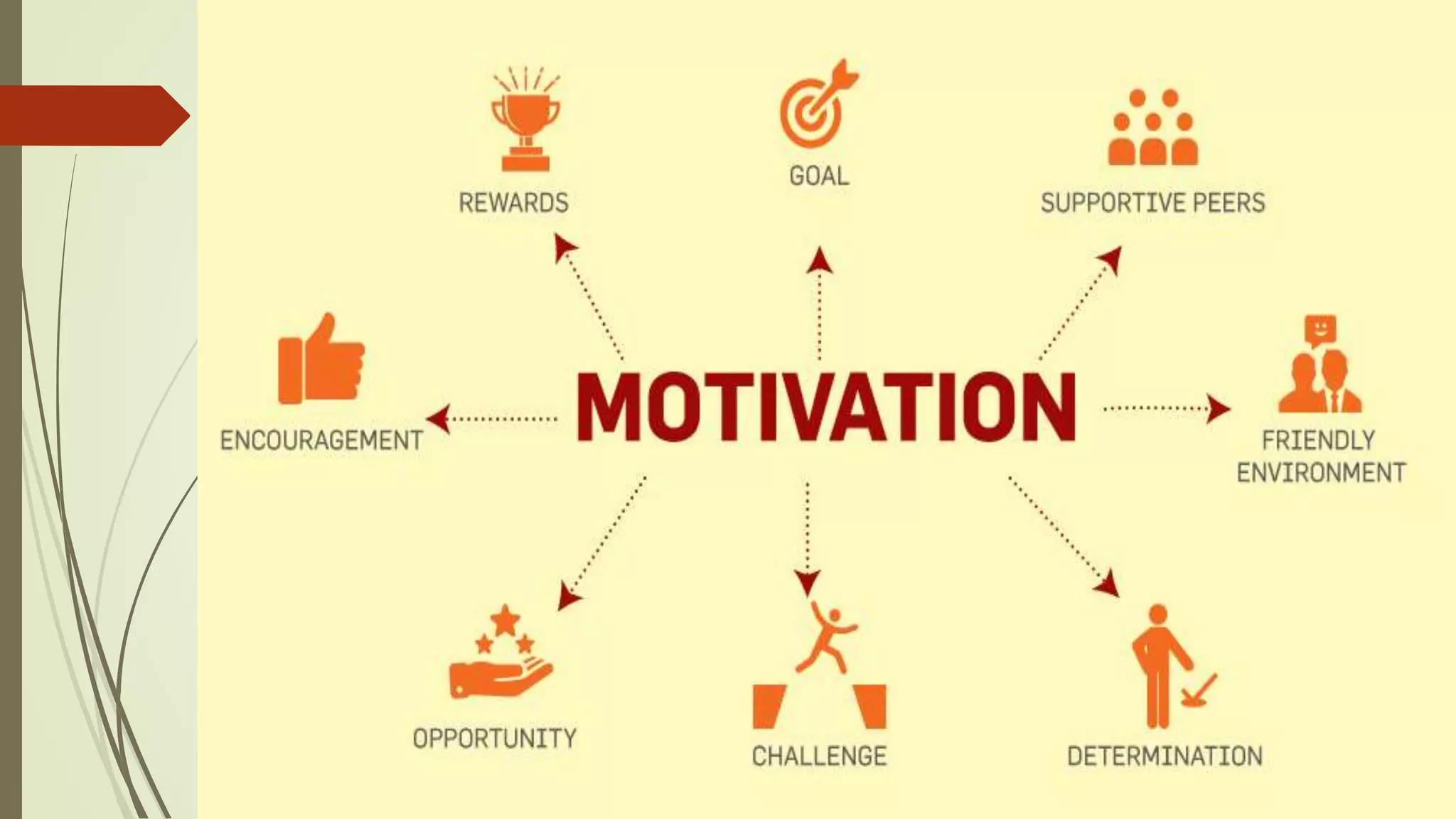
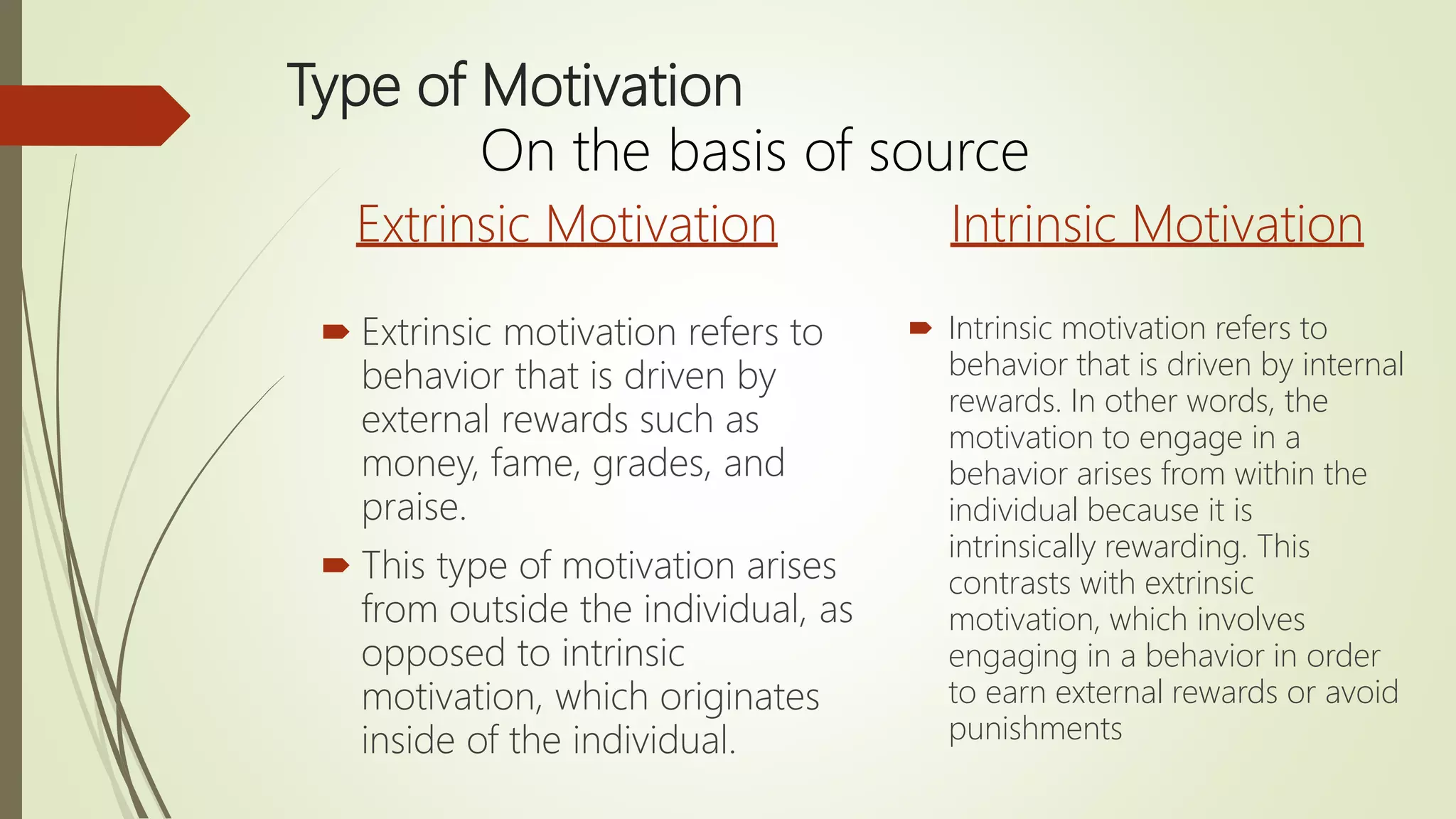
Motivation refers to factors that direct and energize behavior. There are two categories of motives: primary motives related to basic biological needs, and secondary motives related to psychological needs. Motivation comes from both intrinsic factors within an individual and extrinsic factors outside the individual like rewards and incentives. Herzberg's two-factor theory identifies motivators like achievement, recognition, and responsibility that improve job satisfaction, and hygiene factors like salary, status, and job security whose absence can cause dissatisfaction. The ideal situation has high levels of both motivators and hygiene factors.