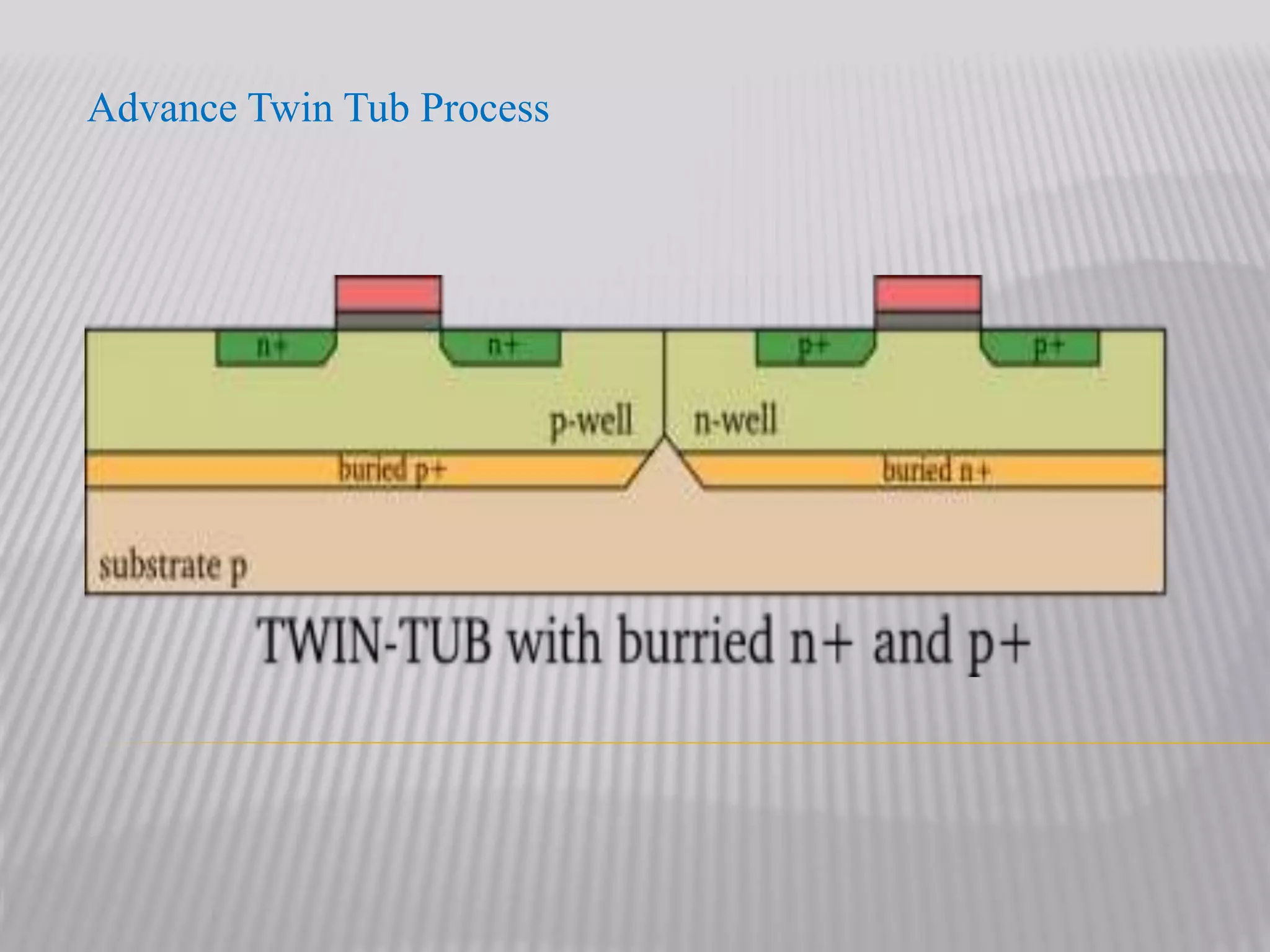
The twin well process allows for separate optimization of n-type and p-type transistors. It involves depositing a lightly doped epitaxial layer on an n+ or p+ substrate, then forming n-wells and p-wells in this layer through independent doping steps. This allows the dopant concentrations to be carefully tuned to produce desired device characteristics for both transistor types. The key steps are tub formation through n-well and p-well implantation and diffusion, polysilicon gate formation, and contact definition and metallization to connect the transistors. The main advantage is obtaining balanced performance from n-type and p-type transistors through separate well optimization.