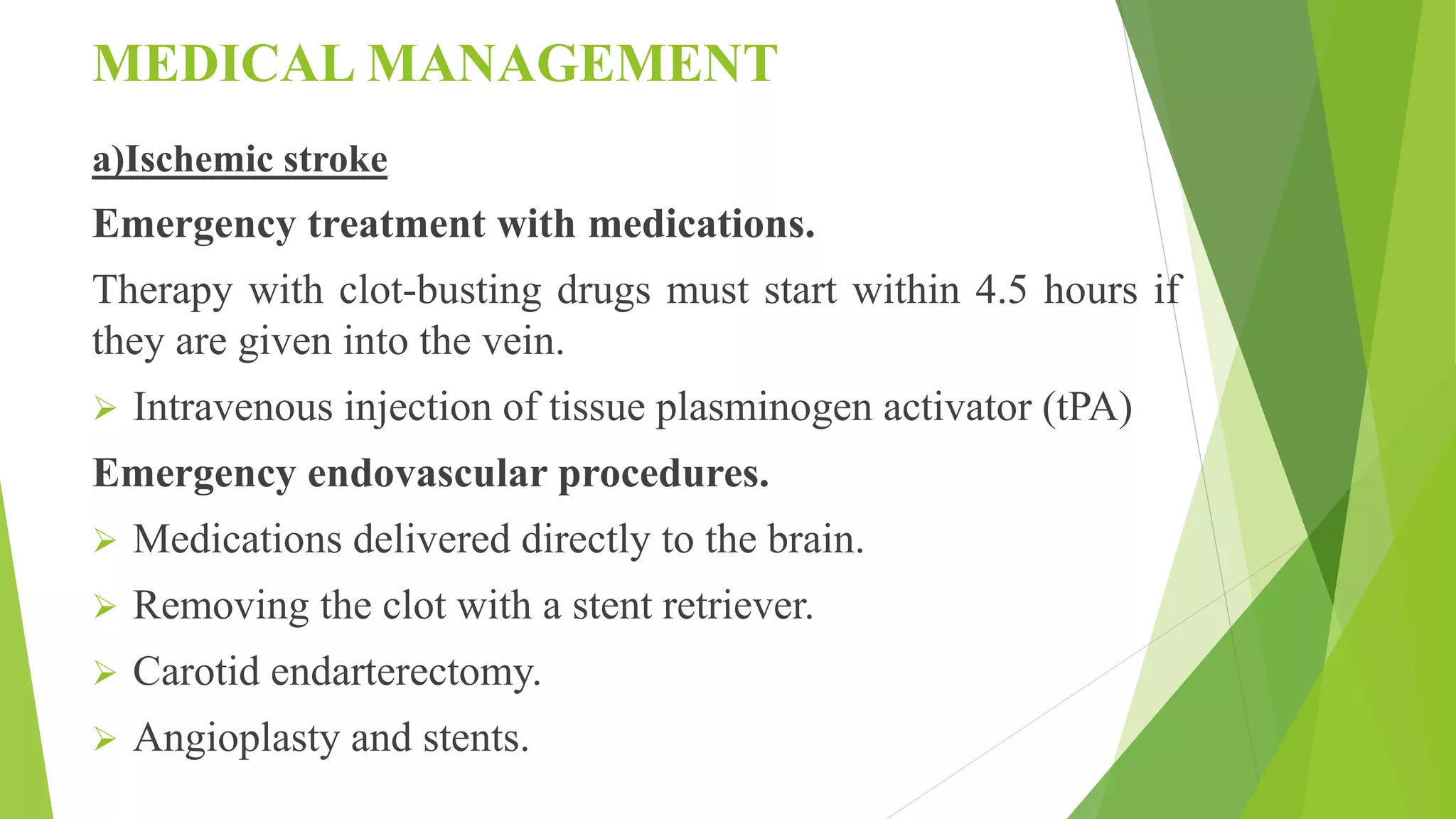
A cerebrovascular accident (stroke) occurs when blood supply to the brain is interrupted, leading to brain cell death, and is a leading cause of death and disability in India. Risk factors include lifestyle choices, medical conditions, age, race, and sex, with ischemic strokes being the most common type. Prevention strategies focus on managing high blood pressure, cholesterol, and lifestyle changes, while treatment varies based on stroke type, including emergency medications and potential surgical interventions.