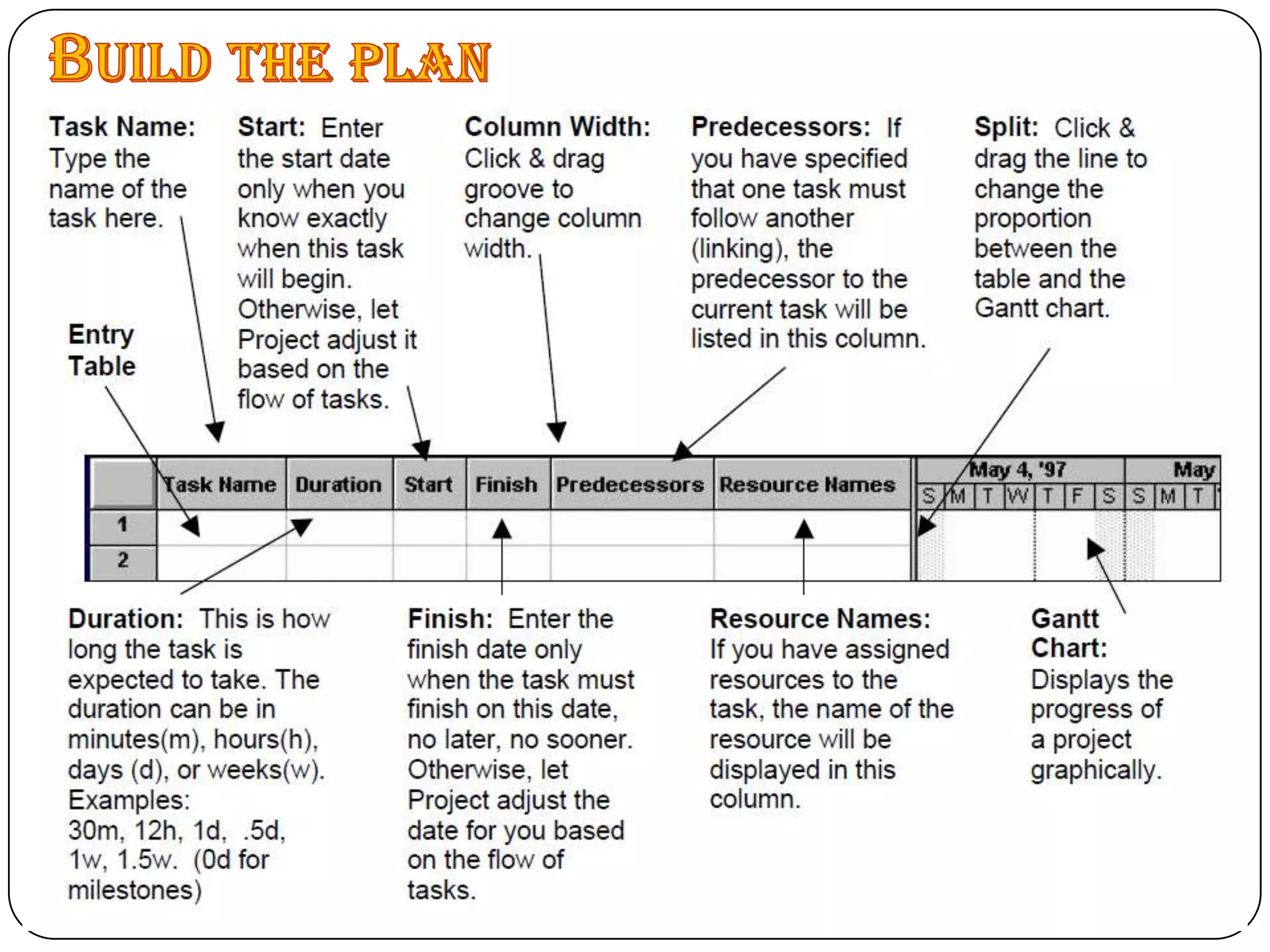
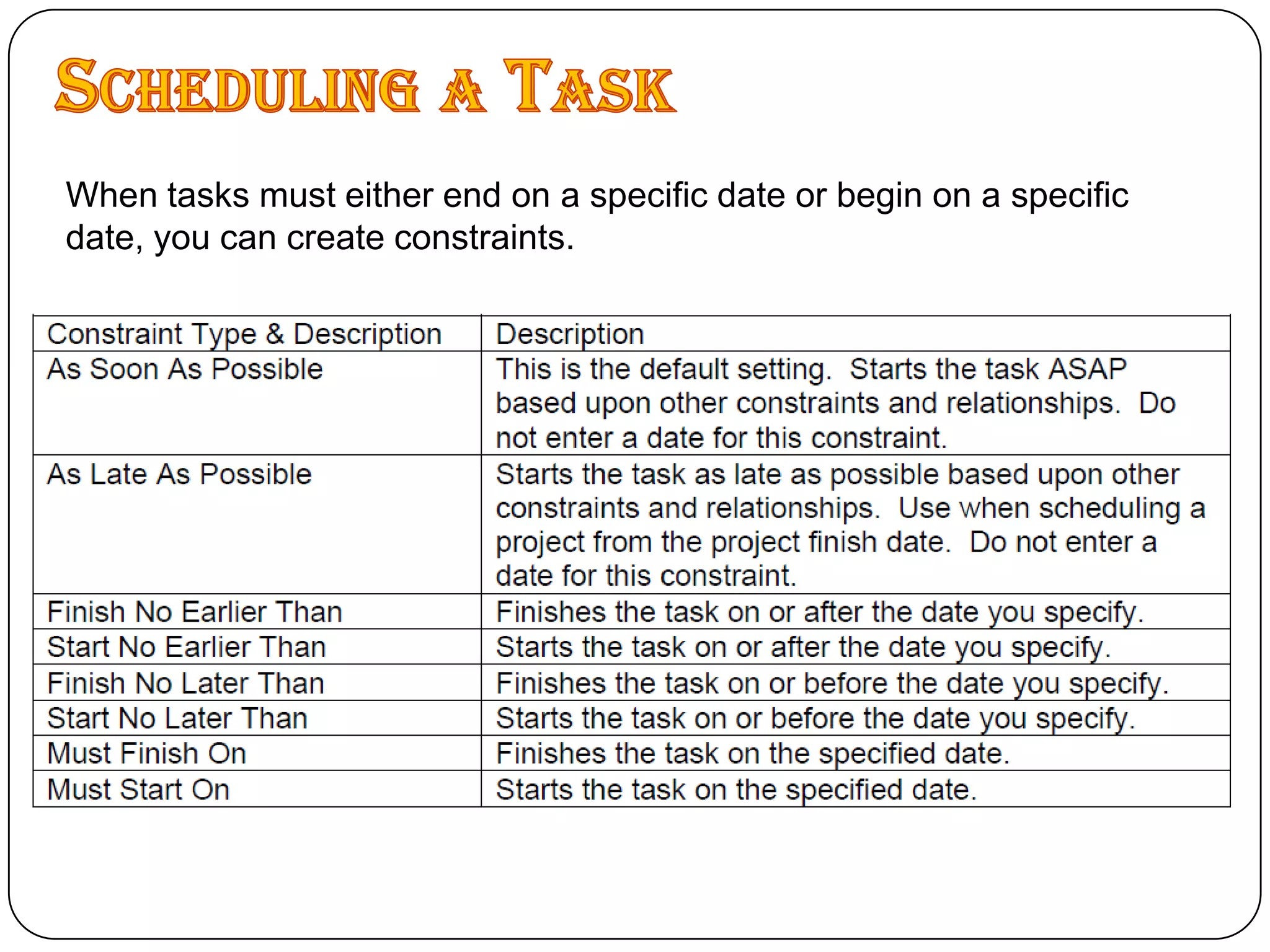
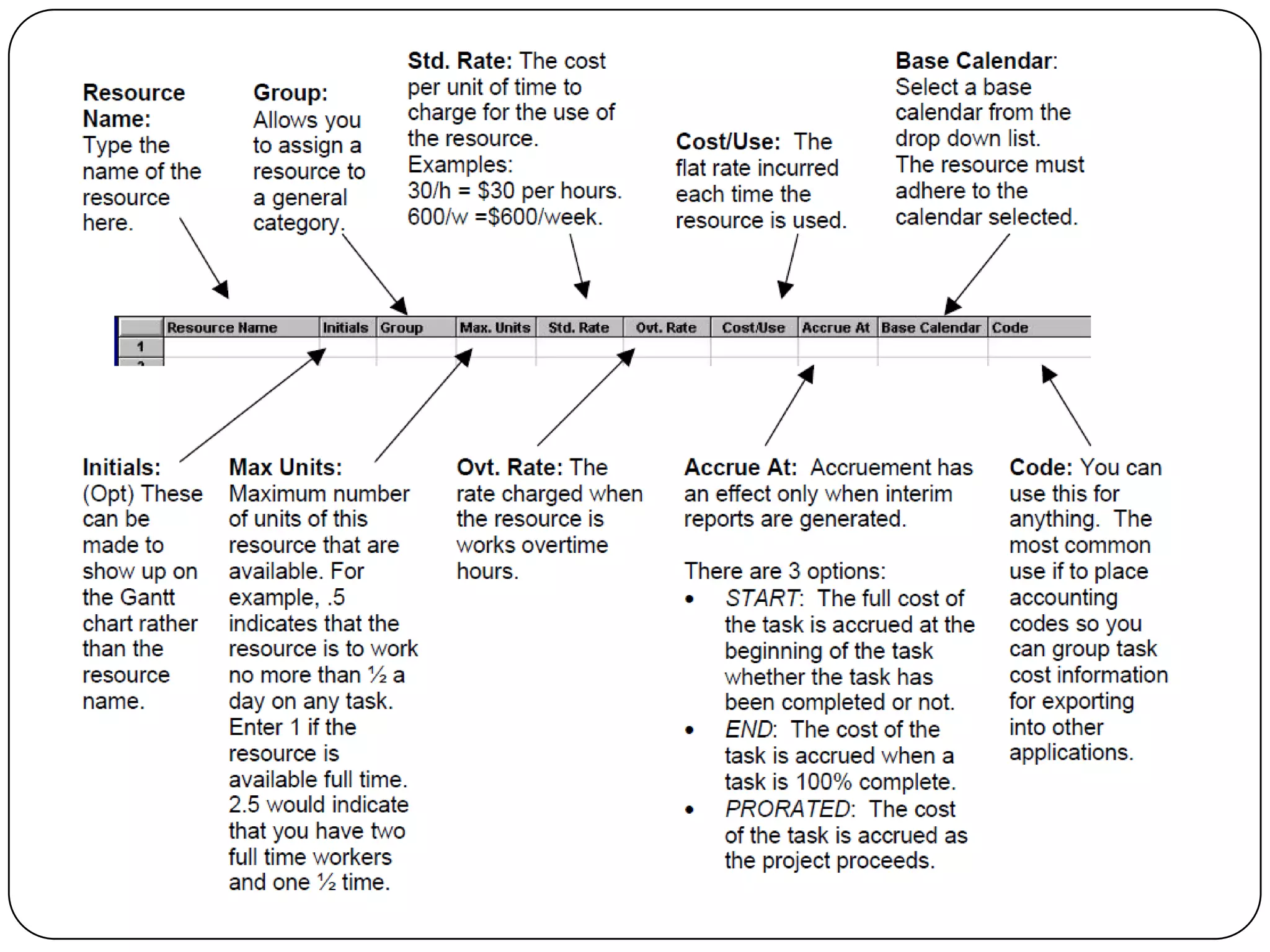
