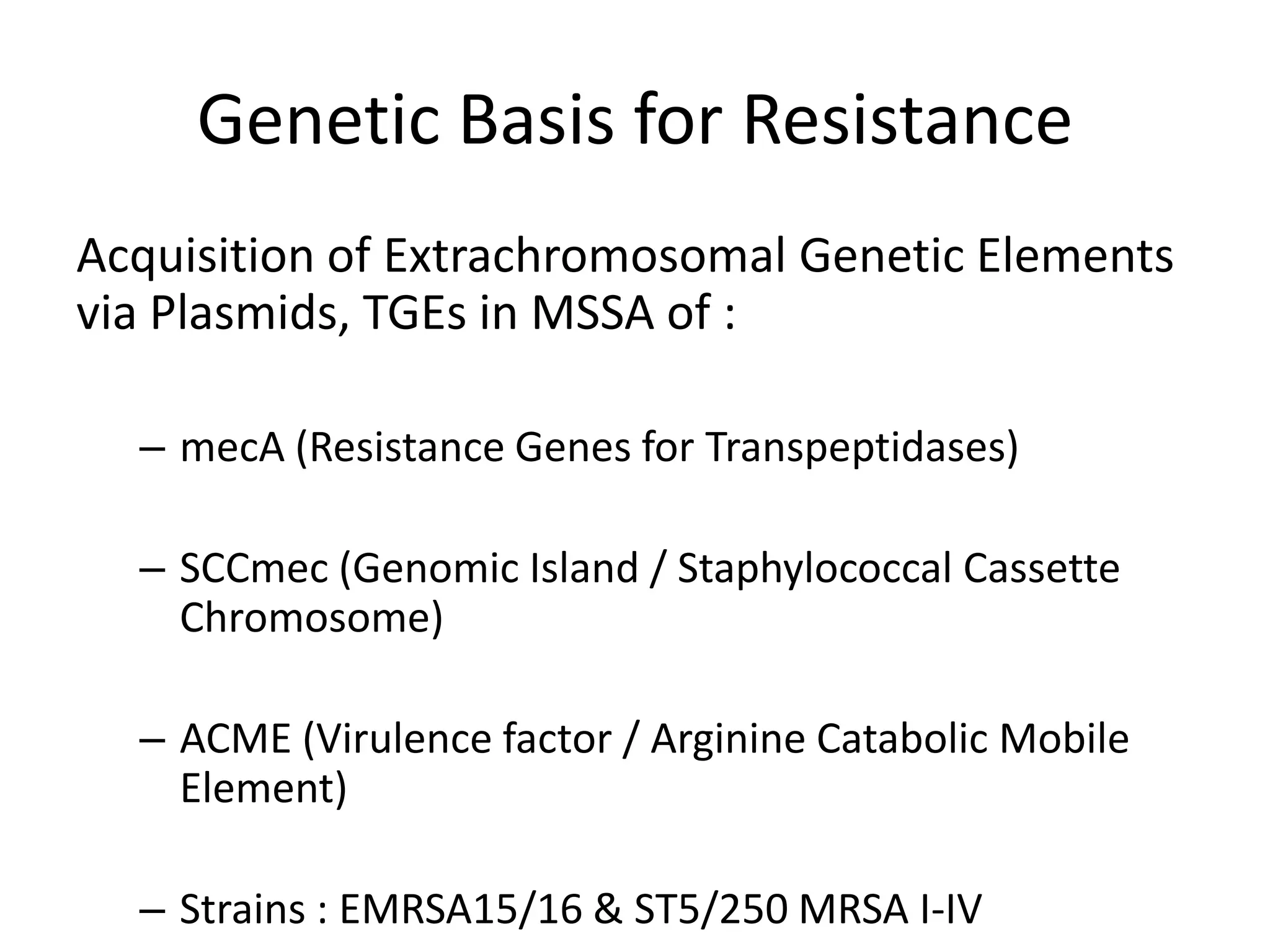
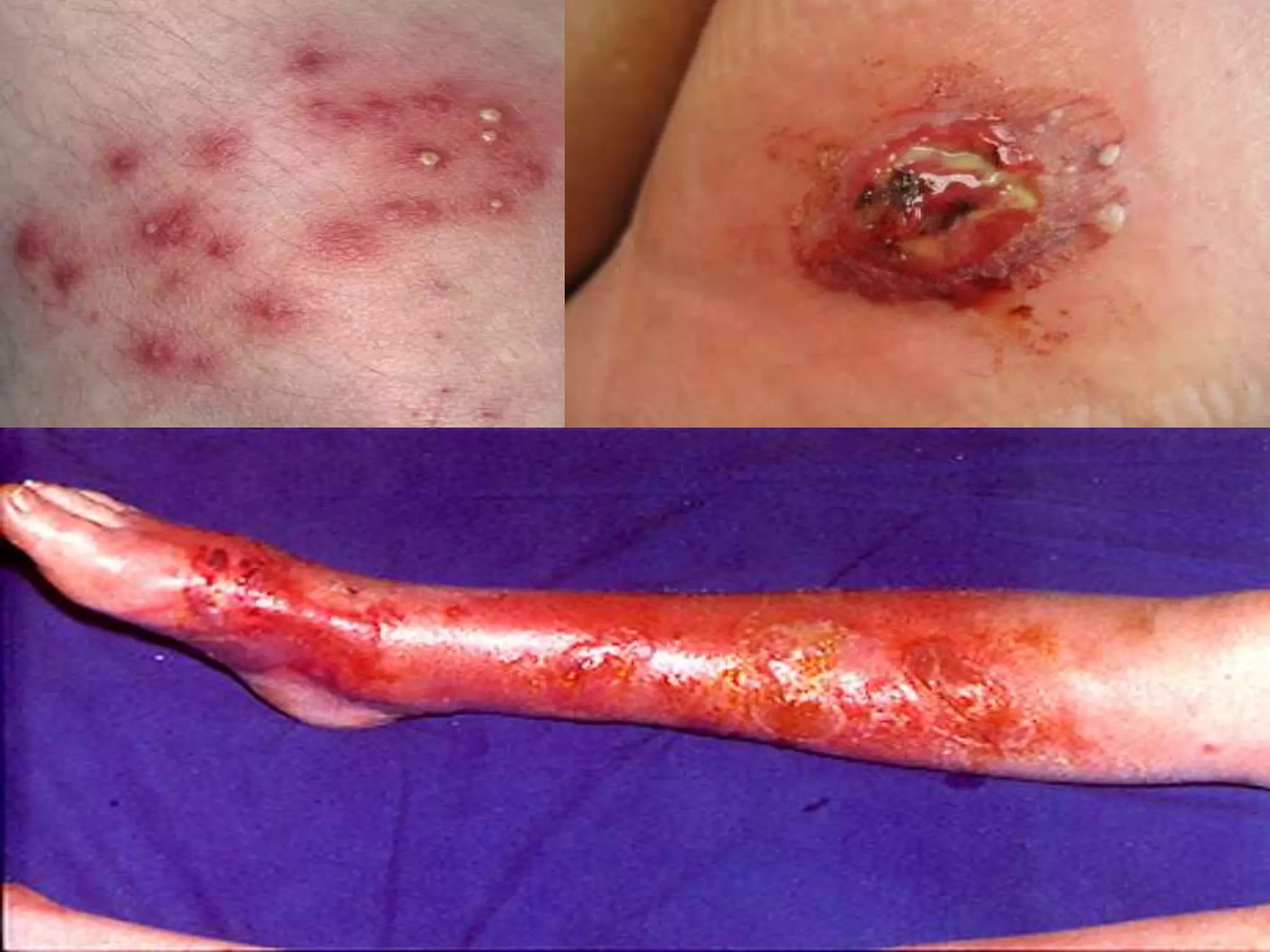
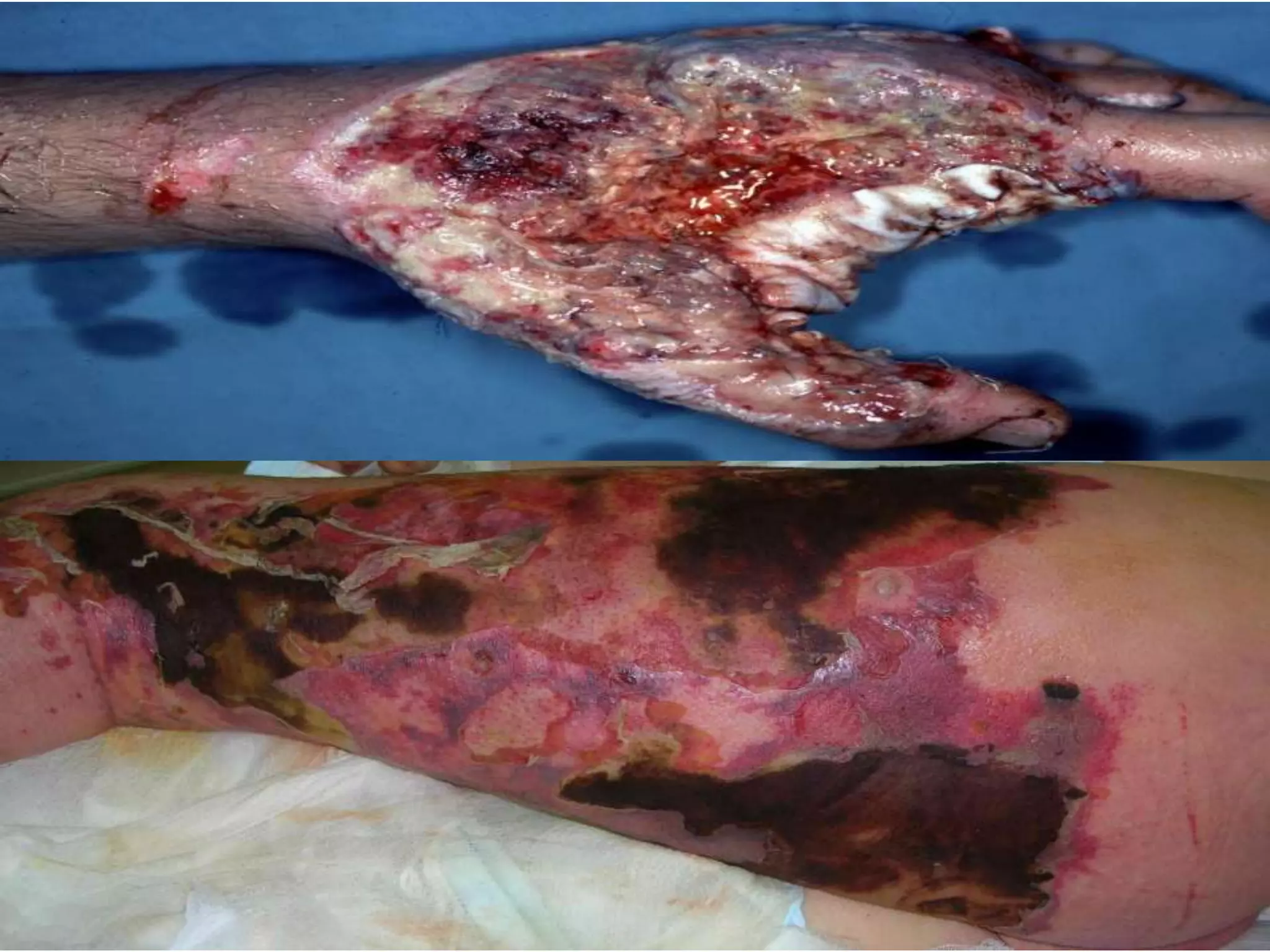
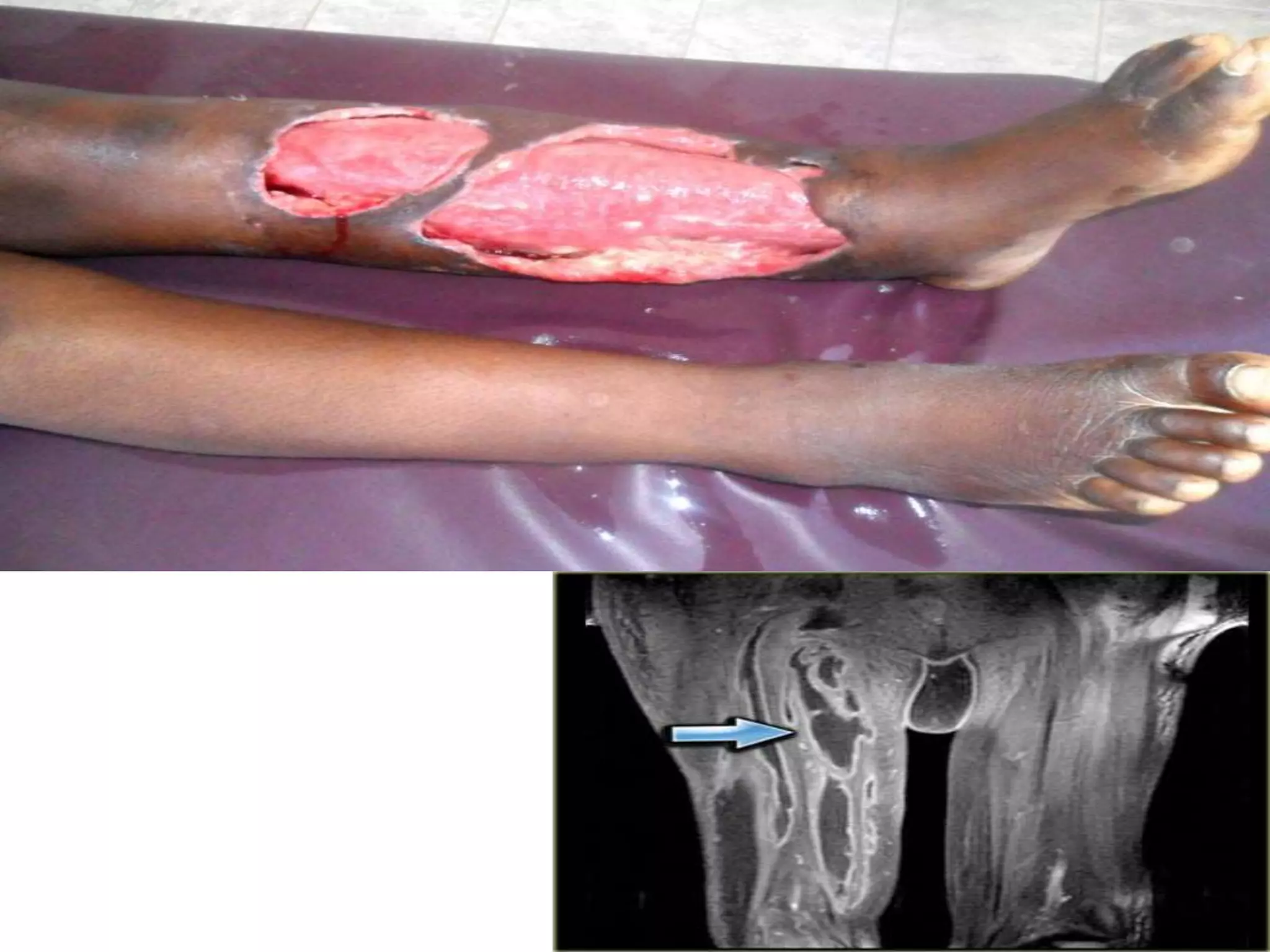
MRSA, or methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, is any strain of S. aureus that has developed resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics through natural selection. It was first identified in 1963 and an outbreak was investigated by the CDC in 2001. MRSA commonly colonizes the nose, respiratory tract, skin wounds, and IV catheters. Resistance is conferred by the mecA gene and SCCmec genomic island acquired via mobile genetic elements. MRSA infections can range from superficial skin infections to life-threatening conditions like sepsis, pneumonia, or necrotizing fasciitis. Diagnosis involves culture, PCR, or latex agglutination tests. Treatment depends on the strain but may include van