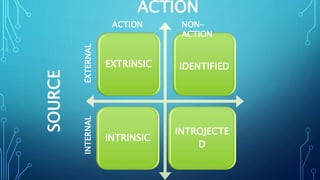
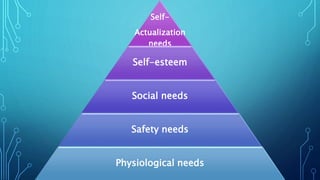
This document discusses motivation in an educational context. It defines motivation as the desire within an individual that stimulates them to act. There are four types of motivation: extrinsic, intrinsic, identified, and introjected. Need-based theories of motivation are also discussed, including Maslow's hierarchy of needs which posits that individuals are motivated to fulfill physiological, safety, belongingness, esteem, and self-actualization needs. The document emphasizes that motivation is important for educational institutions as it helps students and teachers achieve learning objectives and pursue goal-directed efforts.