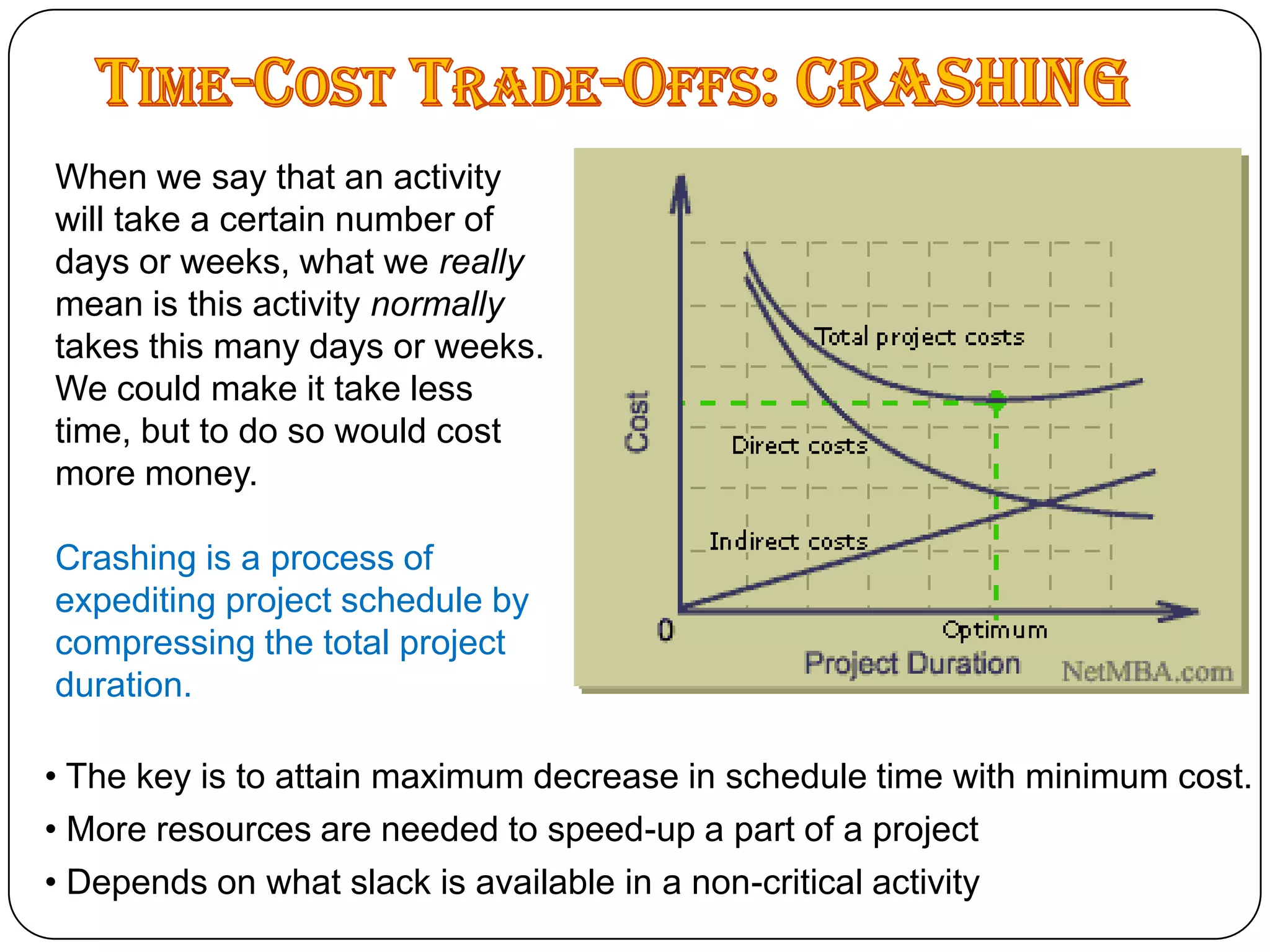
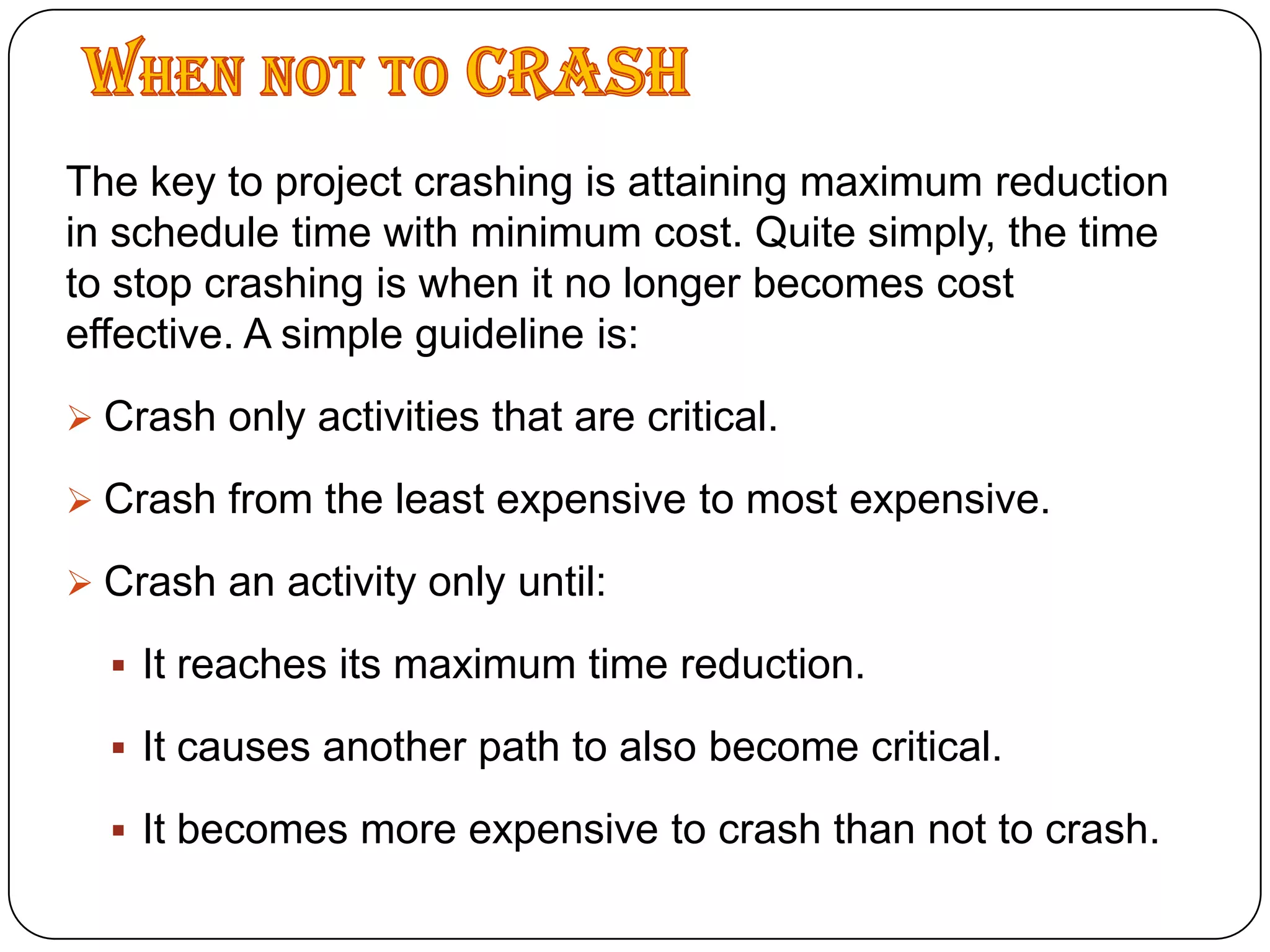
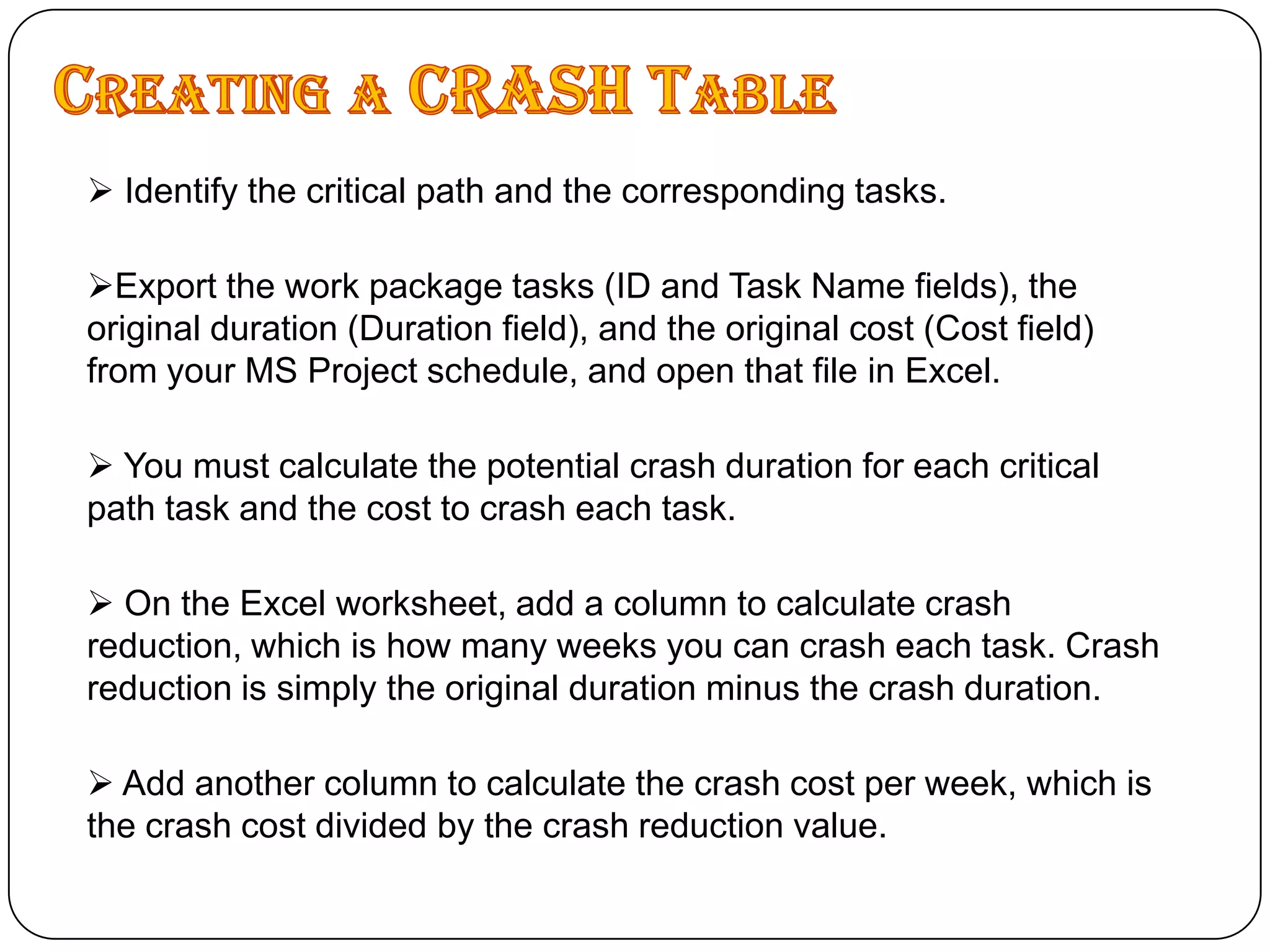
Microsoft Project is a project management software that allows users to define tasks, assign resources and track schedule and budget. It was first released in 1984 and helps project managers plan by creating Gantt charts and calculating critical paths. Key features include task scheduling, resource allocation, budget tracking and progress monitoring. The software allows defining projects, building plans, assigning resources, tracking progress against baselines and closing completed projects.