This document discusses project organization structures. It begins with an introduction that defines a project organization as a temporary setup formed to achieve specific project goals using specialists from different departments. It then outlines several common project organization structures:
- Line structure organizes workers in a clear hierarchy. Functional structure groups workers by specialty. Line and staff combines these with specialized staff supporting line managers.
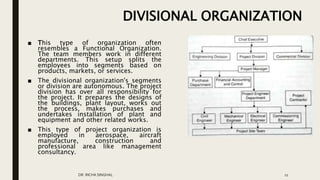
- Divisional structure segments the organization by products/markets with autonomous divisions. Matrix structure combines functional departments and project teams, creating dual reporting relationships.
The document explains advantages and disadvantages of each structure and concludes with an overview of how a responsibility matrix maps organizational roles to work packages.