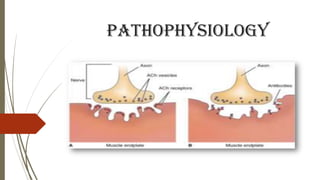
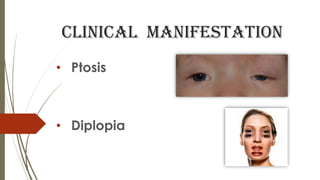
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease affecting the neuromuscular junction, leading to fluctuating muscle weakness, particularly in women during childbearing years and men aged 50-70. Symptoms include ptosis, diplopia, impaired speech, and generalized weakness, with muscle fatigue worsening throughout the day, often triggered by stress or illness. Management involves anticholinesterase drugs, corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and possibly thymectomy, along with supportive nursing care.