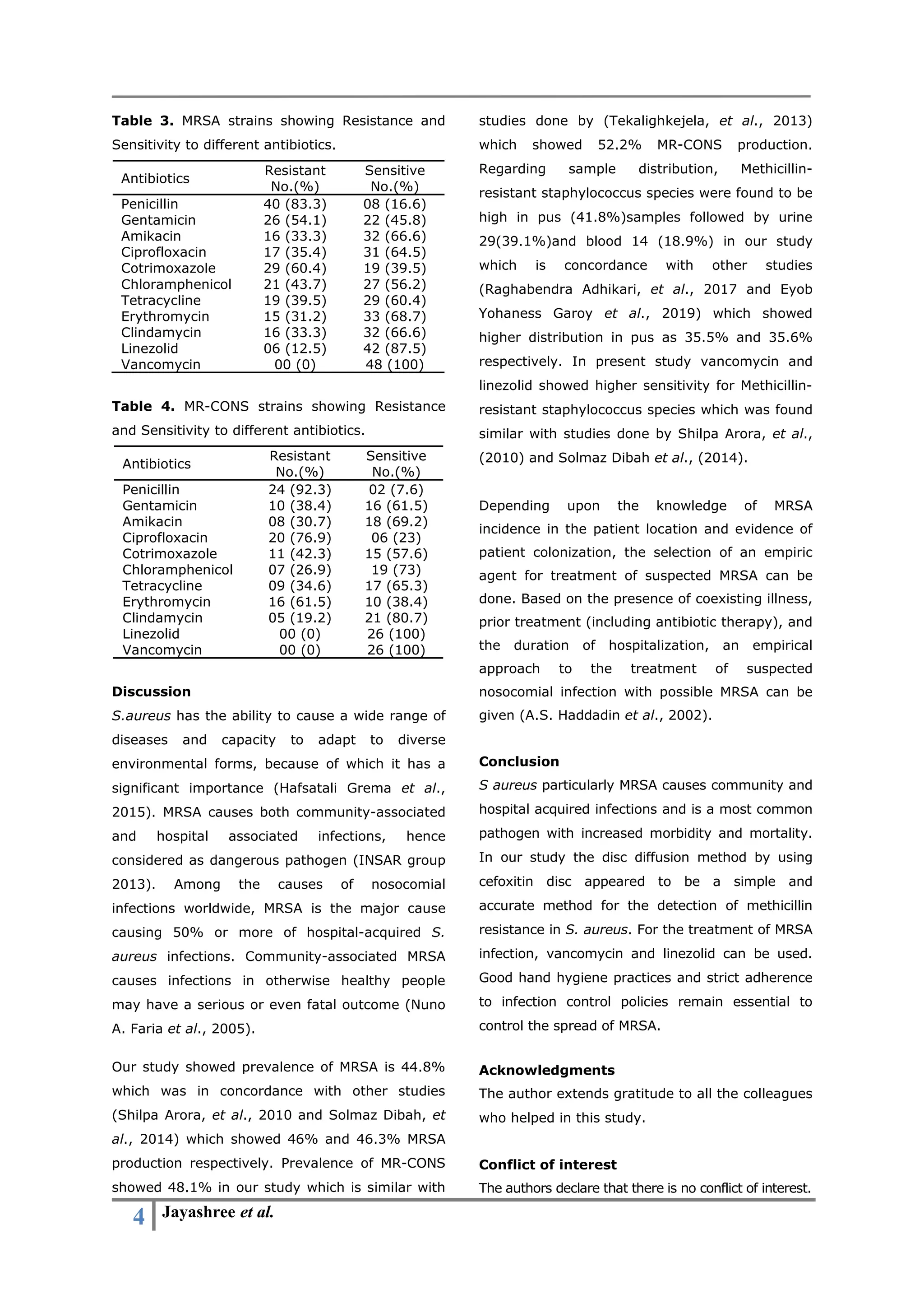
The study investigates methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in clinical samples, revealing that 45.9% of 161 isolates were MRSA, with the highest resistance found in pus samples. The research highlights a concerning increase in MRSA prevalence, with detection performed using disc diffusion methods showing high antibiotic sensitivity to vancomycin and linezolid. The authors emphasize the necessity of effective infection control measures to combat the rising threat of MRSA infections in healthcare settings.